In the digital age, choosing the right ERP system can determine the operational efficiency and competitiveness of a business. Between the two popular choices today – On-premise ERP and ERP cloud (cloud computing) – Each model has its own advantages and disadvantages, directly affecting investment costs, flexibility, security and scalability. The following article will help businesses Comparing On-Site ERP and Cloud ERP comprehensively, thereby making the most optimal choice for long-term management and development needs.
1. Introduction to ERP and the importance of choosing the right solution
In the context of increasingly strong digital transformation, ERP plays a role as a core technology platform that helps businesses operate efficiently, control risks and make quick decisions. However, choosing the right ERP model – especially between internal ERP (On-Premise) and ERP Cloud – not only affects investment costs but is also directly related to the scalability, security and long-term strategy of the business.
1.1. What is ERP?
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is an enterprise resource planning system that integrates all core functions such as accounting, finance, purchasing, sales, inventory management, manufacturing and human resources on a single platform.
Modern ERP systems not only help automate processes but also provide real-time data, thereby supporting management to make faster and more accurate decisions.
Some Outstanding benefits of ERP including:
- Increase operating efficiency: Minimize manual operations, avoid errors due to repetitive data entry.
- Optimize workflow: Connect departments across the business, making processes seamless and transparent.
- Improve decision making: Thanks to the data being aggregated and analyzed instantly.
1.2. Reasons to compare Internal ERP and Cloud ERP
Comparing On-Site ERP and Cloud ERP is an indispensable step in the process of choosing a technology solution for your business. Each model has its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, security, customization, and deployment speed.
- Internal ERP Often suitable for large businesses with strong IT teams, strict security requirements and deep customization.
- ERP Cloud is an ideal choice for small and medium-sized businesses thanks to its low initial investment cost, easy expansion, and automatic updates from the supplier.
Understanding the differences between these two models will help businesses correctly assess their needs, minimize the risk of misdirected investment, and maximize the value that the ERP system brings.

2. Definition and basic characteristics when comparing Internal ERP and Cloud ERP
Understanding the difference between Cloud ERP and On-Premise ERP is an important first step in helping businesses choose the right solution for their operating model, budget, and growth goals. Below is a detailed analysis of the definition and core features of these two types of ERP.
2.1. ERP Cloud
Cloud ERP is an increasingly popular choice in the digital age, when businesses need a flexible, scalable system that is less dependent on physical infrastructure. This model is suitable for organizations that prioritize rapid digital transformation and optimize IT operating costs.
- Define: Cloud ERP is an enterprise resource planning system that is deployed and hosted entirely on a cloud computing platform. Instead of being installed locally, all software and data are operated through remote servers managed by the service provider.
- How to access: Users only need a device with internet connection to log in to the system via web browser or mobile application. This allows flexible access from any location and time, especially useful for remote working model.
- Service model: Cloud ERP is often provided under the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model, meaning that businesses subscribe to the software in a package. The supplier will take care of all maintenance, upgrades, security and system operations.
- Outstanding advantages:
- Low initial investment cost, no need to buy separate server.
- Easily scale up usage according to actual needs.
- Automatically update versions and patch security vulnerabilities periodically.
- Supports flexible integration with other applications and platforms.

2.2. Internal ERP (Traditional/On-premise ERP)
ERP On-Premise is a suitable solution for businesses with strict requirements on data security and control. Although it requires large investments in infrastructure and technical personnel, this model provides absolute initiative in ERP system management.
- Define: ERP On-Premise is an ERP system installed directly on the server and IT infrastructure of the enterprise. All data and software are stored internally, the enterprise has complete control over operations.
- Infrastructure requirements: To deploy ERP On-Premise, businesses need to invest heavily in hardware such as servers, network equipment, and security tools. In addition, they need an internal team of technicians to operate and troubleshoot.
- Internal management: From installation, configuration to maintenance and system upgrades, all are proactively carried out by the enterprise. This requires abundant IT resources and a methodical technology management strategy.
- Outstanding advantages:
- Maximum control over data and operating processes.
- Suitable for businesses with high requirements for internal security.
- Deep customization according to industry and organization size.

3. Compare the key differences between On-premise ERP and Cloud ERP
Choosing between Cloud ERP and On-Premise ERP is one of the important strategic decisions of businesses in the process of digital transformation. Below is a detailed comparison table of 4 important factors to help business owners and accountants understand the difference between these two models:
3.1. Investment and operating costs
ERP Cloud: Significantly lower starting costs due to no need to invest in hardware or physical servers. Businesses only need to pay a monthly or annual subscription fee, which includes most maintenance costs, system updates and technical support from the supplier.
ERP On-Premise: Requires large initial investment costs for software licenses, servers, network equipment, and in-house deployment teams. In addition, maintenance, upgrade, and troubleshooting costs arise frequently and are not included in the initial investment, resulting in a higher total cost of ownership (TCO) in the long run.
3.2. Deployment model and speed
ERP Cloud: Rapid deployment thanks to the vendor's existing infrastructure, typically taking 3–6 months, and can even be completed within 90 days for a standard project.
ERP On-Premise: Deployment is more complex and time-consuming, possibly lasting 6–12 months or several years for large-scale projects, due to the need for hardware preparation, system configuration, and thorough on-site testing.
3.3. Customization and upgradeability
ERP Cloud: The system usually allows configuration of interface options and basic processes for each industry. However, the level of deep customization (custom code, complex workflow) may be limited due to the shared structure (multi-tenant). In return, upgrading is automated, helping businesses always use the latest version without affecting operations.
ERP On-Premise: Provides deep customization of the entire system to suit specific business needs. However, upgrades can lose old customizations, require a lot of resources and time, and pose a risk of disruption to operations.
3.4. System security and data control
ERP Cloud: Security is provided by the provider, often integrating encryption technologies, firewalls, AI monitoring and international standards such as ISO 27001, GDPR. However, businesses need to trust third parties with their data and focus on internal management of access authorization.
ERP On-Premise: Enterprises have full control over data on their own systems, suitable for fields requiring high security such as banking, finance, and healthcare. However, it comes with the responsibility of securing the entire system – from firewalls to backups – and the cost of maintaining a dedicated technical team.

4. Choose the right solution for your business
Choosing between ERP Cloud (cloud-based deployment) and ERP On-Premise (internal deployment) It depends not only on budget but also on the business's operating strategy, security requirements and the level of flexibility desired. Below are comparisons and suggestions to help businesses make the right decision.
4.1. When to choose ERP Cloud?
Cloud ERP is suitable for businesses that value flexibility, deployment speed and rapid scalability without having to invest heavily in technical infrastructure.
- Limited initial investment costs: Suitable for newly established businesses or SMEs, helping to optimize initial budget without needing to invest in servers, network equipment or internal IT team.
- The need for flexibility and rapid scalability: Allows expansion of the number of users, modules or features according to each stage of business development.
- Prioritize remote and mobile working: Employees can access the system anytime, anywhere with just an internet connection, helping to increase efficiency and maintain continuous operations.
- Don't want the burden of managing IT infrastructure: The supplier undertakes all maintenance and system updates, ensuring stable operation without the need for an in-house technical team.
- Want to always be updated with the latest technology: ERP Cloud is regularly updated with features and security, helping businesses stay ahead of technology trends without interrupting operations.
4.2. When should you choose On-Premise ERP?
On-Premise ERP is suitable for organizations with high requirements for data security, deep customization capabilities and already have a solid internal technology foundation.
- High demand for customization: Suitable for businesses with specific processes that require software adjustments to suit individual operations.
- Require strict data control and security: Ideal for industries such as banking, healthcare, finance – where sensitive data needs to be absolutely controlled internally.
- Ability to invest in IT infrastructure and dedicated staff: Large enterprises can maximize the benefits of owning their own system, ensuring high performance and long-term stability.
- Don't want to depend on internet connection or external providers: The system still operates even without internet, suitable for environments with high requirements for availability and independent security.
5. Dedicated Solutions for Financial Automation – How to Complement ERP
In the context of businesses increasingly transforming into digital, specialized financial automation solutions are becoming a powerful assistant for the finance and accounting department. Not only helping to streamline business processes, these tools also play a perfect complementary role to the ERP system - especially when businesses are considering Comparing On-Site ERP and Cloud ERP to choose the appropriate operating model.
5.1. The role of financial automation in business
Financial automation offers many practical benefits for cost and cash flow management, including:
- Streamline manual processes: Minimize repetitive data entry, limit the risk of errors in processing invoices, payments and debts.
- Increase processing speed: Shorten the time it takes to collect debts, approve expenses, and reconcile invoices, helping businesses respond faster to financial fluctuations.
- Enhanced spending control: Allows budget visibility, overspending alerts, and more accurate financial decisions.
- Support for financial data integration in sync with ERP: Enhances seamlessness between processes, regardless of the ERP system on-premise good cloud-based.
5.2. Core features of a financial automation solution
An effective financial automation system typically includes the following features:
- Processing and managing input invoices: Automate the process of checking, comparing invoices with PO and GR, warning of discrepancies, checking supplier validity and storing electronic invoices according to prescribed standards.
- Business expense management: Real-time budget tracking, automatic approval support, generate cost reports analyzed by multiple criteria.
- Management of per diem expenses: Automate ticket booking, track accommodation, food, and travel expenses for each employee and trip; integrate spending limits and business trip approval processes.
- Electronic bill: Support mass invoice issuance, custom invoice templates, direct authentication integration with tax authorities.
- Debt control: Automatic debt reminders according to schedule, debt status tracking, overdue debt warnings, creating debt analysis reports by subject.
- Flexible integration with ERP systems: Synchronize data with popular ERP platforms such as SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics… via API, suitable for both internal ERP and cloud ERP.
- Connecting capital sources: Providing supply chain finance solutions, supporting businesses to access effective working capital financing packages.
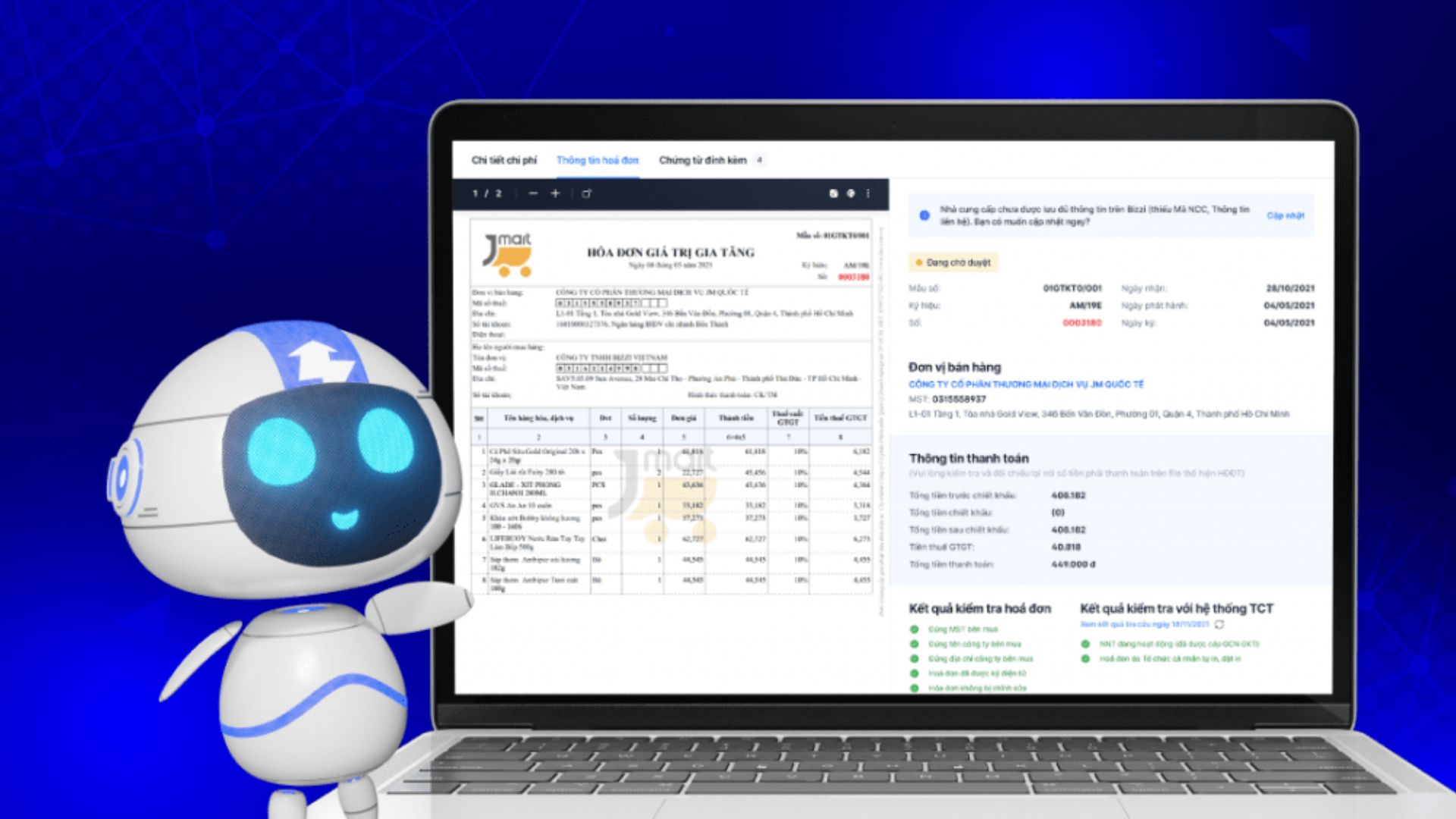
5.3. Reasons why businesses should consider a financial support solution
Compared to a basic financial module in an ERP system, a dedicated financial automation solution offers:
- Greater depth of expertise: Focus on thoroughly solving financial process bottlenecks that traditional ERP finds difficult to fully meet.
- Complements ERP, not replaces it: Enhance the operational efficiency of existing ERP systems – regardless of the business choice Internal ERP or cloud ERP, without changing the entire infrastructure.
- Optimize cost - efficiency - implementation time: Compared to upgrading the entire ERP, implementing a dedicated financial add-on solution saves budget and is faster to deploy.
To improve the efficiency of invoice management as well as automate the financial and accounting processes of the business. Register to experience Bizzi's comprehensive solution suite today!
- Link to register for a trial of Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/
6. Conclusion
Job Compare Internal ERP vs Cloud ERP It is necessary for businesses to choose the right solution for their goals, budget and security level. Cloud ERP is flexible, scalable and has low initial costs - suitable for businesses that are undergoing digital transformation. Meanwhile, internal ERP is suitable for organizations that need deep customization and tight control over internal data systems.
When integrated with specialized solutions such as financial automation from Bizzi, the ERP system will be even more effective, helping to process invoices quickly, reduce risks and optimize operations. Businesses should consult experts before investing to ensure long-term effectiveness.


