Many businesses have implemented electronic invoicing in practice, but still... lack of a proper electronic invoicing management process.Invoices are received, accounted for, and stored in a fragmented manner, while the risk lies in the input data itself: suppliers, transactions, costs, and cash flow.
The emergence of Decision 2799/QD-CT, replace Decision 1447/QD-TCTThis shows a clear shift in the tax authority's management mindset: from managing invoice formats to Control risks associated with electronic invoices and documents throughout their lifecycle.In reality, many businesses have adopted electronic invoices, but A systematic process for managing electronic invoices has not yet been established.This leads to risks related to taxes, costs, and cash flow, even though it appears "legal" on the surface.
This article by Bizzi focuses on:
- Clarify the core content of each decision.
- Analyze the changes in Electronic invoice management process 1447 and 2799
- Business construction guide Internal procedures according to CFO standardsThis is linked to cost and cash flow management, and goes beyond mere compliance.
Context for issuing regulations on electronic invoice management
Decisions 1447 and 2799 were issued in the context of widespread adoption of electronic invoices, but with increasing risks of fraud, illegal invoice use, and tax evasion, forcing tax authorities to shift from post-audit to continuous control throughout the usage process.
Policy developments over different periods
- Period 2021–2023: The focus of the policy is to popularize electronic invoices across the entire business system. The main goal is to replace paper invoices, standardize data, and ensure that businesses issue and use invoices in the correct format as prescribed.
- Period 2024–2025: Once adoption rates have reached high levels, the focus shifts to... Risk management, fraud detection, and tax evasion prevention.Electronic invoices are no longer viewed as administrative documents, but rather as... risk data source It needs to be monitored continuously.
Shifting responsibilities
- Previously: the tax authorities were the inspectors, and businesses responded afterward.
- Currently: businesses must Proactively control input invoices, suppliers, and document flow.before the tax authorities intervened.
From the CFO's perspective, this is no longer just a "tax law" story, but rather... the problem of managing costs, cash flow, and financial risks.To apply them correctly, businesses need to understand the content of each decision, rather than just knowing the document's name or effective date. This is also the reason. Electronic invoice management process 1447 its limitations gradually became apparent and it was upgraded to Electronic invoice management process 2799, with higher demands for risk control right from the start of use.

The basic content of the Electronic Invoice Management Process 2799 according to Decision 2799/QD-CT
Electronic invoice management process 2799 It is designed as a continuous risk control system, covering the entire lifecycle of electronic invoices and documents, rather than focusing solely on issuance and storage. Decision 2799 was issued to establish this. a unified process for managing, monitoring, and mitigating risks. in the use of electronic invoices and electronic documents, instead of only taking action after violations have occurred.
The core issue is not about "tightening management," but about:
- Standardize operating procedures.
- Expand the scope from invoices to all related electronic documents.
- Enhance the ability to detect and warn of risks early.
From a CFO's perspective, this is the framework. Preventing financial control – Preventive control, rather than checking for consequences.
Text information
- Document type: Decision
- Number, symbol: 2799/QD-CT
- Issuing authority: Tax Department
- Date of issuance & effective date: August 6, 2025
- Summary: Issuance of the Procedure for Managing Electronic Invoices and Electronic Documents
- Nature: Replacement document, standardization of risk management processes.
Businesses should store the full text of Decision 2799 in PDF/XML format in their internal legal files as a basis for developing processes and conducting periodic reviews. The processes outlined in Decision 2799 focus on three main pillars:
- Taxpayer data management: Update, categorize, and monitor the risk levels of businesses and suppliers during the use of electronic invoices and documents.
- Monitoring electronic invoices and documents: It involves not only monitoring formal validity but also analyzing usage behavior, frequency, transaction relationships, and any unusual signs.
- Detecting and handling violations: Establish a warning mechanism, classify risks, and intervene early before tax and cost consequences arise.
Regarding the division of responsibilities:
- The tax authorities play a role in disclosing information, monitoring, and providing warnings.
- Businesses must Self-monitor input invoices and related documents. within the internal system
This provides the legal basis for CFOs to build an internal system for controlling invoices and expenses within the business.
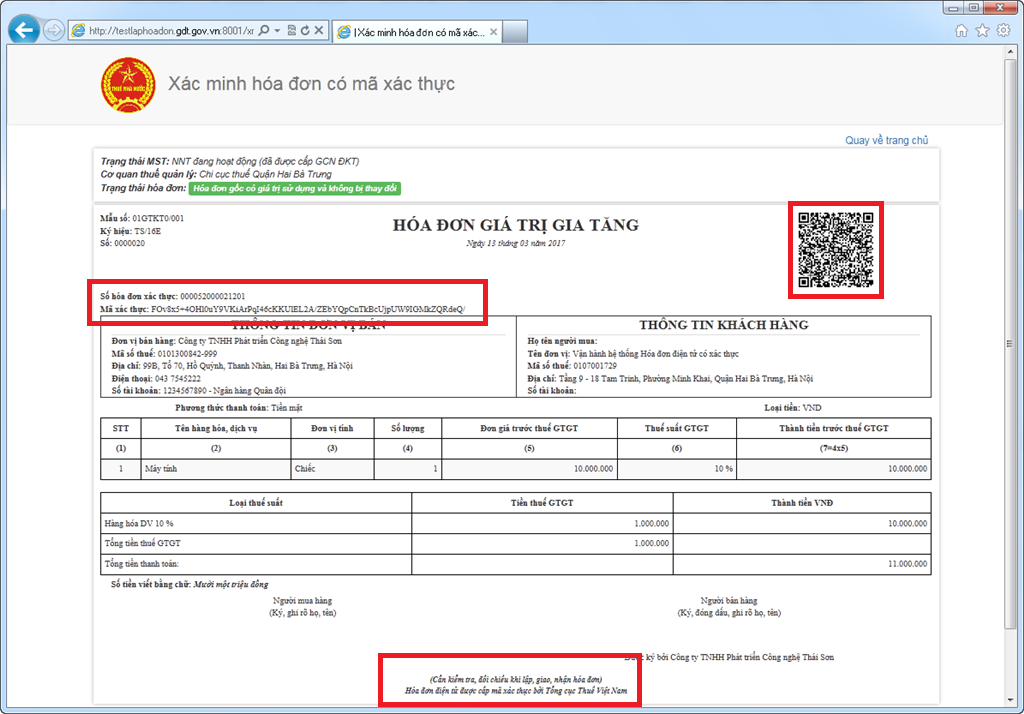
The basic content of Decision 1447/QD-TCT on the management of electronic invoices.
Electronic invoice management process 1447 This is the first management framework issued during the electronic invoice popularization phase, serving as a foundation for the issuance, use, and storage of invoices in accordance with regulations.
Decision 1447 laid the foundation for the management of electronic invoices in the initial phase of implementation. The focus of the document is:
- Control the issuance and use of invoices.
- Ensure compliance with administrative regulations.
- Standardize storage and reporting.
The scope of regulation is still narrow, mainly revolving around electronic invoices, not fully covering electronic documents and not delving deeply into risk management.
Text information
- Document type: Decision
- Number, symbol: 1447/QD-TCT
- Issuing authority: General Department of Taxation
- Date of issue: October 5, 2021
- Summary: Issuance of the Electronic Invoice Management Procedure
Businesses should still retain Decision 1447 for reference with internal procedures developed before 2025.
In the current legal framework, Decision 1447 holds historical significance. This document has been replaced by Decision 2799 to meet the higher risk management requirements in business operations.
Comparison of Electronic Invoice Management Process 2799 and Electronic Invoice Management Process 1447
From a financial management perspective, the difference between Electronic Invoice Management Procedure 1447 and Electronic Invoice Management Procedure 2799 The issue lies not in the invoicing technique itself, but in the extent to which businesses proactively manage risks and take responsibility for invoice data throughout their operations.
This comparison table shows the differences not only in legal content, but also in How businesses should organize their financial and accounting systems..
| Criteria | Decision 1447 | Decision 2799 |
| Role | Initial platform | Replacement text |
| Scope | Electronic bill | Electronic invoices and documents |
| Focus | Administrative compliance | Risk control |
| Corporate responsibility | Passive | Proactive |
| Impact on the CFO | Short | High |
See more about the Top 22 electronic invoicing software. here
How should businesses establish an electronic invoice management process to comply with Decision 2799?
To meet the requirements of Decision 2799, businesses need to design electronic invoice management process as part of a financial control system, not just a formal accounting process.
The process for managing electronic invoices should not be developed to "cope" with legal regulations, but rather to... Control tax risks, costs, and cash flow from the outset.Invoices are the first point of contact for expenses; if they are miscontrolled, the entire subsequent budgeting system will be disrupted.
CFO-standard framework for electronic invoice management processes. It usually includes:
- Centralized invoice processing
- Legal and supplier risk assessment
- 3-way matching
- Approval based on budget and limits.
- Data storage and management reporting
Here, Bizzi plays the role of central financial control systemIt connects invoice, expense, budget, and accounts payable data – it is not a replacement for accounting software.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Electronic Invoice Management Process according to Decisions 2799 and 1447
Below are answers to frequently asked questions regarding the two decisions mentioned above.
Does Decision 2799 completely replace Decision 1447?
Have. Electronic invoice management process 2799 replaced Electronic invoice management process 1447, with the scope expanding to include electronic documents and requiring businesses to proactively manage invoice risks.
From a legal and operational standpoint, Decision 2799/QD-TCT has replaced Decision 1447/QD-TCT in guiding the process of managing electronic invoices. However, this does not mean that businesses can completely "ignore" Decision 1447.
Decision 1447 remains a foundational milestone, reflecting the early thinking behind electronic invoice management: focusing on proper issuance, use, and storage. Decision 2799 inherits that foundation but expands to include risk management and electronic documents, while shifting the focus of responsibility to businesses.
For the CFO, the important thing is not which documents are "still in effect," but whether internal processes have been upgraded to meet the new management mindset.
Are small businesses required to follow the procedures outlined in Decision 2799?
Decision 2799 does not differentiate between large and small businesses in the requirement to manage electronic invoices and electronic documents. The difference lies in the complexity of the process, not in whether or not it is implemented.
Small businesses typically have fewer invoices and suppliers, but are more vulnerable to the risk of fraudulent invoices due to a lack of independent oversight. If errors occur, the impact on cash flow and costs can be significant relative to their scale.
Therefore, for small businesses, Decision 2799 should be understood as:
- No cumbersome procedures required.
- However, minimum control points are mandatory: centralized reception, legal verification, transaction reconciliation, and data storage.
Does a valid tax invoice mean a valid expense?
No. This is one of the most common misconceptions in cost management.
An invoice can include:
- Formally valid for tax purposes.
- Valid code issued
- Not included in the list of illegal invoices.
However, it will still not be accepted as a valid expense if:
- Not for production or business purposes.
- There were no actual economic transactions involved.
- Not in line with budget or internal spending policy.
Decision 2799 emphasizes that businesses must manage their own risks, rather than relying solely on "getting their taxes done." This is where CFOs need to clearly distinguish between tax compliance and cost management.
What should businesses do when a supplier is considered high-risk?
When tax authorities or internal data systems identify a supplier as showing signs of risk, businesses should not react impulsively by "stopping all transactions," but should instead follow established procedures.
The steps to follow include:
- Review your transaction history and past invoices.
- Examine the relevance of costs to business operations.
- Escalating control: requiring additional documents, contracts, and acceptance reports.
- Reassess payment terms and budget limits.
In essence, this is supplier risk managementIt's not just about processing invoices. CFOs need comprehensive data to make decisions, rather than just reacting to external alerts.
How does the electronic invoicing process affect budgets and cash flow?
Invoices are the starting point of expenses. If the invoice management process is weak, the budget will be disrupted from the input stage and cash flow will be stagnant at the output stage.
An electronic invoice management process in accordance with the spirit of Decision 2799 helps to:
- Prevent overcharges from occurring at the time of invoice receipt.
- Control the timing of debt recording, avoiding unreasonable early or late payments.
- Improve cash flow forecasting with centralized invoice data.
For the CFO, electronic invoices are not just accounting documents, but... Early signs of future cash flow pressure.
Is it necessary to change the accounting system when implementing Decision 2799?
In most cases, Businesses do not need to change their core accounting system.What needs to change is pre-accounting control layer.
Decision 2799 has the strongest impact on:
- Invoice receiving and verification process
- How to assess supplier risk
- Pre-accounting expense approval flow
If the accounting system only records data after the invoice has been accepted, the business needs to add a supplement. intermediary financial control system to meet the new requirements.
What metrics should a CFO track from electronic invoice data?
In electronic invoice management processCFOs should monitor the rate of risky invoices, invoice processing times, budget deviations, and their impact on cash flow. Electronic invoice data allows CFOs to track many key management metrics, not just for tax purposes, including:
- Rejected or adjusted invoice rate
- Cost breakdown by supplier and risk group
- Invoice processing time from receipt to approval
- Difference between invoice – contract – budget
- Trends in unexpected expenses
These metrics help CFOs transition from past reports luxurious control and forecast.
Conclude
The process of managing electronic invoices is no longer a single compliance requirement of the accounting department, but has become a comprehensive process. a crucial component in a business's risk, cost, and cash flow control system.The replacement of Decision 1447/QD-TCT by Decision 2799/QD-TCT clearly shows a shift from "administrative invoice management" to data-driven risk management.
If Electronic invoice management process 1447 To lay the foundation for the issuance, use, and storage of electronic invoices in the initial phase, Electronic invoice management process 2799 requiring businesses to Proactively develop internal processes.This allows for early risk detection, transaction reconciliation, and invoice control during the operational process – without waiting for tax authorities to conduct an audit.
From a CFO's perspective, the electronic invoice management process under Decision 2799 needs to be designed as a closed financial control chain, include:
- Centralized invoice collection and risk classification.
- Legal review alongside cost control.
- Three-way matching is used to protect your budget.
- Storing traceable data facilitates auditing and management analysis.
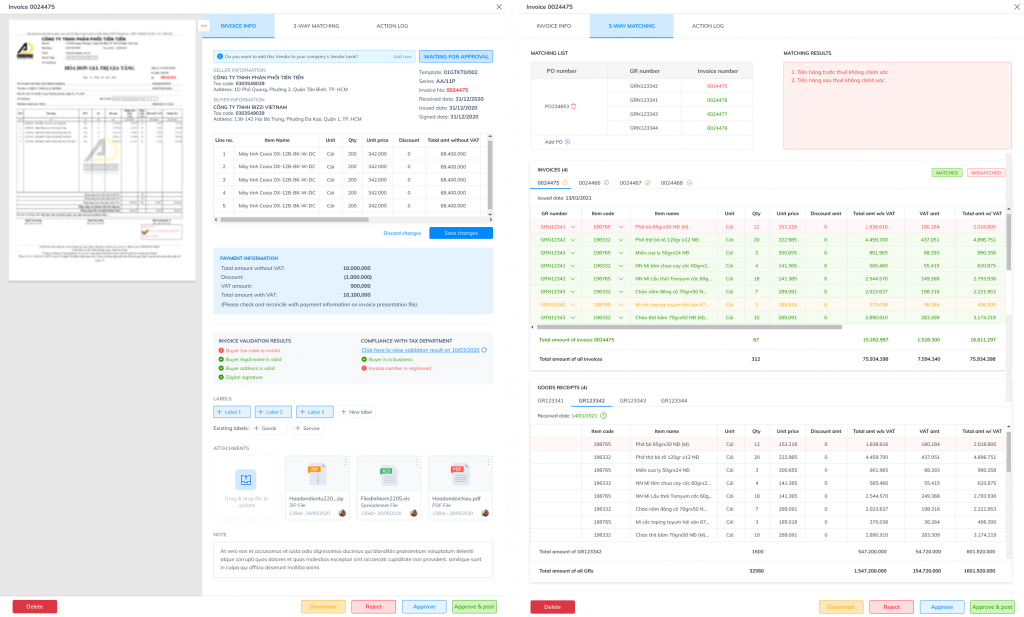
In that context, Bizzi is not a replacement for accounting systems or ERP., which plays a role Control and automation layer for electronic invoice management processes. For businesses. Specifically:
- Bizzi assists in receiving, extracting, and standardizing incoming electronic invoice data.
- Automatically reconcile invoices with contracts, purchase orders, and incurred expenses.
- Issue warnings about invoice and supplier risks right from the start of the process.
- Providing real-time invoicing data to CFOs for tracking expenses, budgets, and cash flow.
When implemented correctly, Electronic invoice management process according to Decisions 2799 and 1447 It not only helps businesses comply with regulations, but also becomes a A crucial data platform for modern financial management.where CFOs can make faster, more accurate decisions and control risks at their source.
Register here to receive a one-on-one consultation on invoice management solutions for your business: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/


