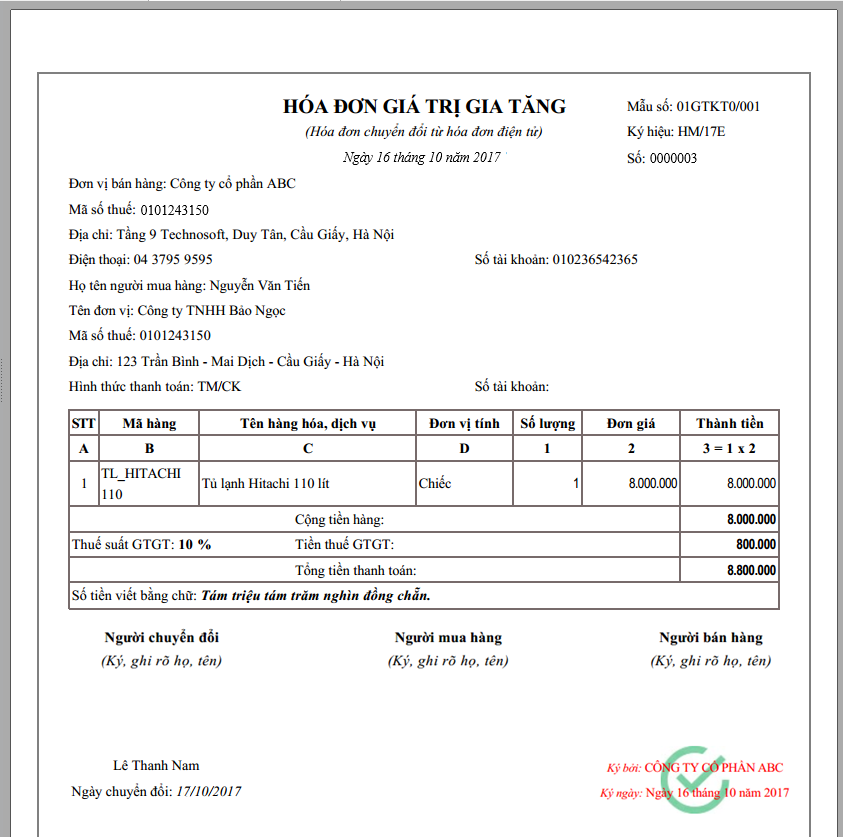
Electronic bill is an inevitable trend in the digital age, required by Vietnamese law to be applied to businesses, organizations, and individuals doing business from July 1, 2022..
This change is driven by the roadmap for mandatory e-invoice implementation under Government Decrees, aiming towards a digital economy and requiring businesses to apply technology to optimize processes.
So what is the future of e-invoicing in Vietnam – from legal compliance to financial automation? Let’s follow the article below by Bizzi to find the answer.
The future of electronic invoices – an irreversible trend
Electronic invoices are an important pillar to promote digital transformation in financial activities, according to the Government's goal of building a digital economy. The conversion to electronic invoices is a mandatory legal requirement, required by Vietnamese law to be applied to businesses, organizations, and individuals doing business from July 1, 2022, clearly stipulated in Decrees 119/2018/ND-CP and 123/2020/ND-CP.
Global context
Around the world, many governments have been promoting the application of electronic invoices (e-invoices) to ensure transparency in tax management, prevent fraud, and modernize commercial activities.
In Vietnam
According to the roadmap of the General Department of Taxation, 100% enterprises have and will have to deploy electronic invoices. This is no longer an option, but has become a mandatory requirement to synchronize with the national tax management system.
This transformation is not just an administrative requirement but also a driving force for the digital economy. The e-invoice market in Vietnam is witnessing an impressive growth rate. According to valuation, the market size reached 63.60 million USD in 2024 and is expected to increase to 256.51 million USD in 2033, maintaining a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 16,76% during the period 2025-2033.
This figure confirms that e-invoicing has become a large-scale technology field, going beyond the limits of a mere legal requirement to become an important segment in the digital financial infrastructure.
However, not many businesses have exploited the potential of automation and financial integration from electronic invoices to:
- Shorten the reconciliation and payment process.
- Reduce the risk of error and fraud.
- Optimize cash flow and cost management.
This shows that e-invoices are not only an “obligation” to comply with the law, but also an opportunity for businesses to digitize their comprehensive financial and accounting processes. Implementing e-invoices helps businesses professionalize their operations, save time and costs, increase transparency and compliance with the law, and facilitate international integration and digital economic development.

Legal framework for electronic invoices in Vietnam
Thus, understanding and complying with the legal framework not only helps businesses ensure legality, but also opens up opportunities to effectively automate financial and accounting processes.
Key legal documents
Electronic invoices in Vietnam are regulated by the important decrees and circulars, in there:
- Decree 123/2020/ND-CP: Detailed regulations on electronic invoices and documents when selling goods and providing services.
- Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC: Instructions on management, use, storage and connection of electronic invoices with tax authorities.
- Decree 70/2025/ND-CP & Circular 32/2025/TT-BTC: updates important changes such as handling erroneous invoices, synchronization with financial reports, expanding applicable objects and standardizing XML format.
Decree 70/2025/ND-CP, issued by the Government on March 20, 2025 and officially taking effect from June 1, 2025. This Decree amends and supplements 40/61 Articles of Decree 123/2020/ND-CP, demonstrating the Government's great efforts in tightening data management and standardization.
The key new points of Decree 70/2025/ND-CP focus on standardizing data formats, ensuring technical standards on data types and data lengths for the transmission and storage of electronic invoices. More importantly, this Decree clarifies regulations on e-commerce invoices, requiring exporters to electronically transfer commercial invoice data to tax authorities.
At the same time, the implementation of Electronic Invoices from Cash Registers with electronic data transfer connection to tax authorities is also strongly promoted, especially for business households and retail sectors.
In addition, businesses need to update relevant documents to ensure full compliance with current legal regulations.
Mandatory requirements for electronic invoices
- Standard XML format: Ensure compatibility with electronic tax management systems.
- 10 year storage: Ensure data retrieval when required for testing.
- Direct connection with tax authorities: Invoices are certified by the tax authority before issuance.
- Digital signature: Authenticate the issuer and ensure the integrity of the invoice.
Future changes
- Standardize invoice formats: Aiming to synchronize data nationwide, helping to reduce errors and shorten processing time.
- Synchronize with financial and tax reports: Helps businesses seamlessly connect invoices with accounting books, creating more automatic and accurate tax reports.
Challenges for Vietnamese businesses when implementing electronic invoices
Although Vietnam has completed the mandatory conversion roadmap, most businesses have only stopped at the “minimum compliance” level. This includes the ability to create, send and store valid e-invoices. However, they have not yet exploited the potential for automation and financial integration that structured e-invoice data (XML) brings. This is the biggest operational gap that is preventing businesses from optimizing financial efficiency.
Large volume of invoices and difficult to control invoice life cycle
For businesses with high transaction volume, such as F&B, retail, or logistics, processing incoming invoices is a huge challenge. For example, a large coffee chain can process about 11,000 invoices per month. Manually managing the entire invoice lifecycle (create – send – pay – cancel – adjust) and controlling debts becomes extremely complicated.
Internal governance processes are often fragmented and overly reliant on manual approvals. Multiple layers of approvals significantly slow down invoice processing, sometimes leaving invoices “pending” for days, resulting in delayed payments and strained supplier relationships.
Not integrated with ERP/accounting
A major technical barrier is data fragmentation. Many businesses, especially small and medium-sized enterprises or those using legacy systems, rely on different “point solutions” for each function (e.g., separate POS systems, warehouse software, ERP and e-invoices from multiple providers). This fragmentation leads to “data silos,” where information is isolated and mismatched due to the lack of common standards for transaction identifiers and APIs.
The direct result is the burden of manual data entry. Accounting staff must re-enter invoice data across multiple platforms, eliminating the core benefits of automation and increasing the risk of errors. Statistics show that over 66% businesses are facing errors on 1% of their total invoices, with 20% to 30% of invoices containing exceptions that require manual intervention. These errors not only slow down the process but also directly lead to legal risks in terms of tax and audit.
The gap between the e-invoicing system (ensuring compliance) and the ERP system (the core of operations) is a significant barrier to digital transformation. If e-invoicing data cannot be exchanged seamlessly with ERP, the value of investing in both systems will be limited. This suggests that CFOs need to shift their investments from basic e-invoicing solutions to specialized financial automation platforms with open integration capabilities (Open API) to ensure continuous data flow and eliminate inefficiencies.
Legal risks
Mandatory use of electronic invoices with GDT codes helps reduce tax risks (legal compliance). Specifically, errors in invoices (customer information, amount, tax rate) or improper storage can lead to administrative fines, tax arrears or disputes with customers.
However, if this large volume of electronic invoices still has to be processed and reconciled manually, it will increase internal operational risks (incorrect data entry, incorrect reconciliation, fraud).
Therefore, to minimize overall risk, businesses must add a layer of input invoice processing automation (IPA) and 3-way matching technology on top of the basic e-invoice compliance layer. Compliance is a necessary condition, but automation is a sufficient condition for comprehensive risk management.
Overall, these challenges show that simply implementing e-invoicing as required by law is not enough; businesses need to adopt automation and seamless integration to optimize processes and reduce risks.
The Future: E-invoicing not just for compliance, but for financial automation
In the future, e-invoicing will go beyond its regulatory compliance role to become a financial automation tool, helping businesses reduce costs, optimize business processes, and provide data for more accurate decision making.
Electronic invoices become the center of financial data
In the digital age, the e-invoice is no longer a digitized paper document. In structured XML format, authenticated by tax authorities, the e-invoice becomes the most reliable source of financial data. This data acts as the “hub” connecting all financial and administrative processes, transforming the role of the invoice from recording transactions to providing instant data for accounting, reconciliation, reporting, and cost analysis.
Integration with management systems and tools
Data integration is key to breaking down data silos. Strategic integration needs to be implemented on three levels to create a unified financial ecosystem:
Level 1: Integration with ERP/Accounting System (GL Posting)
- The goal is to synchronize electronic invoice data directly into the General Ledger and Accounts Receivable (AP/AR) modules of leading ERP systems such as SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, Odoo, FAST, or MISA.
- The key benefit of this integration is the complete elimination of manual data entry, ensuring consistent financial and tax data, updated in real-time.
Level 2: Integrated Expense Management and Accounts Receivable (ARM/AP)
- Input electronic invoices are used as original documents, automatically linked to payment requests or business expense reports (T&E).
- This integration enables budget control by department or project and instant spending tracking. Structured invoice data (XML) is perfect for automatically extracting and categorizing expenses, helping CFOs move from noted cost of control costs before they occur, thereby optimizing cash flow.
Level 3: Integration with Digital Finance and Banking Systems
- Connecting e-Invoices with B2B payment gateways and banking systems allows for real-time automation of payment processes and bank reconciliation.
High technology application
Automate Invoice Processing (IPA) using AI/RPA
Invoice Processing Automation (IPA) is the next big thing. Businesses are leveraging Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), combined with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) technology, to process large volumes of incoming invoices.
Specifically, virtual robots (e.g. Bizzi Bot) will automatically collect electronic invoices (XML) from different channels (email, supplier portal), extract and classify data, then check the validity and verify tax data. This solution helps to minimize manual data entry, allowing accounting teams to move from processing paperwork to analyzing costs and profits, creating higher strategic value for the business.
Dedicated financial automation platforms act as a deep, complementary technology layer that connects disparate modules of the ERP/accounting system. This strategy allows CFOs to focus on specialized RegTech/FinTech solutions with strong integration capabilities, reducing implementation costs and accelerating the adoption of new technology without having to completely change the existing ERP infrastructure.
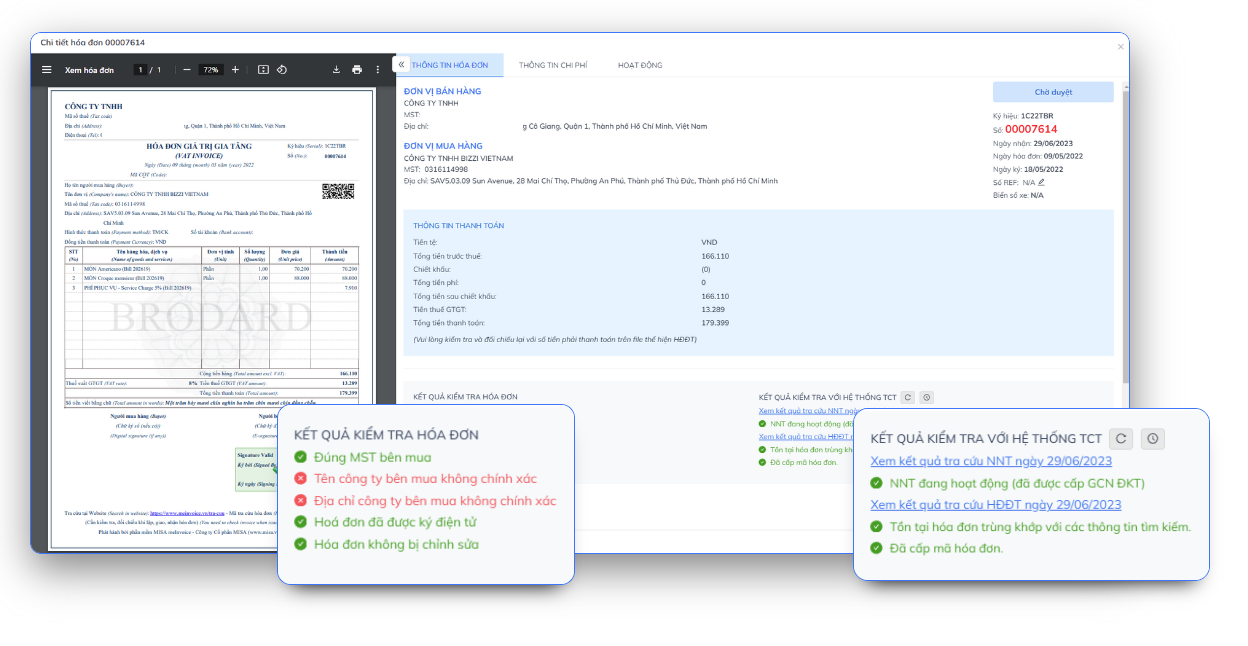
Automating Internal Controls: 3-Way Matching
For effective risk management and cost control, automating the 3-way matching process is a must. This is an internal control technique to verify the validity of invoices before payment by matching three core documents: Purchase Order (PO), Goods Receipt Note (GRN/RR), and Invoice.
The strategic purpose of 3-way matching is to prevent fraud (payment of fake or duplicate invoices) and ensure that businesses only pay for goods that have actually been ordered and received in full.
In the e-invoice environment, automated systems use structured XML data to perform real-time PO, GRN and Invoice reconciliation. The platform is capable of handling complex cases such as 1 PO – multiple INV – multiple GR with an accuracy of over 99%. When the system detects a discrepancy (e.g., the quantity on the invoice is different from the PO), the invoice will be retained and automatically notified for processing, preventing erroneous payments.
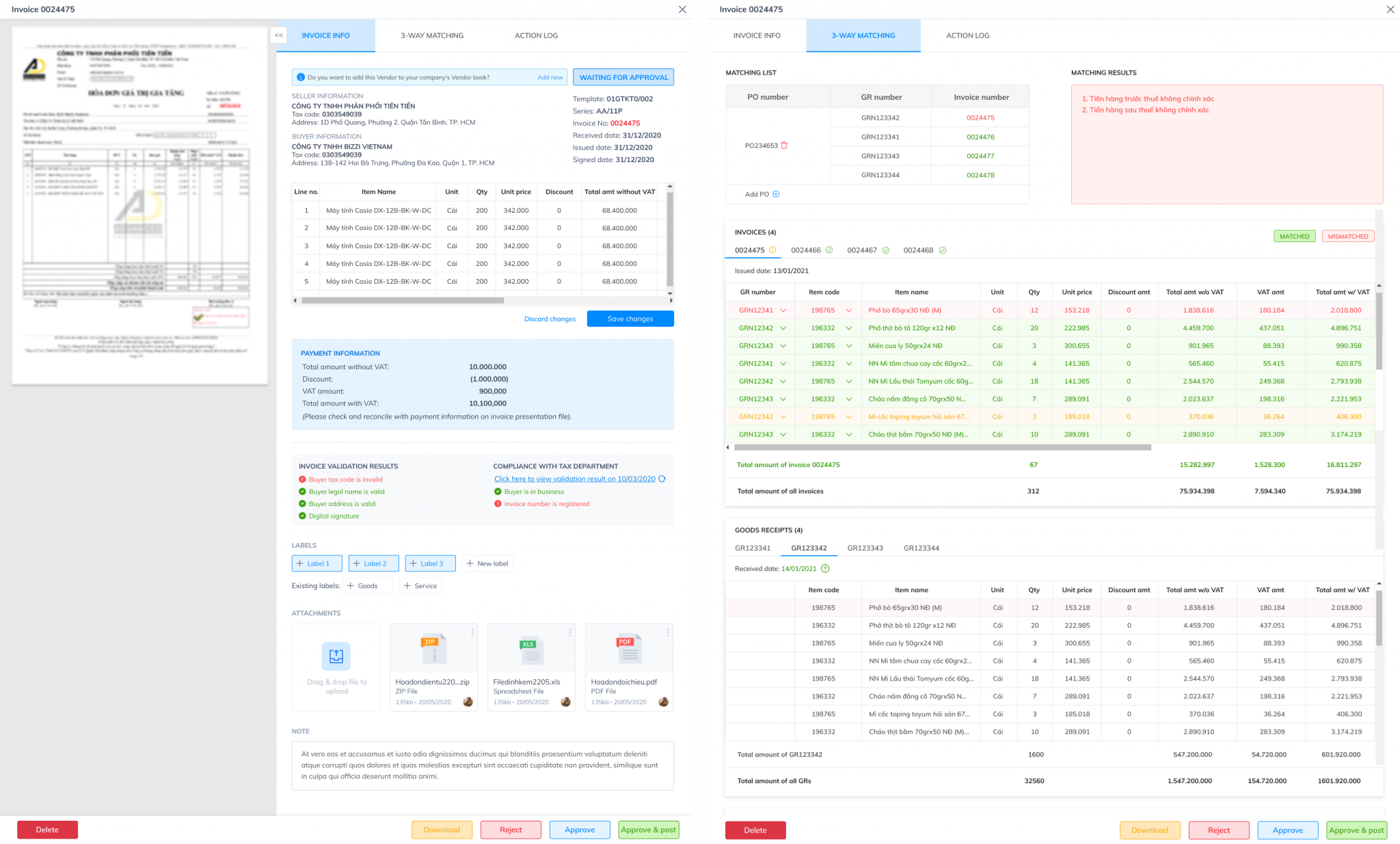
Automating 3-way matching transforms the role of Accounts Payable (AP) from a traditional cost center to a cost optimization function. By automatically detecting errors, avoiding overpayments, and enabling early payment discounts, AP becomes a proactive cash flow management tool.
For multinational and FDI companies, strict internal control requirements according to international standards (e.g. SOX) make automatic 3-way matching a core mechanism. Therefore, the application of electronic invoices must be linked to the 3-way matching system to achieve dual compliance: compliance with Vietnamese taxes (Decree 70/2025) and compliance with global financial governance.
Upgrading from basic compliance to automated e-invoicing delivers clear quantifiable benefits, generating a significant return on investment (ROI):
- Cost Reduction: Businesses can save from 50% to 70% in costs related to printing, physical storage and invoice management each year. The General Department of Taxation estimates that the application of electronic invoices can help the Vietnamese economy save more than 1,000 billion VND each year.
- Increased Efficiency Gain: Automation reduces manual work in the invoice processing process by more than 80%. Invoice processing time can be reduced from weeks to just days. A prime example is Highland Coffee, which reduced its invoice processing time from weeks to just days thanks to AP automation. Automated approval processes can even reduce payment processing time by 99%.
- Cash Flow Optimization: Fast processing ensures on-time payments, helps take advantage of early payment discounts and speeds up capital turnover.
Bizzi B-invoice – Comprehensive solution for Vietnamese businesses
Bizzi B-invoice is a comprehensive electronic invoice solution provided by Bizzi, fully meeting the regulations of Vietnamese tax authorities.
- Not only guaranteed Perfect Compliance by generating legal standard XML/PDF invoices and connecting directly to GDT for authentication codes, but also focusing on automating internal financial processes.
- Provide End-to-End Lifecycle Management (issue, send, pay, cancel, adjust) and the ability to store electronically for at least 10 years
- Perform Deep Integration by synchronizing financial and tax data with existing ERP systems.
- Support Expanding Strategic Automation By connecting specialized modules such as Expense Management and Accounts Receivable (ARM), the Electronic Invoice becomes the center of cost management.
- By applying AI/RPA and 3-way matching automation, the solution helps reduce the risk of payment errors and improve processing speed.
Key features of B-invoice
- Compliance with legal standards
- Generate XML/PDF invoices as required.
- Connect directly to the tax authority to get the authentication code.
- Manage the entire invoice lifecycle
- Full support for all stages: release, send, payment, cancellation, adjustment.
- Customizable by brand
-
- Allows designing logos and custom invoice templates to match business identity.
- Batch export
-
- Issue multiple invoices at the same time by order or customer, saving time for large businesses.
- Storage and retrieval
-
- Store for at least 10 years.
- Easy to look up, download, and print when needed.
- ERP/accounting integration
-
- Synchronize financial and tax data with major ERP systems such as SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics, Odoo...
- Reduce manual data entry, improve accuracy.
- Expand automation
- Connect with other Bizzi modules: Expense – expense management, ARM – debt management, Travel – business trip expense management.
In short, B-invoice helps Vietnamese businesses optimize the electronic invoice process, comply with the law and improve the efficiency of comprehensive financial management.
Benefits for business Upgrade to automated e-invoice with B-invoice
Upgrading to automated e-invoice is not only about legal compliance, but also a strategic step to help businesses optimize financial efficiency and prepare for comprehensive digital transformation.
Save time
- Reduce up to 70% of manual operations compared to traditional invoicing processes.
- HR can focus on higher value tasks instead of manual data entry and reconciliation.
Transparent & Accurate
- Reduce the risk of errors, duplication and fraud with automated invoice checking and validation.
- Increase the reliability of financial data for businesses and tax authorities.
Easily scalable
- Easily integrates with many different departments and processes: accounting, purchasing, sales, accounts receivable, costs…
- Help businesses expand without increasing manual workload.
Support CFOs in making quick decisions
- Provide real-time reports on costs, debts, and taxes.
- Help CFOs make decisions based on accurate and timely data, improving financial management efficiency.
Preparing for the digital financial future
- In line with the trend of comprehensive digital transformation.
- Create a platform to apply high technologies such as AI, RPA, data analysis in corporate financial management.
Conclude
In the context of increasingly strong digitalization, e-invoices are no longer just a legal requirement but have become a core component of the financial ecosystem, supporting businesses to optimize operations and develop sustainably.
Electronic invoices in Vietnam are moving from "compulsory compliance" luxurious “strategic tool” to automate finances. That’s why we talk about the future of e-invoicing in Vietnam – From legal compliance to financial automation;
Bizzi.vn is ready to accompany Vietnamese businesses on the journey of digitalizing cost and financial management with the B-invoice solution. Confidently a comprehensive electronic invoice solution, helping Vietnamese businesses transform their finances and prepare for the digital future, B-invoice is suitable for the comprehensive digital transformation trend thanks to its features of automating the electronic invoice process, fully complying with legal regulations and supporting direct connection with tax authorities.
Register here now for free consultation: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/