Capital budget is an important part of financial management for every business. If you are looking to learn What is capital budgeting?, how to make effective capital budgeting, or the difference between capital budgeting and operating budgeting, this article will give you full and detailed answers.
Capital budget management is not only an accounting problem, but also a strategic factor that helps businesses invest in the right direction, optimize cash flow, and sustainable development in the long term.
This article will help you understand the concept of capital budgeting, distinguish it from operating budgeting and guide you on how to make effective capital budgeting.
1. What is capital budgeting? Definition and core features
Before going into the method of establishment and management, we need to understand clearly What is capital budgeting?.
Capital budgeting is a long-term financial plan that describes the allocation and use of a business's capital resources for major investment projects such as purchasing fixed assets, expanding production, or investing in research and development (R&D).
These expenses are often related to CapEx (Capital Expenditure), include:
- Purchase of fixed assets: Factories, machinery, means of transport, information technology systems.
- Development investment: R&D (research & development), branch expansion, acquisition of other companies.
- Infrastructure Improvements: Upgrade production line, expand warehouse.
For example:
- A steel manufacturing company invested 10 billion to buy a new production line.
- A technology company spends 5 billion on product research and development (R&D).
Salient features of capital budgeting
Capital budgets have several distinct characteristics compared to other types of budgets:
- Long-term investment: Usually over several years, not monthly costs.
- Large asset value: Involving investments from several hundred million to billions of dong.
- Has strategic impact: Direct impact on competitiveness and long-term growth.
- Associated with CapEx: Expenses are amortized over time rather than recorded at one time.
When researching What is capital budgeting?, you need to remember this is not just a financial plan, but a foundation for business planning. future and investment strategy. 
2. Distinguish between Capital Budget and Operating Budget
Many people when learning What is capital budgeting? often confused between capital budget and operating budgetDistinguishing clearly between these two types of budgets helps businesses manage finances accurately and make reasonable investment decisions.
The comparison table below will help you understand the difference:
| Criteria | Capital budget | Operating budget |
| Purpose | Long-term investment, increasing production capacity, expanding scale | Daily operations, maintenance |
| Time | Many years (3-5 years or more) | Monthly, quarterly or yearly |
| Characteristic | Amortized over time, not recorded as an expense immediately | Record all expenses in the current accounting period |
| For example | Buy machinery, build factories | Pay monthly salaries, electricity and water bills, and marketing |
Capital budgeting helps businesses expand and improve their production capacity in the long run, while Operating budgeting ensures smooth day-to-day operations. These two types of budgets complement each other, but need to be managed separately to ensure financial transparency.
3. The role of Capital Budgeting in optimizing business Costs & Cash Flow
Understanding What is capital budgeting? is just the first step. More importantly, you need to be aware strategic role its impact on the financial performance and long-term development of the business.
3.1. Optimizing the use of capital and resources
Capital budgeting helps businesses allocate capital resources reasonably, avoiding spreading investments or wasting on ineffective projects.
- Help businesses invest in the right focus, avoid wasting resources on ineffective projects.
- Ensure capital is allocated reasonably between growth and maintenance projects.
- Create a basis for control investment costs, improve capital efficiency.
3.2. Risk management and strategic decision making tools
Investment decisions often involve significant financial risk. Capital budgeting serves as a filter, help businesses:
- Forecast market, cash flow and interest rate risks.
- Board of Directors make the right decision on whether to invest or stop the project.
- Limit the situation of "emotional investment" leading to capital loss.
3.3. Foundation for long-term financial planning
A well-constructed capital budget will become compass for long-term financial activities, support:
- Growth strategy planning.
- Attract capital from investors or banks.
- Ensure transparency and compliance with accounting regulations.
Case Study: Lessons from capital budget management failures – Mai Linh
Mai Linh Group (MLG) used to be one of the largest taxi companies in Vietnam, with a nationwide presence. However, in 2011–2013, Mai Linh faced a financial crisis, largely related to poor strategic capital budget management (CapEx). Here is a detailed analysis:
Current status & data
- As of June 30, 2012, Mai Linh's total assets were about VND 5,580 billion, while liabilities were VND 4,690 billion, accounting for 841% of total capital.
- Interest expense in the first 6 months of 2012 was about 272 billion VND, equivalent to about 18,241 TP3T of revenue.
- Accumulated loss by the end of 2012 amounted to 481 billion VND, equivalent to about 55% of charter capital.
- Mai Linh used to borrow short-term capital for long-term investment – that is, using short-term capital to carry out projects that require long payback periods. This created liquidity risks when principal/interest payments came due.
- Management and financial costs are too large compared to operating capacity: business management costs account for about 10% of revenue, much higher than competitors in the same industry.
Major mistakes in capital budget management at Mai Linh
From the above data, we can draw some very clear mistakes in planning and management. capital budget:
- Expanding investments too quickly without realistic cash flow assessment
Mai Linh invested in many new vehicles and expanded operations in many provinces and cities, but vehicle usage in these areas was low, resulting in cash flow not being enough to cover initial investment costs and maintenance costs. - Using short-term loans for long-term investments
Short-term loans with high interest rates are used to buy fixed assets or taxis, which take many years to pay back. When the loan comes due, liquidity problems arise because there is no capital reserve or the cash flow is unstable. - Interest and financial costs are too high
Interest accounts for a large part of financial costs, reducing gross profit and the ability to reinvest. Borrowing at high interest rates from sources other than banks also increases the cost of capital. - Lack of focus and priority in capital budget allocation
Mai Linh invests widely: new cars, expanding locations, brands, sometimes real estate, while not focusing on upgrading technology, managing the ride-hailing application system or improving user experience - this gives competitors a greater advantage. - Poor risk management and lack of provisioning
Failure to anticipate worst-case scenarios such as revenue losses, rising fuel costs, strong technological competition, or changes in market demand; lack of reserve funds to contain crises when costs exceed forecasts.
Consequence
- Large accumulated losses: up to nearly 481 billion VND in 2012, accounting for more than half of charter capital.
- Overwhelming finance/interest costs: most of the gross profit is spent on interest and administrative expenses, resulting in low or negative net profit.
- Liquidity is threatened: The company does not have enough money to pay interest, due debts, salary debts, social insurance debts; must sell assets, liquidate vehicles.
- Losing market share to competitors using technology models: competitors like Grab (ride-hailing model) with low operating costs and faster response to technology have gained the upper hand. (Although during Mai Linh's difficult period, Grab just entered; but most of the strategic failures are related to technology competitors, user demand shifting to applications.)
Lessons learned
Based on Mai Linh's failure, valuable lessons can be drawn for all businesses when making capital budgets:
- Capital budgeting is based on actual cash flows, not just expectations.: Accurately estimate inflows and outflows to ensure the project has a positive NPV and IRR exceeding the cost of capital.
- Prioritize projects with high profits and high efficiency: should not invest in areas of low demand or low performance.
- Do not borrow short term to invest long term: choose the right source of capital in terms of term and cost, to avoid liquidity risk.
- Tight financial cost management: negotiate low interest rate loans, reduce non-bank loans with high interest rates.
- Building reserves and managing risks: have a reserve fund for unexpected expenses, closely monitor financial indicators — debt/equity, short-term/long-term debt, interest expense compared to revenue.
4. 5-step guide to effective capital budgeting
Understand What is capital budgeting? That's not enough, you need to know how to budget scientifically.
Capital budgeting is a strategic process that requires a combination of financial analysis, cash flow forecasting and risk managementHere are five basic steps to effective capital budgeting:
Step 1: Identify and propose potential projects
- Collect ideas from departments: production, marketing, R&D.
- Identify projects that have big impact to long-term productivity or profitability.
- For example: Expanding a new factory, purchasing ERP software, investing in an AI system.
Step 2: Estimate cash flow and associated costs
- Identify initial investment costs: machinery, personnel, implementation costs.
- Forecast future cash flow that the project will generate.
- Create multiple scenarios: optimistic, neutral, pessimistic.
Step 3: Evaluate and select the optimal project
- Using analytical methods such as NPV, IRR, Payback Period.
- Compare projects based on net profit, risks and strategic objectives.
- Priority is given to projects that have Positive NPV and high IRR.
Step 4: Implement and allocate budget
- Develop detailed implementation plans for each phase.
- Capital allocation based on priority and project progress.
- Make sure to have reserve funds for unexpected situations.
Step 5: Monitor and evaluate effectiveness
- Monitor project progress and capital utilization.
- Compare actual results with original estimates to make timely adjustments.
- Periodic reports to management and shareholders.
5. Common capital project evaluation methods (NPV, IRR, Payback Period)
When you understand clearly What is capital budgeting?, the next step is to evaluate the project to choose the optimal investment option. To choose the optimal investment project, businesses often use 3 common methods: NPV, IRR, and Payback Period.
5.1. NPV – Net Present Value
- Define: Measures the present value of future cash flows minus the initial investment cost.
- Recipe:
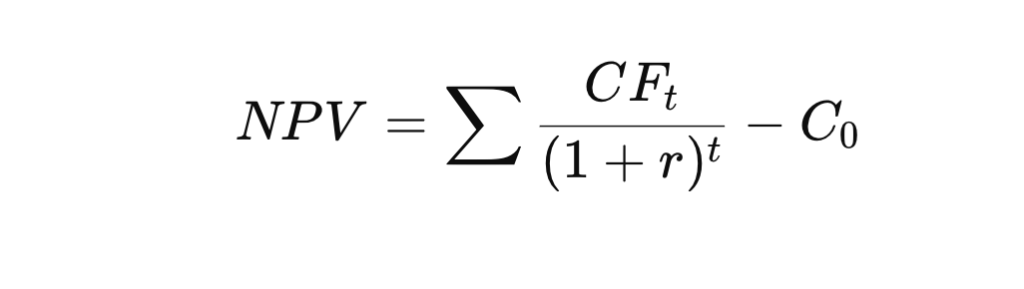
In there:
- CFt: Cash flow in year t
- r: Discount rate
- C0: Initial investment cost
For example:
- Initial investment: 500 million
- Annual cash flow: 150 million, lasting 4 years
Discount rate: 10%
→ Calculate NPV = 15 million (project is feasible because NPV > 0)
5.2. IRR – Internal Rate of Return
- Define: Discount rate at which NPV = 0.
Meaning: The higher the IRR, the more attractive the project. - Standard: IRR > expected interest rate of the business → accept the project.
- For example:
With the above data, IRR ≈ 12%. If the business expects 10%, the project is accepted. accept.
5.3. Payback Period – Payback period
- Define: The period of time required for the accumulated cash flow to cover the initial cost.
- Advantage: Easy to calculate, intuitive.
- Disadvantages: Does not take into account the time value of money.
- For example:
Investment cost: 500 million
Annual cash flow: 150 million
→ Payback Period = 500 / 150 = 3.33 years
Comparison table of capital project evaluation methods
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantages |
| NPV | Accurately reflects current value, easy to compare. | It is difficult to estimate the discount rate accurately. |
| IRR | Shows easy to understand profitability. | It can be confusing if cash flow fluctuates. |
| Payback Period | Easy to calculate, fast. | Ignores the time value of money and post-payback cash flows. |
6. Conclusion: Optimizing capital budgeting with financial and accounting automation
Understand What is capital budgeting? And effective planning is a useful stage in business management.
Manage capital budget Not only is it an accounting practice, but it is also a strategic foundation that helps businesses maintain their healthy cash flow, minimizing risks and optimizing investment efficiency. A properly prepared and closely monitored capital budget will help businesses:
- Invest in the right projects high rate of return.
- Minimize waste and loss of capital during implementation.
- Ensure financial transparency and increase shareholder and investor confidence.
However, many businesses still have difficulty in data collection, track CapEx and analyze project performance. This can easily lead to:
- Investment decisions are based on emotional instead of exact data.
- It takes a lot of time to compile data from many departments.
- Failure to promptly detect risks and ineffective projects.
Bizzi.vn – Capital budget management automation solution
With the platform Bizzi Expense, businesses can:
- Collect capital expenditure data from multiple sources at once automatic and accurate, reducing manual errors.
- Support analysis and provision correct input data for project evaluation methods such as NPV, IRR, Payback Period.
- Create visual reports to help management make quick and accurate decisions based on real-time data.
- Enhance financial transparency, ensuring compliance with legal regulations and accounting standards.
Explore Now Bizzi Expense – Capital Expenditure Management Automation Solution to see how Bizzi helps businesses optimize their capital budgeting and management processes.
Take control of your finances and optimize your capital budget today with Bizzi.vn, thereby improving investment efficiency and promoting sustainable growth for your business.


