What are operating costs and why do they play such an important role in a business? Financial experts say that good cost control helps increase profits, optimize resources, and improve a business's ability to withstand risks.
Let's join Bizzi to learn more about what operating costs are, their roles and how to optimize operating costs in the current volatile economic context.
What is Operating Cost? The Role of Operating Cost
Operating Cost are all expenses necessary for a business to maintain its daily operations, except for the cost of direct materials and direct labor (included in the cost of goods sold).
This term is often used in parallel or interchangeably with a number of similar concepts such as Operating Expenses (Opex) good Overhead CostHowever, there are still certain differences between them in terms of scope and purpose of use.

Explanation of related terms
- Operating Cost – general term for operating costs.
- Operating Expenses (Opex) – focus on operating costs other than cost of goods sold, e.g. selling and administrative costs.
- Overhead Cost – indirect costs, not directly related to the product (e.g. office rent, electricity and water, depreciation).
Create a comparison table of operating cost, operating expense, overhead cost (Unique features: Create a comparison table of terms to increase clarity and reduce confusion. Cost of Retrieval.)
| Terminology | Define | Scope includes | Distinguishing notes |
| Operating Cost | Total cost required to operate the business | Includes Opex and indirect manufacturing costs | The most comprehensive concept |
| Operating Expenses (Opex) | Recurring expenses in regular operations | Administrative staff salaries, rent, software, marketing, etc. | Excluding cost of goods sold (COGS) |
| Overhead Cost | Indirect costs, not associated with product manufacturing | Electricity, water, maintenance, administration | As part of Operating Cost |
Operating costs do not include direct materials or direct manufacturing labor — as these are included in cost of goods sold (COGS).
Correctly understanding and distinguishing these types of costs helps businesses avoid errors in calculating profits, building budgets and evaluating financial performance.
The Importance of Operating Costs in Business
Operating costs are more than just a number on a financial statement — they are an indicator of the health of a business. Keeping operating costs under control helps organizations balance operational efficiency and profit growth.
Here are three key roles of operating costs:
- Control spending effectively
According to many studies, More than 601,000 businesses fail in the first 3 years. because of poor control of operating costs.
→ Close monitoring helps avoid waste and detect unnecessary costs.
- Optimizing profits
Reducing operating costs by 5–10% can double profits, especially for businesses with thin profit margins.
- Sustainable development platform
Transparent operating costs help:
- Easy to forecast cash flow.
- Improve the ability to raise capital and attract investors.
- Ensure business stability even in recession.
Classification of operating costs in business: Fixed and Variable
After understanding the definition of operating costs, let's learn about 2 typical classifications of operating costs in businesses.
Fixed Costs (Fixed Costs)
Fixed costs are expenses that do not change with output or activity levels over a given period of time. These expenses must be paid whether a business produces 0 or 10,000 units of a product.
Common types of fixed costs:
- Renting premises: Office and factory rent – usually signed long-term contract, fixed monthly payment.
- Fixed staff: Including management salary, administrative staff, accountant - paid monthly, regardless of product quantity.
- Salaries are often considered a variable cost, but in the context of financial management, managerial or administrative staff salaries are counted as fixed costs because they do not vary with output.
- Depreciation of fixed assets: Machinery, equipment, vehicles, ERP software – are allocated equally over the accounting period.
- Administrative costs: Legal fees, audit fees, office insurance…
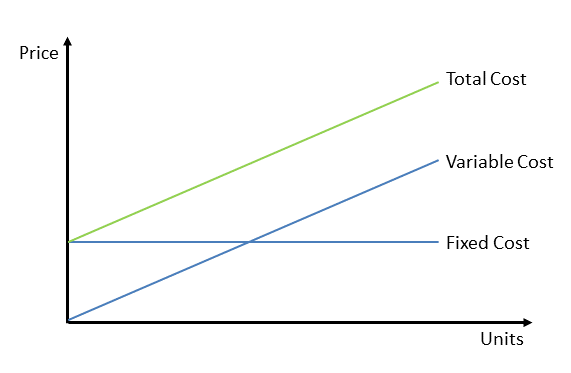
Variable Costs
Variable costs are expenses that increase or decrease with the level of activity or output. When more is produced, costs increase; when less is produced, costs decrease.
Common types of variable costs:
- Direct materials: Production materials, packaging, accessories.
- Utilities by usage: Electricity, water, gas – usually proportional to the number of production shifts.
Shipping – logistics: Delivery and warehouse fees are incurred based on the number of orders. - Seasonal labor: Wages paid to overtime workers and collaborators based on working hours.
- R&D or flexible marketing costs: Costs for researching new products or seasonal advertising campaigns.
Fixed and Variable Cost Comparison Table
| Criteria | Fixed Cost | Variable Cost |
| Define | Expenses constant according to campaign scale | Expenses flexible change by efficiency or scale |
| Characteristic | Stable, predictable, difficult to cut in the short term | Flexible, increase or decrease according to marketing activities |
| Specific examples | Marketing staff salary, office rental fee, CRM software | CPC/CPA advertising, KOL/KOC commission, POSM printing costs |
| Advantage | Helps maintain stable and long-term operation | Easy to control and adjust for performance |
| Disadvantages | Cash flow pressure if revenue is low | Can increase dramatically as campaign expands |
| Role in strategy | Platform for maintaining marketing systems and building long-term capacity | Fast growth lever, suitable for short-term campaigns |
Businesses need to balance fixed and variable costs to ensure stability while taking advantage of flexibility and optimizing ROI in each stage of marketing strategy.
How to Calculate and Account for Effective Operating Costs
There are many ways to calculate operating costs, depending on the field and scale of operation. Below are 02 formulas for calculating operating costs according to cost management and financial reporting.
Basic formula (according to cost management)
This formula is suitable for internal management when a business wants to calculate the total operating costs in a period to analyze the break-even point.
- Calculation: Operating Cost = Variable Cost + Fixed Cost
- In there:
-
- Fixed costs: office rent, management staff salaries, depreciation, administrative costs.
- The variable costs: raw materials, utilities, logistics, seasonal labor.
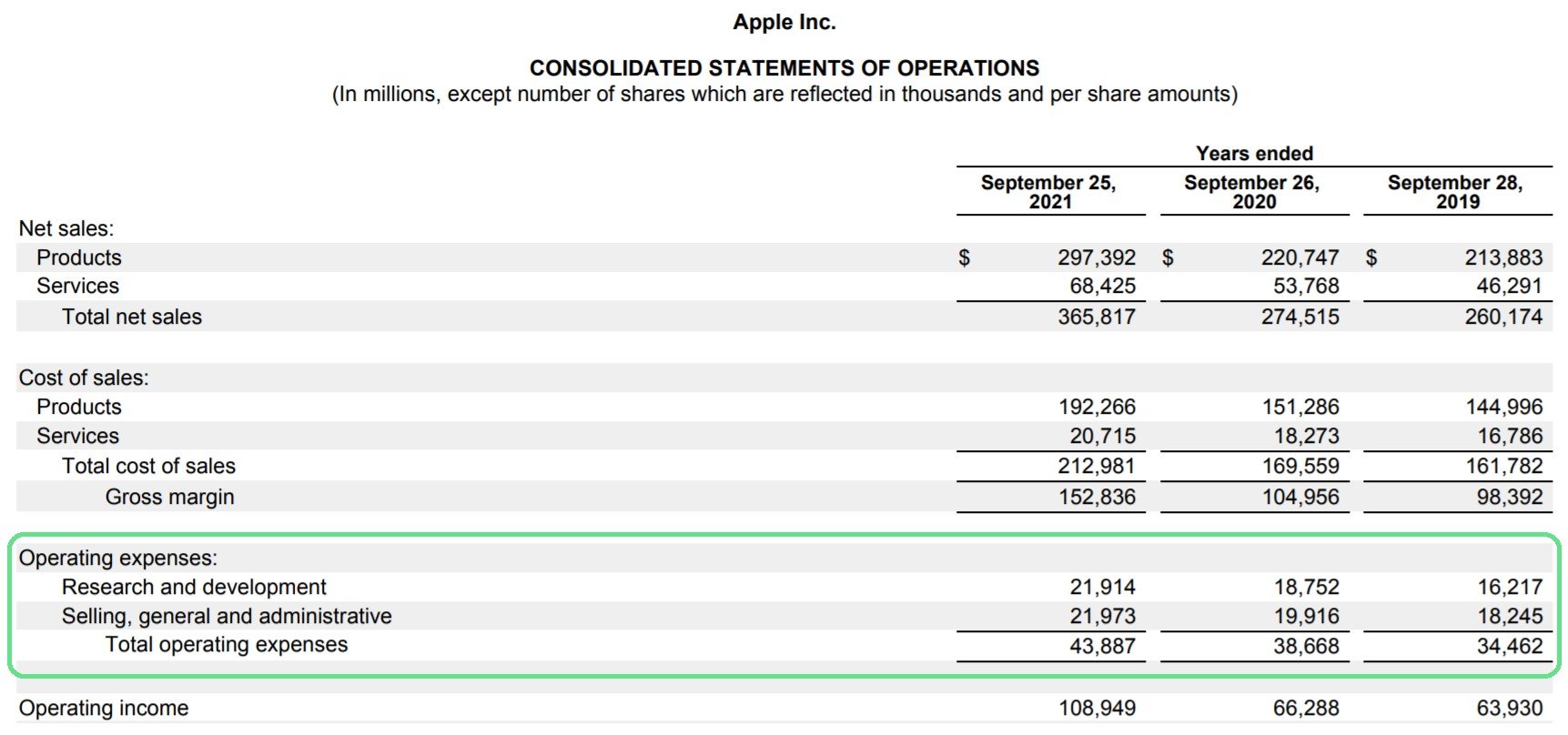
Operating costs on financial statements
Position on the income statement: Operating Expenses (OPEX) are presented after Net Revenue and Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), making up Gross Profit. Operating expenses are then deducted to calculate Operating Profit (EBIT).
Meaning:
- Reflects the costs required to maintain and operate daily business operations (personnel, marketing, management, R&D…).
- Is an important indicator to evaluate management efficiency: how much a business spends to generate revenue.
- Directly affects profitability and cash flow. A business with high revenue but poorly controlled operating costs can lead to low profits.
Operating costs are the “bridge” between revenue – cost of goods sold and actual profits, showing the health of internal management and the ability to optimize the enterprise’s resources.
What is the operating cost optimization strategy?
In the context of Vietnamese enterprises increasingly under pressure on profits, operating costs become an important "lever" determining the ability to survive and develop. Not just stopping at cutting expenses, optimizing operating costs is a process. reengineering the entire operating system — from internal processes to management tools.
From the perspective of Bizzi.vn, businesses can deploy optimal strategies based on two main pillars: Automation technology and Improve operating procedures.
Technology application: The key to reducing operating costs
When financial and accounting processes are still dependent on humans and manual processing, businesses not only lose time but also face the risk of errors, data loss and lack of transparency.
Financial and accounting process automation platforms such as Bizzi.vn Bring about a quantum leap in cost management thanks to:
- Automate invoice and document processing, reducing manual data entry time by up to 80%.
- Digitize the spending approval process, helping managers control budgets in real time.
- Real-time budget control: Bizzi.vn's system helps administrators track each expense by department, project, or supplier, ensuring spending is always within budget.
- Seamless integration with ERP (SAP, Oracle, Netsuite…), ensuring smooth data flow without hidden costs.
- Automated report generation & cost trend analysis: Support leaders to make faster decisions, based on transparent and continuously updated data.
This is proof that applying technology not only helps save human resources, but also reduces the risk of errors - which is the cause of cost loss. Bizzi.vn is not only automation software but also a comprehensive financial management platform, helping businesses transform cost management from reactive to proactive, thereby improving operational efficiency and profitability.
Review and improve operating procedures
Along with technology, continuous review and improvement of processes is also an important strategy. Many organizations waste budgets not because they spend too much, but because their processes are cumbersome, overlapping, and lack control over workflow.
Businesses can apply the following methods:
- Periodic cost review to eliminate non-value adding items.
- Optimizing resources through flexible working models (hybrid/remote).
- Process improvement according to the Pareto principle (80/20): Focus on 20% customers or processes that deliver 80% value, thereby allocating resources appropriately.
Combining both technology (Bizzi.vn) and lean management methods, businesses not only cut operating costs but also improve overall performance, creating a sustainable foundation for long-term growth.
Bizzi is a financial and accounting automation platform that acts as an AI assistant for accountants, helping businesses process invoices, manage expenses, control budgets, and automate expense approval processes efficiently, using AI and RPA technology to process invoices automatically.
What are the frequently asked questions about operating costs?
Below is the FAQ (Frequently Asked Questions) about operating costs, answered briefly - clearly - easy to apply:
How much of the operating cost is reasonable for 1.3T of revenue?
There is no absolute “standard” number for every business, because the operating cost ratio depends on the business model, size, industry and stage of development. However, according to average financial reports:
- Retail/Trade: 15–25% revenue.
- Production: 10–20% (since most of the cost is in the cost price).
- Service: 25–40% (by personnel costs indirect accounts for a high proportion).
- General rule: The lower the operating cost ratio → the higher the profit margin. Businesses should set KPIs to reduce operating costs by at least 5% per year.
How should small businesses control operating costs?
For small businesses (SMEs), controlling operating costs is vital. An effective strategy should ensure both economical and productive.
- Create a detailed cost budget: Separate fixed and variable costs for close monitoring.
- Regular Review: Check your monthly expenses to spot waste.
- Prioritize technology solutions: Use business financial management software, electronic invoices to reduce manual accounting costs.
- Apply the 80/20 principle: Focus on optimizing the "heaviest" expenses (e.g. premises, logistics).
Are operating costs tax deductible?
Yes, most reasonable, eligible operating expenses are deductible when calculating corporate income tax, if:
- Have legal documents (electronic invoices, contracts, receipts).
- Direct costs of business operations.
- Payment according to regulations (bank transfer for invoices > 20 million).
- Note: Expenses that do not serve production and business activities, or exceed the limit (such as entertaining guests above the allowable ceiling) will not be deductible.
Conclude
Hopefully, through the information above, readers can better understand what operating costs are, their roles and how to calculate operating costs most accurately. Strictly controlling operating costs helps businesses easily forecast their budgets, avoiding the situation of "bloating" the apparatus when revenue increases rapidly. Technology is the key to reducing operating costs. In the context of businesses increasingly under pressure to optimize costs and improve performance, technology is the most important lever.Automation and digitalization not only help reduce costs but also create a transparent, standardized control system – the foundation for sustainable growth. Explore Bizzi.vn See how top businesses optimize operating costs today.


