Activity-Based Costing (ABC) is a method of calculating costs by activity, putting costs “in the right place”. The ABC method in management accounting was born to answer the question: “How many resources are we spending on each activity, each product, each customer?”
This article will clarify the nature of ABC method in management accounting through conceptual analysis, process introduction and practical examples for visualization.
Why do businesses need to care about the ABC method in management accounting right now?
Businesses need to pay attention to the ABC method in management accounting. because it helps to distribute types of business expenses more accurately, especially indirect costs, thereby providing reliable information for strategic decision making.This also helps businesses better understand their cost structure, identify value-creating activities and find ways to optimize to enhance competitive advantage in a volatile market.
Competitive landscape and cost pressures
Businesses now have to compete on price and improve the quality of their products and services. The operating model is increasingly complex: multi-product, multi-channel, multi-market. In particular, indirect costs (management, IT, marketing, logistics, customer care, etc.) are taking up an increasingly large proportion of total costs.
When still using traditional allocation methods (based on labor hours or output), costs are easily distorted, making it difficult for businesses to accurately determine which products are profitable and which are negative capital.
The "pain" that businesses are facing
- Management is unsure which products, services, or segments are actually profitable.
- Always in a state of "the more you sell, the more you lack money" because indirect costs increase but you don't know where they come from.
- The finance and accounting department wanted a more realistic costing method, but was concerned that ABC was complicated and difficult to implement.
The role of ABC in solving cost problems
The Activity-Based Costing (ABC) method helps calculate costs based on each actual activity, bringing costs back to the right placeInstead of allocating overhead costs according to a single criterion, ABC analyzes costs according to each value-creating activity.
In short, ABC was born to clearly answer: “How many resources are we spending on each activity, each product, each customer?”
What is Activity-Based Costing (ABC)?
The ABC method provides detailed information on how costs are generated by specific activities, thereby helping businesses accurately price, optimally manage costs and correctly assess the profitability of each product and service.
What is ABC in management accounting?
In ABC in management accounting (Activity-Based Costing) is a costing method based on the principle: Activities consume resources – and products (or customers) consume activities.
Accordingly, ABC identifies and groups activities into cost pool (Activity cost pools), then use cost factors (cost drivers) to allocate costs from activities down to individual products, services, customers, or sales channels more accurately.

The nature and core arguments of the ABC method in management accounting
- Costs not directly attributable to the product, which arise when a business carries out its activities.
- Want to measure the right cost, must measure the activities and activity consumption levels of each cost object.
- ABC shifts perspective from “departmental costs” luxurious “activity-based and value-based costs”.
History and background of ABC
The ABC method in management accounting began to be mentioned in the late 1980s by Johnson & Kaplan, and was quickly widely applied in manufacturing enterprises. ABC appeared in the context of a sharp increase in the proportion of indirect costs, causing traditional allocation methods to no longer accurately reflect real costs.
Nowadays, ABC is not only used in manufacturing but also strongly applied in:
- Services & logistics
- Banking & Healthcare
- SaaS & software
- Retail & e-commerce
Core Structure & Components of ABC Method in Management Accounting
The core components of ABC include identifying and analyzing activities, determining “cost drivers,” collecting costs for each activity, and finally allocating costs to products based on their activity usage.
Must-know concepts
ABC method (Activity-Based Costing) is a modern accounting model that helps allocate indirect costs (overhead costs) accurately. By linking them to the actual activities that generate the costs, the ABC method provides more detailed information for strategic decision making and effective management of business operations..
The key concepts in the ABC method are listed below.
1. Activity
Is a group of related jobs that consume resources to create a product, service or added value for customers.
For example: receive orders, set up machines, check quality, pack, deliver, handle complaints.
2. Activity Cost Pool
Is where all costs incurred for a particular type of activity are collected.
For example: “Quality control” costs include QC staff salaries, testing materials, and measuring equipment depreciation.
3. Cost Driver
Is a measure of the level of activity used by the cost object.
For example: Number of machine setups, number of orders, number of machine running hours, number of customer support tickets.
4. Cost Object
Is the product, service, customer, sales channel or contract that the business wants to calculate the exact cost.
5. Resource Drivers vs Activity Drivers
Choosing the right driver helps to correctly reflect the cause-and-effect relationship between costs and cost-bearing objects.
- Resource driver: used to allocate costs from resources (labor, electricity, depreciation, etc.) to activities.
- Activity driver: used to allocate costs from activities to products, services, or customers.
Cost hierarchy
| Activity level | Characteristic | For example |
| Unit-level | Generated by each product unit | machine hours per product |
| Batch-level | Batch generation | machine setup cost per batch |
| Product sustaining | Product maintenance and development | product research, own marketing |
| Facility-level | Maintain infrastructure | factory costs, security, general management |
Correctly understanding the hierarchy of activities helps avoid "cost leveling" according to product quantity, limiting price distortion.
Value-creating vs. non-value-creating activities
- Value-added activities: create real value, customers are willing to pay.
For example: assembly, design, order processing. - Non-value-added activities: does not create value, often causes waste
For example: waiting, over-shipping, repeat testing, error correction.
ABC provides foundational data to identify and eliminate non-value-added activities.
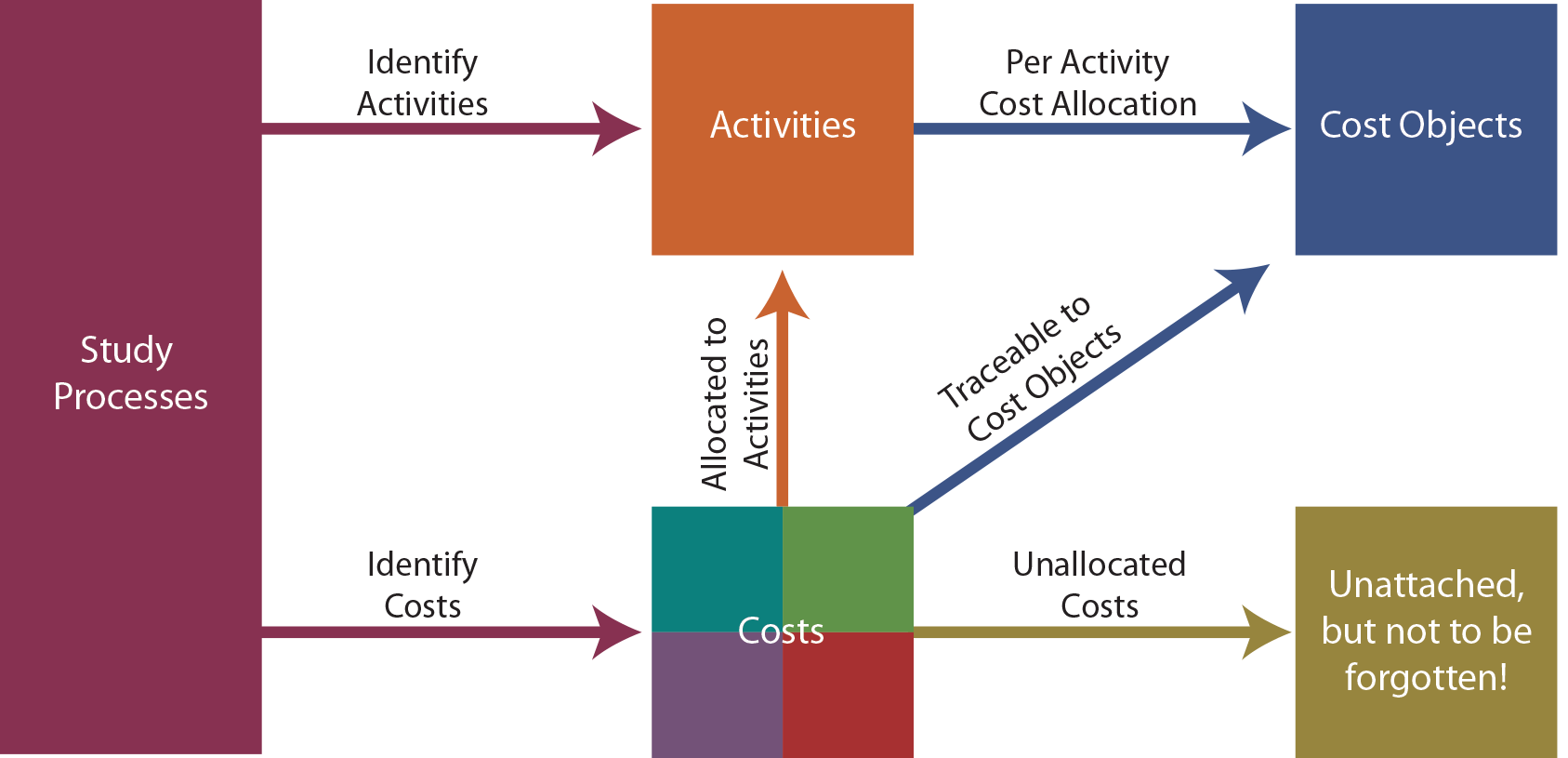
ABC (Activity-Based Costing) method implementation process
Below is a 7-step process for implementing the ABC method in management accounting.
Step 1 – Define Scope and Objectives
- Define the scope of implementation: enterprise-wide, a single plant, a single product line, or a single customer group.
- Clarify the questions to be answered: Which products are being mispriced? Which customers cost a lot to support? Which sales channels are losing money?
- Set specific goals: increase cost accuracy, support pricing strategy, optimize product structure.
Step 2 – Identify and list activities
- Redraw the main business process chain from input to output (purchasing – production – sales – customer care).
- List activities step by step in the process: ordering, warehousing, processing, inspection, packaging, shipping, warranty.
- Communicate with departments to avoid missing out on “behind the scenes” activities such as internal reporting, meetings, and troubleshooting.
Step 3 – Group activities into Cost Pools
- Group activities that are similar in goals, characteristics, and drivers into the same cost pool to optimize the number of pools.
- For example: “input quality inspection”, “in-line inspection”, “final inspection” → common cost pool “Quality inspection”.
- The goal is detailed enough for analysis, compact enough for long-term operation.
Step 4 – Collect costs for each Cost Pool
- Collect resource costs: salary, allowance, electricity, water, depreciation, materials, maintenance...
- Use resource drivers to allocate resource costs to cost pools.
- For example, allocate quality engineer salaries according to the proportion of time spent on each activity.
Step 5 – Identify Cost Drivers for Each Activity
- Select drivers that have a clear cause-and-effect relationship with the cost of the operation.
- For example:
- Cost pool “Setup machine” → Cost driver “Number of setups”
- Cost pool “Order processing” → Cost driver “Order number”
- Avoid choosing drivers just because they are easy to collect but do not reflect the true nature of the cost.
Step 6 – Calculate the Activity Rate
Using the formula:
Activity Rate=Total Cost PoolTotal Driver PoolActivity Rate=Total Driver PoolTotal Cost Pool
For example:
Cost pool “Quality Check” costs 200 million, total number of checks 1,000 →
Each test costs 200,000 VND.
Step 7 – Allocate costs down to product/service/customer
- Determine how many driver units each cost object consumes.
- Multiply the number of driver units by the activity rate, plus the direct costs (raw materials, direct labor) to get the ABC costing.
- Compare with traditional prices to assess the level of deviation and find the cause.
Illustrative example
Products A and B have the same raw material cost. However, product B requires more machine setups and more inspections.
- Traditional method: The prices of A and B are almost the same.
- According to ABC: The overhead cost allocated to B is much higher then B's profit margin is low or at a loss.
From there, businesses need to answer:
- Should the selling price of B be adjusted?
- Can production process B be optimized?
- Should B be removed from the product portfolio?
Applying ABC method in business administration
The ABC method applied in business administration helps improve operational efficiency: Improve decision-making ability, minimize resource waste and enhance competitiveness.
1. Calculate the correct cost and analyze multidimensional profits
- ABC helps determine the exact cost for each product, service, order or customer.
- Businesses can clearly see which products are truly profitable and which products are being "eroded" by indirect costs.
- Profit analysis is not only by product but also by customer – sales channel – market, helping to make accurate decisions instead of just relying on emotions.
2. Eliminate non-value-added costs & optimize processes
- Through operational analysis, businesses can easily identify redundant steps: repeated testing, error correction, waiting, unnecessary transportation, etc.
- Combining ABC with Lean/Kaizen helps cut waste, shorten lead-time and improve operational efficiency.
- Non-value-added activities can be reduced, automated, or eliminated altogether to optimize costs.
3. Support strategic decisions
ABC provides foundational data for making strategic decisions such as:
- Should a product line be continued or discontinued?
- Should you produce it yourself or outsource it?
- Which customer segment should I focus my resources on to maximize profits?
- Price products based on real costs, not on emotions or market levels.
Advantages, disadvantages & common misconceptions about ABC method in management accounting
Correct and complete understanding of the ABC method is an important condition before implementation.
Outstanding advantages of ABC
- Increase cost accuracy, especially in businesses with multiple products, multiple variants, or complex service structures.
- Provides insight into costs by activity and by customer, helping to understand where costs are being spent and why.
- Creating the foundation for strategic cost management, not only serves the purpose of calculating costs for reporting but also supports business decision making.
Disadvantages and barriers to implementation
- Collecting detailed data is time-consuming and resource-intensive., especially if the business is operating on distributed Excel and lacks a synchronized system.
- Requires a shift in thinking from financial accounting (recording) to management accounting (analysis - decision) perspective.
- The ABC model is easily outdated. If operating procedures change continuously without the technology system to support updates.
Common Misconceptions About ABC
- “ABC must deploy the entire company
In practice, it can be as simple as starting small, with one shop floor, one product line, or one customer group to test and optimize.
- “ABC will completely replace traditional accounting”
False. ABC is additional class to serve decision making, not to replace financial statements.
- “ABC is only suitable for large corporations”
Not exactly. Small and medium enterprises can completely apply, if you know how to narrow down the scope and have supporting technology tools.
Technology & software supporting the implementation of the ABC method in management accounting
The ABC (Activity-Based Costing) method helps businesses calculate correctly and fully costs by activity, by product and by customer. However, ABC only truly delivers when supported by technology., because the nature of ABC requires detailed, constantly updated data and the ability to analyze in depth.
The role of ERP, EPM and ABC software
Many businesses want to implement ABC but are “stuck” because:
- Data is scattered across many Excel files, many departments, difficult to synchronize.
- Manually synthesizing cost pool and cost driver → error-prone, slow, inconsistent.
- The model cannot be updated when the manufacturing process or cost structure changes.
ERP systems such as SAP, Oracle, Odoo, Microsoft Dynamics acts as a platform for storing and managing the business's operational data. And ERP takes care of the actual data, the system EPM – typically the Sactona solution will be responsible for management analysis and financial planning. Combined with specialized ABC software - automating complex operations helps reduce the risk of errors - increase speed - ensure transparency in cost management.
The three combined systems help the application of ABC method in management accounting not only become a cost calculation problem, but also a tool to create competitive advantage and optimize profits.
Connect ABC with cost data from Bizzi
In the ABC model, the accuracy of cost data is vital. Bizzi acts as the system collect – standardize – attach costs to the right objects, creating an ABC-ready data platform.
Bizzi IPA + 3-way matching
Minimize errors due to manual data entry and ensure ABC input data is accurate and transparent.
- Automatic collection and testing input invoices.
- Perform 3-way reconciliation (Invoice – PO – GRN) to ensure cost validity.
- Automatically classify and transfer costs to the correct accounting account, department, and cost bearer.
Bizzi Expense / Travel
Operating costs are directly tied to business operations rather than being lumped into overhead costs.
- Record actual expenses from employees by project - department - order - customer.
- Connect electronic documents, invoices, approval and payment history.
- Create a fully allocated data source for ABC's cost pool.
Offload the cost aggregation step to the cost-pool
Instead of manual processing, businesses turn to cost analysis and optimization – the true nature of ABC.
- Eliminate data entry and consolidation from multiple Excel, multiple disparate systems.
- Significantly reduce data preparation time for ABC on a monthly/quarterly basis.
- Create foundational data to automate attribution and profit analysis by audience.
In short, Bizzi makes the application of ABC method in management accounting feasible and effective, especially for businesses with a large number of invoices and many departments involved in operations.
EPM / Sactona – ABC-based decision making layer
For ABC to be of maximum value, cost data needs to be modeled, analyzed, and linked to business plans. This is the role of an EPM system like Sactona. Sactona is an Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) platform developed by Outlook Consulting (Japan) and exclusively distributed by Bizzi in Vietnam.
Sactona turns ABC data into a living, visual, and strategic tool, helping finance not only report but also drive business decisions.
1. Activity-Based Costing
- Sactona allows to set up cost pools, cost drivers, cost objects based on ABC data.
- Directly connect to budget and forecast plans, creating a comprehensive cost picture by activity, product, customer, and sales channel.
2. “What-if” analysis and strategic decision making
- CFOs and FP&A teams can simulate scenarios:
- Changing product mix → what is the profit impact?
- Change in operating structure → how about operating costs and efficiency?
- From ABC data, Sactona helps build What-if models, allowing for quick decision making based on real data, instead of emotional estimates.
3. AI & Automation Improve ABC Efficiency
- WHO: Suggests optimal cost driver based on historical data.
- Machine Learning: detect the unusual cost patterns, warns of the risk of increased costs or waste in a particular activity.
- RPA (Robotic Process Automation):
- Automatically update operational figures from ERP / Bizzi.
- Rerun the ABC model periodically (monthly, quarterly) without rebuilding from scratch.
Combining ABC + Sactona + AI/RPA helps the cost model become a living tool, reflecting reality and supporting fast and accurate decision making.
AI and Automation in Advanced ABC
When ABC is supported by smart technology, the cost model is not only accurate but also becomes a living tool, continuously reflecting business operations.
1. AI – Suggesting optimal cost driver
- Based on historical data and cost patterns, AI can recommend the appropriate cost driver for each operation.
- Helps reduce manual analysis time and increase the accuracy of cost allocation.
2. Machine Learning – Anomaly Detection
- The system learns from cost and activity history to detect unusual patterns.
- Timely warning of unreasonable cost activities, helping administrators to quickly adjust.
3. RPA (Robotic Process Automation) – Automatically update models
- Automatically collect data from ERP / Bizzi, update cost pools and cost drivers.
- Rerun the ABC model periodically (monthly/quarterly) without rebuilding it from scratch.
- Helps keep the ABC model realistic and ready for strategic analysis.
Which industries should apply the ABC method in management accounting?
The Activity-Based Costing (ABC) method is especially useful for businesses with large indirect costs, diverse products/services, and multiple operating channels, because ABC helps allocate costs accurately by activity, product, customer, or channel.
1. Production & Logistics
- Businesses with many product lines and many processing stages: ABC helps determine the real cost for each product and shipment.
- Logistics, warehousing, transportation: evaluate costs by route, by customer, by order, helping to optimize operations and improve profit efficiency.
2. Banking, insurance & financial services
- Analyze the cost of serving each type of account and each customer segment.
- Understand the processing costs of each transaction and each channel (branch, online, mobile app), thereby optimizing operating costs and designing more effective products and services.
3. Healthcare, hospitals & education
- Determine the real cost of each treatment or training program.
- Support in designing service packages, reasonable tuition fees and making strategic decisions on investment, human resources and equipment.
4. Technology, SaaS & E-commerce
- Calculate the cost of serving each user, each order, each marketing channel.
- Evaluate Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) and Cost-to-Serve at a granular level, helping to optimize marketing strategies and resource allocation.

Answers to frequently asked questions about the ABC method in management accounting
Refer to the summary content related to the ABC method below to help managers have a multi-dimensional perspective on the ABC method.
1. What is ABC used for in management accounting and how is it different from the traditional method?
- ABC Purpose: costing accurate according to activity, analyze profits by product, customer, sales channel, thereby supporting strategic decision making.
- Different from traditional method: Traditional methods often allocate indirect costs based on labor hours or output, which can easily cause price distortion, while ABC is based on actual cause and effect, accurately reflect the cost of each activity.
2. What is a cost driver and how to choose a driver to avoid cost deviation?
- Driver cost: is a measure that reflects level of activity of the cost object (e.g. number of orders, number of machine setups, number of machine running hours).
- Select the correct driver: must have clear causal relationship with cost, do not choose driver just because it is easy to measure, avoid skewed allocation and distort cost.
3. Can ABC completely replace the traditional method?
- ABC does not completely replace traditional accounting.
- Often used in parallel: traditional accounting serves financial reporting, while ABC provides detailed information for management and strategic decision making.
4. What is Time-Driven ABC (TDABC) and how is it different from classical ABC?
- TDABC: cost allocation based on time spent on each activity instead of relying on multiple complex cost drivers.
- Distinctive: simpler, easier to deploy, reduces the need for detailed data collection for each activity.
- When to use: Businesses with many repetitive activities, large indirect costs, want to deploy ABC quickly and maintain easily.
5. Should small businesses apply ABC?
- May apply, but should start small, for example, a product line, a department, or a customer group.
- Benefits: understand costs, optimize processes, make informed decisions without overloading resources.
6. How can ABC be combined with ERP / EPM / Bizzi?
- ERP: Collect data on costs, time, and activity volume.
- Bizzi: Automate invoice collection, tag costs by project, department, order → standardize data for ABC.
- EPM / Sactona: ABC modeling, running “what-if” scenarios, analyzing profitability by product, customer, channel.
- Result: Reduce manual, increase accuracy, turn ABC into a tool strategic management and quick decision making.
Conclude
In short, applying the ABC method in management accounting is a way to help businesses clearly see costs by activity, product, customer, instead of just by the total number of departments. The ABC method is suitable for any business with large indirect costs, diverse activities and need detailed cost analysis to make accurate strategic decisions. Businesses can apply ABC to a cost segment, a product line or a factory, then expand when data and internal capacity are ready.
In general, the ultimate goal when applying any method to operations and management is not just to "calculate the right cost" but above all to "put resources in the right place to maximize profits and customer value". The ABC method in management accounting when combined with ERP, Sactona and AI solutions will become easy and accurate. Strategic decision making is no longer a theoretical model.
Bizzi not only fully integrates with ERP systems but also exclusively distributes EPM – Sactona solutions in Vietnam. To receive consultation and experience, register here: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/


