Contactless payment and touchless invoice processing are not just trends, but ways for businesses to upgrade their operations to be faster, more accurate, and more secure. However, to achieve true "touchless" success, businesses cannot start with the payment process; they must standardize data and automate the AP process from the ground up.
This article will provide comprehensive information to explain what a Touchless Invoice is, as well as analyze the nature of contactless payment.
What is contactless payment?
Contactless payment is a fast, convenient, safe, and hygienic payment method suitable for small transactions, using tokens instead of physical card information for security.
What is the concept of contactless payment?
Contactless payment is a form of payment where users do not need to insert their card into a POS machine, swipe the card, sign their name, or enter a PIN (within certain limits). The transaction was carried out by dab, bring near, or scan code using devices with integrated digital payment technology.
The core of contactless payment is the transmission of payment data via near-field communication (NFC) or QR code encryption without friction, making transactions faster and more secure.
Popular types of contactless payments today
Here are some common forms of contactless payment:
Payment via NFC (Near Field Communication)
This is the most common type, using short-range radio waves. Users simply bring their card/phone/watch close to the POS machine.
Include:
- Contactless card (Visa payWave, Mastercard Contactless)
- Digital wallets that support NFC: Apple Pay, Google Wallet, Samsung Pay
- Smartwatch: Apple Watch, Galaxy Watch
Characteristic: Fast, no card swiping required, and highly secure thanks to tokenization.

Payment via QR Code
Users scan QR codes to make payments, a practice popular in Vietnam thanks to the VietQR standard and the QR codes of e-wallets.
Types of QR codes:
- Static QR code: a fixed code, the buyer enters the amount themselves.
- Dynamic QR code: code changes with each transaction, automatically fills in amount and invoice information.
- Cross-border QR codes: Vietnam – Thailand, Singapore, Malaysia…
Advantage: No POS required, suitable for SMEs, high speed.

Wearables Payment
Pay with watches, bracelets, rings, etc., via NFC or tokenization.
For example:
- Garmin Pay
- Fitbit Pay
- RingPay (smart ring)
Convenient: Suitable for fitness, bus/metro rides, and small purchases.

Tap-to-Phone / SoftPOS (turns your phone into a POS machine)
The seller's phone uses NFC to receive contactless payments.
Allow:
- No traditional POS machine required.
- SMEs, shippers, and small shops can all accept contactless Visa/Mastercard.
This is a major trend in banking and Fintech – Biometric Payments. This means you...No need to touch cards or scan QR codes, just use biometrics:
For example:
- Face scanning (FacePay)
- Fingerprint on the phone
- Palm recognition (Amazon One – palm scanning)
Although not yet widespread, this is a natural evolution of contactless technology.

How contactless payment works
Contactless payments operate based on near-field communication (NFC) technology or two-way encryption (QR code). Depending on the type of contactless payment, the detailed mechanism varies, but they all follow four main steps:
-
The payment gateway device (Card/Phone/Watch) generates a “one-time transaction code”.
When a user brings their card or phone close to the POS machine:
- The device is not sending the actual card number (PAN).
- Instead, it sends a tokenized payment token or one-time transaction code (cryptogram).
This mechanism is called Tokenization – it helps ensure security because the real data is not leaked.
-
POS and NFC/Encryption devices exchange data via these platforms.
If it's NFC:
- Transmission distance: 1–4 cm
- Speed: a few milliseconds
- The card/phone sends encrypted information via short-range radio waves.
If it's a QR code:
- Buyer scans the QR code → phone sends data via the bank's/e-wallet's API.
Both ensure there is no physical contact.
-
The issuing bank (Issuer) performs the verification.
The POS sends data packets to:
- Acquirer Bank
- Then forward it to the card issuer (Visa/Mastercard, etc.).
- Then it goes to the bank that issued the buyer's card.
Bank check:
- Is the token valid?
- Are there duplicate transactions?
- Does the device recognize the registered cardholder (Face ID, PIN, fingerprint)?
- Is the account balance/credit limit sufficient?
If valid → Approve. Invalid → Decline. It all happens in 0.2–1 second.
The POS system receives the response and completes the transaction.
- The POS displays "Approved".
- The money is either held or paid immediately, depending on the type of transaction.
- Tokens expire after the transaction → cannot be stolen and reused.
What are the benefits of contactless payments?
Contactless payment offers benefits in terms of speed, convenience, and security for both users and businesses.
For users
Transactions are 2–3 times faster than with traditional chip cards/swipe cards.
- Simply bring your card/phone close to the POS terminal and it will process it in less than 1 second.
- No PIN required for small transactions → further reduces processing time.
No contact required — Reduces hygiene and infection risks.
- No touching POS terminals, no cash exchange.
- Particularly useful in crowded places: supermarkets, convenience stores, and food and beverage outlets.
Superior security thanks to Tokenization
- Don't use your real card number → reduces the chance of theft.
- Each transaction generates a dynamic cryptogram, making it impossible for hackers to reuse.
- Combining FaceID and fingerprint recognition when using e-wallets → multi-layered security.
For retail businesses
Contactless payments offer numerous benefits to retail businesses, including:
Increase service speed – reduce queues.
- Fast payment → increased throughput at the counter.
- Reduce congestion during peak hours, especially for the F&B, fashion, and minimart industries.
Reduce the risks associated with handling cash.
- Minimize losses or errors when counting money.
- Reduce costs associated with managing, counting, and transporting cash.
Easily integrates with modern POS systems.
- Most modern POS systems are NFC/QR-ready.
- Optimize the omnichannel experience by integrating with e-wallets and loyalty programs.
Risks and limitations of contactless payments
Contactless payment is convenient but has drawbacks. Security risks and implementation difficulties.
Main risks
- Security risks:
- Fraudulent transactions due to lost/stolen cards: Lost cards can be used to make numerous small transactions without a PIN, especially as the threshold for PIN-free transactions is raised.
- Sophisticated attacks: Hackers may attempt to modify NFC devices or steal private data.
- ReduceohThe risk of counterfeit cards or e-wallets still exists.
- Business risks:
- Chargebacks: Chargeback transactions can result in lost revenue and fees for the seller.
- Phprocessing High: Implementation may be costly initially due to the need to invest in equipment.
Limitations and challenges
- Unfamiliarity: Older users or those unfamiliar with new technologies may encounter difficulties.
- Infrastructure: Outdated POS machines that are not supported or require upgrades and device synchronization.
- Employee training: Employees need time to familiarize themselves with new procedures to avoid confusion.
- Transaction limits: While they help reduce risk, these limits also restrict the value of payments.
What is a touchless invoice?
Touchless Invoice is a fully automated invoice processing system that requires no data entry or manual human intervention.
The system will automatically:
- Receive invoice from email/provider.
- Read – extract data (OCR + AI).
- Validity check (Tax ID number, date, amount, VAT…).
- Compare with purchase order/gross order or contract.
- Create a payment voucher/payment request form. in ERP.
- Submit for automatic review following the workflow.
- Make a payment Or transfer it to a bank.
It all happened No need to touch:
- No manual data entry required.
- Do not upload invoices to ERP.
- Do not send emails requesting approval.
- No need for manual prompts or follow-ups.
What is the difference between contactless and touchless invoices?
Contactless = Contactless payment (for consumers)
- For use with card/phone when swiping at the store.
- Technology NFCSimply touch or bring it close to the POS machine.
- Small, fast transactions, no PIN required.
- Examples include Apple Pay, Samsung Pay, and contactless Visa/Mastercard cards.
Touchless = Invoice processing without contact (for businesses)
- For internal use accounting and financial processes of the enterprise (AP).
- Fully automatic: Receive – Read – Check – Compare – Submit for approval – Create payment voucher – Make payment.
- No data entry, no uploading of invoice files, no email requests for approval.
- Examples: AP Automation system, Bizzi IPA.
Technology that creates "touchless" in APs
The technology that creates "touchless" payment/invoice management (AP) primarily relies on NFC (Near-Field Communication) and QR codes, combined with Artificial Intelligence (AI), Optical Character Recognition (OCR), and Process Automation (RPA). The main goal is to digitize, extract invoice information, automatically reconcile and approve, minimizing manual intervention (touchfree) throughout the entire AP process, from invoice receipt to final payment.
1. OCR invoice
Read invoices in PDF format, photos, and files sent via email. But OCR simply They only read the text — they don't understand the context. This is a gap that many competitors don't address clearly.
2. IDP (Intelligent Document Processing)
It uses OCR + AI to help the system understand the structure of hundreds of different invoice templates.
- Layout identification
- Understanding data fields
- Automatically classify suppliers and document types.
IDP is a platform that helps increase accuracy to >90–95%.
3. AI recognizes and extracts data.
AI reads line segments and key fields:
- Amount before/after tax
- VAT
- PO Number
- Product code
- Supplier code
Result: The data has been extracted accurately and is ready for comparison.
4. RPA (Robotic Process Automation)
RPA automates all repetitive accounting tasks:
- Download invoices from email
- Save file
- Submit for review via workflow
- Move to ERP
Reduce manual operations by 70–80%.

5. 3-Way Matching Automation (PO – GRN – Invoice)
Automatic matching:
- Quantity receive
- Unit price
- Value bill
This is rare attribute helps the process to really improve. "no-touch"The system automatically verifies for a match, only sending alerts when there is a discrepancy.
6. Auto-posting to ERP
Automatically generated:
- Payment request form
- Payment voucher
- Accounting entries
For ERP systems like SAP, Oracle, Odoo, D365… No data entry or file uploads required.
7. Auto-reconciliation
- Bank reconciliation
- Reconcile vendor ledger accounts payable.
- Matching transactions – invoices – payments
Ensure AP is transparent and does not fall behind schedule with suppliers.
Touchless Invoice Process – Transparent Step-by-Step
Touchless Invoice Processing = from the moment the vendor sends the invoice → to payment and closing the billing cycle → 0 manual operations. Below is the Touchless Invoice Processing process presented step-by-step – clear – transparent, following the actual flow of a modern AP:
1. Vendor sends invoice
- Via e-mail, vendor portal, or API.
- The system automatically receives invoices; no manual downloading is required.
2. Automatic data scanning and extraction system
- IDP + OCR reads PDFs/images.
- Automatically identify invoice template, supplier, and document type.
3. AI verifies validity according to Decree 123.
- Check the tax identification number, symbol, form number, and invoice number.
- Verify that the invoice exists, has not been canceled, and is valid in the tax system.
- Check the date, VAT, and total amount.
4. Automatically check for duplicates
- Match invoice number – date – vendor – value.
- Prevent duplication from the start.
5. Automatic 3-Way Reconciliation (PO – GRN – Invoice)
- Match quantity, unit price, value.
- Matching logic is supported by AI.
- Only issue warnings when there is a discrepancy (exception-based workflow).
6. Payment Request Suggestions
- The system automatically generates a payment draft based on the matched invoice.
- No manual data entry or form creation is required.
7. Automated workflow review (RBAC / ABAC)
- Automatically submit applications for approval to the right people with the right permissions.
- Rules based on limits, expense types, and departments.
- Automated approval reminders – no manual emails.
8. Automatic posting to ERP (Auto-posting)
- Create journal entries, PR/PO updates, payment vouchers, or invoices in the ERP system.
- Two-way synchronization with SAP / Oracle / Odoo / D365 / FAST / Bravo…
9. Reconcile payments & close accounts.
- Automatically match payments, invoices, and bank statements.
- Calculate your PAID/UNPAID status yourself.
- Automatically prepare data for closing.
What are the financial benefits of using Touchless Invoice?
Touchless Invoice = Reduced costs – reduced personnel – reduced errors – increased speed – increased accuracy – increased transparency. Let's analyze the benefits of implementing Touchless Invoice.
1. Significantly reduce invoice processing costs – Save 50–80% in AP costs.
- Manual process: 80,000–150,000 VND/invoice (Data entry, checking, submission for approval, error handling).
- Touchless: only 20,000–40,000 VND/invoice.
2. Shorten Cycle Time from 3–7 days → to just a few minutes
- Automatic receiving – reading – checking – comparing – sending for approval.
- Paying on time reduces penalties and improves your reputation with vendors.
- Take advantage of early payment discounts.
3. Increase AP team productivity (FTE Reduction / Avoided Hiring)
- One person can now handle 3–5 times the number of invoices they previously processed.
- As the volume of invoices increases, there is no need to increase staff.
- Optimizing long-term operating costs.
4. Reduce errors – increase compliance & control
- Automatic validation according to Decree 123 / Decree 70.
- Automatically check for duplicates, check amounts, purchase orders (PO), and gross warrants (GRN).
- A complete audit trail: who approved it, when, and what changes were made → serves audit and tax purposes.
- Reduce the risk of errors leading to disallowed payments.
5. Faster closing 20–40%
- Data is entered into the ERP system in real-time, so it doesn't accumulate until the end of the month.
- Auto-reconciliation helps shorten reconciliation time.
- The chief accountant and CFO have timely data to make decisions.
Risks and bottlenecks if processes are not standardized.
Investing in IDP, MDM, integration layer, matching logic, and governance is essential — prioritized in this order: Vendor data + IDP + Approval rules + Middleware. Correctly implementing these four components will transform the "touchless" concept into a measurable result.
1) OCR is not reading correctly, IDP is required.
Reason
- The invoices come in a variety of formats and templates, with poor quality scans/images.
- Pure OCR only recognizes characters; it doesn't understand layout.
Consequences
- High extraction error rate → requires manual processing.
- Reduced throughput negates the benefits of "touchless" functionality.
Solution (high priority)
- Deployment IDP (OCR + AI) This allows for learning patterns, understanding layouts, and recognizing line styles.
- Invest in image preprocessing steps (deskew, denoise) to improve OCR.
- Establish feedback loop: User corrects the error for the first time — active learning system.
- KPI: Increase accuracy to >95% within 30–60 days of testing.
2) Vendor data is "dirty" and needs cleansing/MDM.
Reason
- Non-standard vendor name, code, tax identification number, and bank account details; multiple aliases.
- The provider sends multiple emails/multiple accounts.
Consequences
- Matching PO/Invoice/GRN failed; duplicate; incorrect ledger.
- Reconciliation errors, delayed payments, and fraud risks.
Solution (high priority)
- Construction Vendor Master / MDM: Standardize name, tax identification number (MST), vendor code, and account number.
- Use the tool data cleansing & rule-based matching for alias pairing.
- Vendors are required to register with accurate information. portal before receiving the invoice.
- KPI: Reduce unmatched vendor rate to <5%.
3) The old ERP system does not support APIs; middleware is required.
Reason
- Legacy systems do not have endpoints for auto-posting; they only support manual import or batch file uploads.
Consequences
- Requires RPA/CSV upload → not real-time, prone to errors → disrupts touchless workflow.
Solution (high priority)
- Design middleware / integration layer:
- It could be an ESB, iPaaS, or a specialized connector (SAP PI/PO, Oracle Integration, Mule, Bizzi connector, etc.).
- Supports data transformation, retry logic, logging, and queuing.
- If that's not possible, use RPA+ validation This is just a temporary step, but a plan to develop an API is necessary.
- KPI: Average time-to-post < 5 minutes; post errors < 1%.
4) The approval process is unclear, making "touchless" impossible.
Reason
- Ad-hoc browsing flow, numerous exceptions, and non-standardized permissions/thresholds.
- Lack of RBAC/ABAC policies.
Consequences
- The automated submission system was interrupted in many places → manual intervention was required → the no-touch goal was not achieved.
Solution (high priority)
- Standardize approval policy: by limit, expense type, project, and department.
- Apply RBAC/ABAC to the workflow engine; there is clear exception handling.
- Train reviewers, commit to SLAs (e.g., review within 24 hours).
- Implement automated escalation and audit trail.
- KPI: Rate auto-approved (no intervention needed) > 85%.
5) Lack of logical rules for 3-Way Matching
Reason
- Matching is either too rigid (exact match) or too loose; it does not support partial/quantity tolerance.
Consequences
- Due to the high exception rate, the AP team had to handle the issues manually.
Solution
- Construction matching engine with: price tolerance, partial-PO logic, rules for freight/discounts.
- Combine AI to predict the reasons for exceptions and suggest actions.
- KPI: Reduce exception rate to <10%.
6) Legal/compliance risks if data is incorrect (Decree 123/Decree 70)
Reason
- The invoice was not validated according to regulations and lacked an audit trail.
Consequences
- Penalties, tax exposure risks, audit failure.
Solution
- Integrate validation checks according to Decree 123/Decree 70 into the validation pipeline.
- Save audit trail immutable (log + file hash).
- Periodic compliance check & reporting.
What is Bizzi Bot – the platform for creating touchless invoices?
Bizzi Bot = IDP + AI + 3WM + Workflow + ERP Integration + Payment Automation, thereby creating a truly touchless invoice process, not just "OCR + submit for approval".
1. Advanced AI + OCR
- Accurately extract Vietnamese invoices with hundreds of complex templates (PDF, images, software exports).
- AI can automatically detect errors, anomalies, and risky tax invoices.
- Validation verification according to Decree 123/ND70, real-time alert.
2. Automatic 3-Way Matching (PO – GRN – Invoice)
- Match unit price – quantity – value in real time.
- Supports partial delivery, tolerance, and multiple line items.
- This is a major difference compared to basic AP Automation solutions (which only offer OCR and workflow).
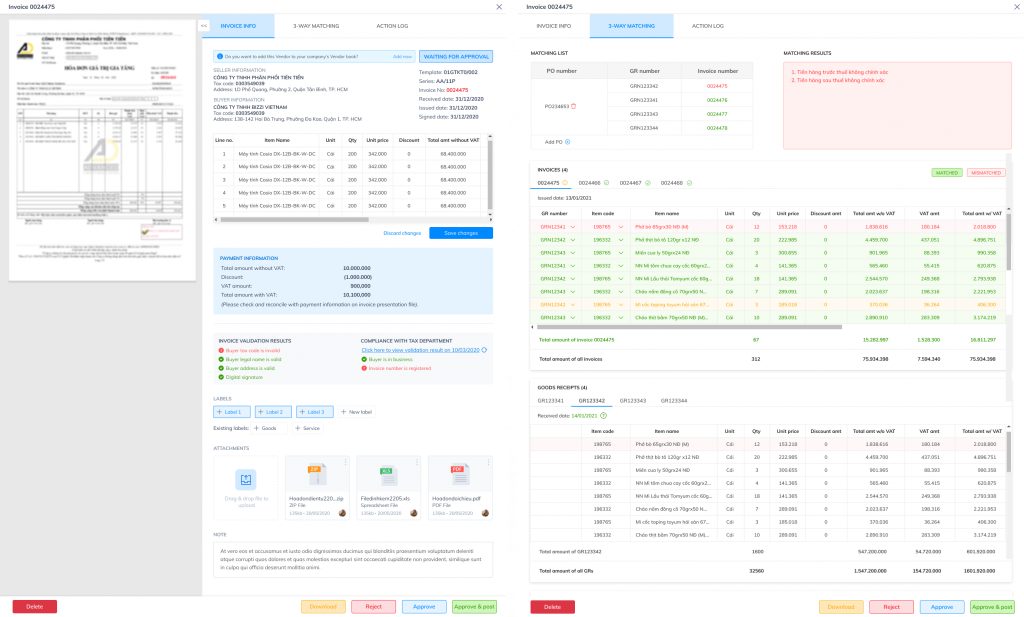
3. Flexible workflow browsing via RBAC/ABAC
Automatically submits applications for approval to the right people, with the right permissions and within the correct limits.
- According to the approval limit
- According to the cost center
- By department
- By document/expense type
No more manual emails, no more approval delays.
4. Two-way ERP integration
Bizzi supports deep integration and real-time synchronization with most popular ERP systems:
- SAP
- Oracle
- Odoo
- Bravo
- MISA
- FAST
5. Touchless Payment – Automate the entire Invoice-to-Pay process.
- Automatic Create a payment request (Personnel Request)
- Submit for review via workflow.
- Automatic payment reconciliation with bank statement.
- Get real-time updates on PAID/UNPAID status.
FAQ about contactless payments
Here are some frequently asked questions about Contactless Payments.
Are contactless payments safe?
Yes. Contactless systems use encryption and tokenization technology, so your card/phone data is not transmitted directly through the scanner. Additionally, each transaction generates a unique, one-time code that hackers cannot reuse. The scanning distance is very short (a few centimeters), reducing the risk of eavesdropping.
Do contactless payments require a PIN?
A PIN is usually not required for small transactions (depending on the bank/issuer). For larger transactions, the POS system may require a PIN or signature for additional authentication.
What is the difference between contactless and QR codes?
| Criteria | Contactless (NFC) | QR payment |
| Use | Tap/bring your card or phone near the POS terminal. | Scan the code using the app. |
| Speed | Very fast (1–2 seconds) | Fast but slower (open app → scan) |
| Internet | No need | Internet access is required to make payments (depending on your wallet/card). |
| Device | A POS system with NFC is required. | Just use the QR code (cheaper for the shop). |
| Security | Very high thanks to tokenization | App dependency & QR code security |
If I lose my phone, will I lose my money?
No. Malicious actors cannot use it for payments without unlocking the device. Apple Pay, Google Wallet, Samsung Pay… all require Face ID/Touch ID/PIN before processing payments. Additionally, you can immediately block any transaction if:
- Remote device lock/loss (Find My iPhone / Find My Device)
- Block or suspend your card via the banking app.
Conclusion: Contactless Payments & Touchless Invoices – Where Should Businesses Start?
While contactless payment is booming in the retail sector, businesses still prioritize back-office automation, particularly in the Accounts Payable (AP) process. Think of touchless invoices as the foundation, and contactless payments as an extension.
Businesses should start with:
- Automate invoice input using OCR and IDP to eliminate manual data entry.
- Standardize the approval process to shorten processing time.
- Integrate ERP, eInvoice, and Payment systems to achieve a seamless, touchless workflow.
- Once the back-office platform is running smoothly, then expand to contactless payment at the point of sale.
Bizzi is a platform that helps businesses implement Touchless Invoice a quick and systematic way thanks to:
- The IDP + OCR unit accurately reads invoice data.
- Connect ERP, eInvoice, and Payment systems according to standards, even for older ERP systems without APIs.
- Standardize approval processes and ensure internal controls.
- Reduce invoice processing time by up to 80% and drastically reduce manual errors.
👉 Hopefully, Bizzi's article above has provided managers with some useful information about the concept of contactless payment and helped them understand the nature of touchless invoices. If your business wants to start the "contactless" journey from AP → ERP → PaymentBizzi is a suitable choice for immediate deployment without requiring changes to the core system.


