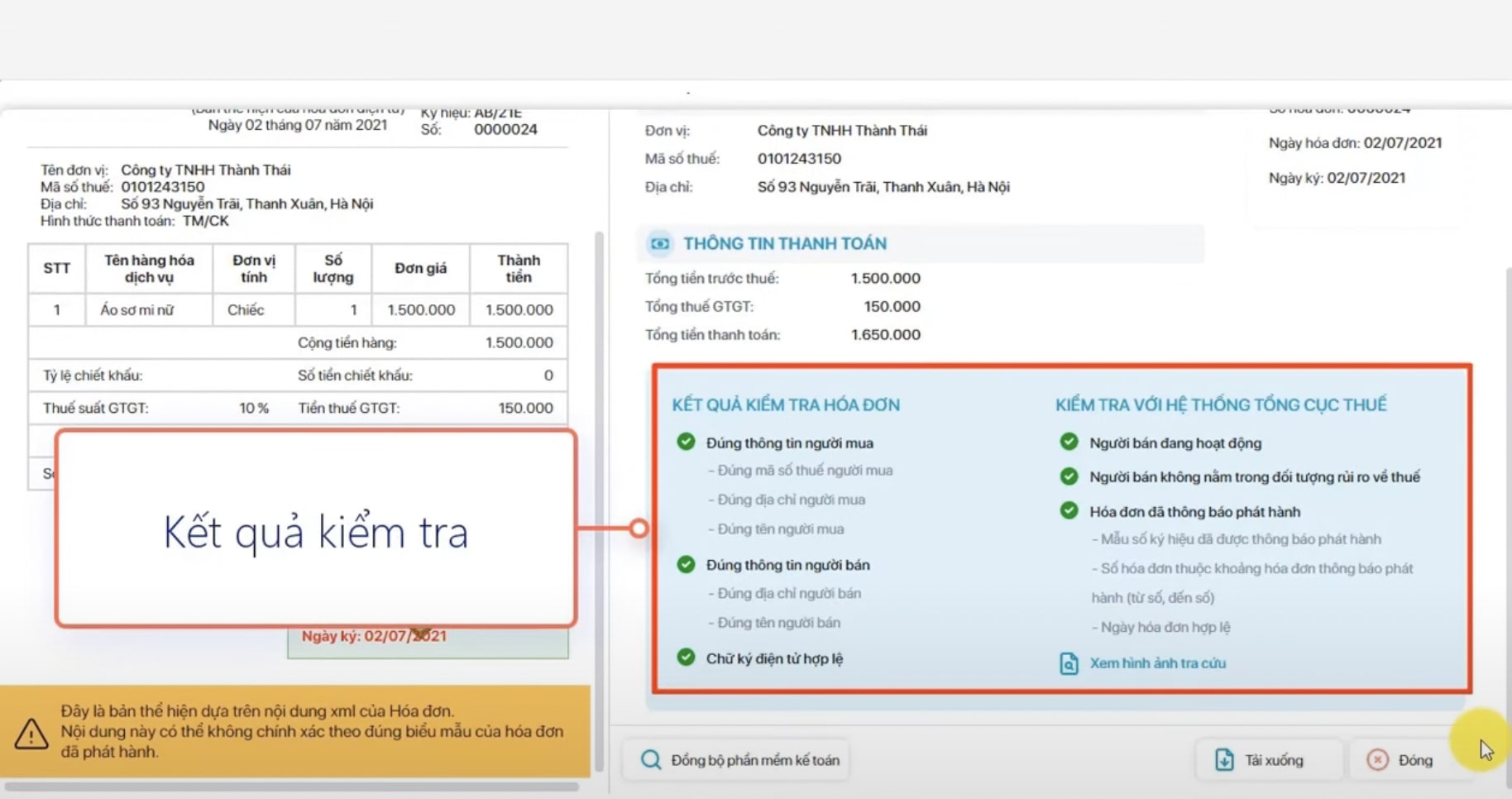
The role of identifying risky invoices is to enable businesses to proactively prevent and protect themselves from legal troubles, maintain transparent business operations, and ensure their tax rights and obligations.
So what exactly is a risky invoice? What are the serious consequences of using or accounting for risky invoices? Let's find the answers in this article by Bizzi, and also explore ways to prevent and handle suspected risky invoices.
What is a risk invoice?
A risk invoice is a type of invoice that is usually issued by the tax authorities.General Department of Taxation) will be placed under strict inspection and supervision.
The term "risk bill" from a legal perspective.
Risk invoice is a term not officially defined in legal documents (Decrees, Circulars), but it is commonly used by tax authorities in practice for tax management, inspection, and auditing.
From a legal perspective, a "risk invoice" can be understood as an invoice flagged with a warning, not necessarily an invoice indicating wrongdoing. Current legislation does not yet have a distinct legal term for "risk invoice."
This is the concept professional by the tax authorities and Tax Risk Management System (TMS) Used for:
- Classify
- Warning
- Selecting subjects for inspection and examination.
How is a risk invoice understood in practice in tax administration?
In practice, risky invoices are typically those showing signs of irregularities or potential violations, including but not limited to the following categories:
Trading risks:
- The transaction was fictitious and did not involve any actual goods or services.
- The transaction does not serve the business operations of the enterprise.
Issuer risk
- Businesses:
- Fleeing from the business address.
- Operations have ceased but the procedures have not been completed.
- Forced to stop using invoices.
- The company has a history of violations regarding invoices and taxes.
Risks related to invoice data
- Invoice data:
- Does not match the system. Electronic invoice of the tax authority
- There are signs of unauthorized modification, replacement, or cancellation.
- The seller's information, buyer's information, and tax identification number are incorrect.
Risks in terms of scale and frequency
- The value of the transaction is unusual compared to:
- Capital scale
- Revenue
- Business registration lines
- Generating a large number of invoices in a short period of time is disproportionate to the business's capacity.
DBusinesses need to understand what a risk invoice is because it has an impact. directly affecting:
- Right to deduct VAT.
- Accepting deductible expenses when calculating corporate income tax.
- There is a risk of being fined, having taxes collected retrospectively, or even facing criminal charges if involved in the buying and selling of invoices.
What are 4 signs to identify a risky invoice?
Invoice risk is not just a matter of "paperwork errors," but a real tax and legal risk. The larger the business, the more invoices it issues, making manual control more susceptible to risks.
The checklist below should be used as a mandatory verification step before accounting, declaration, or deduction.
1. Signs related to the business issuing the invoice
Accountants should be especially vigilant if the seller exhibits one or more of the following behaviors:
- No longer operating at the registered address as indicated on the Business Portal or in a tax authority notification.
- Despite ceasing operations, being subject to enforcement action, and having their tax identification number revoked, they are still issuing invoices.
- The newly established business (only a few months old) has a very large volume of invoices issued, which is inconsistent with its capital, staff, and industry size.
- Included in the list of high-risk businesses in terms of taxation, the company has abandoned its business address following a warning from the tax authorities.
These are the signs They were the first to be scrutinized by the tax authorities., because it is directly related to the buying and selling of invoices.
2. What are the indicators related to the content and value of risky invoices?
Even if the issuing business's invoice appears "normal," it can still be risky if:
- Incorrect tax identification number for the seller or buyer.
- The invoice does not exist in the General Department of Taxation's electronic invoicing system (eInvoice).
- The value of goods/services is unusually high compared to the industry average, scale, or transaction history.
- General descriptions of goods and services, lacking clarity on type, specifications, and quantity, make it difficult to compare with actual operations.
- Issuing invoices at the wrong time according to Decree 123 (issuing before/after the tax liability arises).
These are common errors that can easily lead to the exclusion of expenses and VAT deductions during tax settlement.
3. Signs related to system data and tax filing
Data discrepancies are often a “red flag” in tax risk management systems:
- The invoice data in the tax authority's system does not match the data declared by the business.
- The invoice did not appear in the eTax statement or the invoice usage report.
- Discrepancies between invoices, VAT tax returns, and internal accounting records.
These cases are highly susceptible to post-completion/on-site inspections.
4. Signs related to actual transactions
The invoice is valid in form, but The transaction could not be proven to be genuine. It is still considered high risk if:
- No complete transaction records available.Contracts, purchase orders, warehouse receipts/delivery notes, acceptance reports.
- No bank payment receipts. with transactions of significant value as defined by regulations.
- Delivery to an unknown address.Lack of shipping and delivery documents.
- Ca series of circular buying and selling transactions among many businesses, but does not create real added value.
These are the signs most dangerousbecause it could be considered a fraudulent transaction, such as buying and selling invoices.
What are the reasons why an invoice is classified as a high-risk invoice?
An invoice is not automatically considered risky. This rating typically comes from a combination of factors: corporate legal aspects, the nature of the transaction, the invoicing process, and assessments from a tax risk management system (TMS).
1. Reasons stemming from the sales company
These are the most common causes, stemming from the invoice issuer:
- The business has ceased operations or abandoned its business address, but continues to issue invoices.
- Using a large number of invoices over a short period, then ceasing operations or absconding.
- Frequently changing legal information such as:
- Legal representative
- Head office address
- Business Line
These signs lead the tax authorities to assess the seller's reliability as low, resulting in all issued invoices being placed under risk monitoring.
2. Causes stemming from the nature of the transaction.
Even if the selling business "legally exists," the invoice can still be classified as risky if the transaction does not accurately reflect economic reality:
- There were no actual transactions, only paper deals.
- Fake invoices or circular invoice trading are used for the purpose of:
- Inflating expenses
- VAT tax deduction fraud
- The invoice content does not match the reality:
- Quantity error
- Incorrect unit price
- Incorrect type of goods or services
The tax authorities don't just look at invoices; they compare the entire chain of transactions – cash flow – and actual added value.
3. Causes stemming from errors in the invoice creation and management process.
Many invoices are classified as risky not because of fraud, but because of weak or outdated processes:
- Incorrect invoicing date, tax rate, or tax identification number.
- Failure to keep up with the latest regulations on electronic invoices as follows:
- Decree 123
- Circular 78
- Failure to cross-check invoice data with the tax authority's system before filing.
These errors cause data inconsistencies between businesses and tax authorities, making them susceptible to being automatically flagged as risky by the system.
4. Causes from the perspective of the Tax Authority's Risk Management System (TMS)
Ultimately, an invoice may be classified as risky not only for its own sake, but also because of its association with the overall risk profile:
- The TMS system assesses risk based on:
- Invoice usage history
- Tax declaration behavior
- Legal information of the business
- The invoice relates to a business that has been classified as high-risk or has previously been penalized for tax violations.
In this case, even a "normal" invoice can be scrutinized because it falls within the risk network.
What are the four criteria that tax authorities use to assess and warn about risky invoices?
In practice, tax authorities do not evaluate invoices based on subjective feelings, but rather on a set of legal, data-driven, behavioral, and transaction-nature criteria, integrated into a tax risk management system (TMS).
1. Criteria regarding the legal status of the issuing company
This is the first criterion checked, as it directly relates to the reliability of the seller.
The tax authorities assessed:
- What is the current state of the business?
- Currently operating
- Temporarily suspending business
- Cease operations
- Forced to pay the bill
- Tax identification number revoked
- Businesses have:
- Name in List of high-risk businesses in terms of taxation.
- Prehistoric using illegal invoices or be penalized in relation to invoices
It only requires the issuing company to be in the high-risk group.All related invoices may be subject to monitoring, including those for the buyer.
2. Criteria for invoice content and compliance with Decree 123
Invoices must fully meet the legal requirements regarding form and content as stipulated in Decree 123/2020/ND-CP.
Tax authorities conduct an inspection:
- Does the invoice contain all the required information as stipulated by regulations?
- The information on the invoice matches the data in the tax authority's electronic invoicing system.
- There are signs:
- Edit, delete
- Issuing duplicate numbers or symbols
- Using the wrong invoice template or type.
These discrepancies are usually automatically flagged by the system, without the need for an inspector.
3. Criteria for tax declaration data and invoice reporting
The tax authorities don't just look at individual invoices; they cross-reference data from multiple sources.
- Electronic invoice data
- VAT tax return form
- Report on invoice usage
Key questions:
- Were the invoices declared in the correct period?
- Do the amounts, tax rates, and tax payments match across the reports?
- Is there an unusual discrepancy between tax return data and invoice data in the system?
Any discrepancies could result in the invoice being added to the risk alert list.
4. Criteria for the reasonableness, validity, and legality of costs and transactions.
This is a crucial criterion for determining whether an invoice is acceptable for tax purposes, especially during tax settlement.
The tax authorities assessed:
- Does the invoice accurately reflect the actual business operations of the purchasing company?
- There is a logical connection between:
- Bill
- Contract
- Delivery documents
- Payment documents (especially bank payments)
Even if the invoice is in the correct format, if it doesn't prove a genuine transaction, the expense will still be disallowed and tax deductions will be rejected.
Risk classification by sales invoice and purchase invoice groups.
The classification of risks in sales and purchase invoices focuses on errors in information, form, legality, etc., all of which affect the validity of expenses/revenue.
Risks associated with sales invoices (output invoices)
Risk of incorrect invoice content
- Incorrect customer information (name, tax identification number, address).
- Incorrect product/service information: product name, quantity, unit price.
- Incorrect VAT rate or non-taxable item.
Consequence:
- Discrepancies in accounting records.
- Under-declaring or incorrectly declaring VAT payable.

Sales risk to businesses falls under invoice risk.
- The partner is on a high-risk business list, subject to enforcement action, or under invoice investigation.
- Even if the transaction is genuine, the selling business must still: Explain the nature of the transaction. Simultaneously provide complete documentation: contract, delivery and payment receipts.
Consequence:
- Under review by the tax authorities.
- Increased likelihood of being subjected to in-depth inspections and audits.
Risks of misapplying tax reduction and tax incentive policies.
- Failure to update or misinterpretation of regulations regarding tax reductions and tax incentives for each period.
- Applying the wrong VAT rate or granting preferential treatment to the wrong entity.
Consequence:
- They were ordered to pay back the amount of tax that had been incorrectly reduced.
- Penalized for filing incorrect tax returns.
Risks related to purchase (input) invoices
Receive invoices from businesses with high tax risks.
- The supplier has shown signs of invoicing violations and is being monitored by the tax authorities.
- Unusual changes in legal status (cease operations, absconding).
Consequence:
- Asked to explain the origin of the invoice.
- Risk of expenses being disallowed and input VAT not being deductible.
Received an invoice that is incorrect, missing information, or does not match reality.
- Incorrect tax identification number, name, and address.
- Incorrect tax rate, incorrect description of goods/services.
- Does not match the contract, delivery note, or payment document.
Consequence:
- Not eligible for VAT deduction.
- These expenses are not deductible when calculating corporate income tax.
Received an invoice that was identified as illegal.
- A fictitious invoice, an invalid invoice, or an invoice that does not reflect the actual transaction.
- Use this invoice to claim a reduction in the amount of tax payable.
Consequence:
- Severe penalties were imposed under Decree 125.
- Tax arrears, fines, and potential legal liability may arise.
Receiving invoices as part of a carousel fraud scheme.
- Participating in a multi-tiered chain of transactions does not create real value.
- Businesses only play the role of a "link" in the invoice chain.
Consequence:
- The risk of being considered an accomplice in fraud.
- To avoid penalties, one must demonstrate good faith, genuine transactions, and an independent role.
What are the consequences of using risky invoices? Penalties, back taxes, exclusion of deductions, criminal risks.
Using risky invoices (illegal invoices, fictitious invoices) can have serious consequences such as tax arrears, administrative fines (from 20-50 million VND or more), and, more seriously, facing criminal charges.
Consequences regarding VAT and corporate income tax.
Regarding VAT
- Exclude all input VAT that is ineligible for deduction.
- No distinction:
- Is the company at fault?
- The transaction is real, but the counterparty is risky.
The principle of the tax authorities is that VAT is only deductible when the invoice is legal, valid, and reflects a real transaction.
Regarding corporate income tax
- These types of expenses are invalid when determining taxable corporate income.
- Direct impact on:
- Business results
- Cash flow
- The financial report has been released.
- Administrative penalties for violations according to Decree 125.
- Fines will be imposed for using illegal invoices.
- Remedial measures: cancel the invoice, adjust the tax declaration, pay additional taxes and late payment penalties.
- Criminal risks arise from signs of illegal buying, selling, or use of invoices.
- Tax evasion or large-scale invoice trading can result in criminal prosecution.
- Individuals and commercial legal entities face heavy fines and suspension of operations.
Administrative penalties for violations according to Decree 125.
Punishable behavior
- Using invoices: Illegal, Invalid, Does not reflect actual transactions, Tax declaration based on invoices is risky.
Form of punishment
- Fine depending on the nature and severity of the violation.
- Tax collection VAT and corporate income tax were declared incorrectly.
- Calculate late payment penalties. on the amount of tax that was collected back taxes.
Remedial measures
- Cancel the incorrect invoice.
- Adjusting and supplementing tax returns.
- Submit in full:
- Tax shortfall
- Fine
- Late payment penalty
The reality is: the cost of remediation is often much higher compared to the initial tax benefits.
What are risk invoices and are they tax deductible? What are the conditions for protecting business interests?
Risk invoices may be tax deductible if the business can demonstrate:
- The transaction was real.
- A legally valid invoice at the time it is issued.
- The business is not an accomplice; it was unaware of and could not have known about the seller's infringing conduct.
However, there are also cases where risky invoices cannot be deducted from taxes if the business can prove:
- The actual transaction could not be proven.
- The documentation is incomplete and inconsistent.
- The invoice was identified as illegal or part of a fraudulent scheme.
Conditions for protecting the right to deduct VAT and legitimate expenses.
Businesses need to provide proof. simultaneously four groups of conditions:
Legal transaction documents
- Sales/service supply contract.
- Contract addendum (if any).
- Purchase orders, quotations, and transaction agreements.
Delivery and receipt documents – service performance
- Goods delivery and receipt record.
- Warehouse receipt/delivery slip.
- Shipping and logistics documents.
- Acceptance report (for services).
The documents must suitable in terms of time, quantity, and type. compared to the invoice.
Valid payment documents
- Pay cashless for transactions exceeding the specified threshold.
- Bank statement:
- The right partner
- Correct content
- True value
Electronic data & system reconciliation
- Invoice status:
- Validation check on the electronic invoice system.
- Declared data:
- Matching eInvoice – eTax – accounting records.
- No signs:
- Edit, replace, or cancel irregular invoices.
What is the checklist of documents that need to be prepared when invoice-related risks arise?
Documents proving the actual transaction
- Contract + appendix.
- Electronic invoices.
- Handover/Acceptance Report.
- Warehouse receipt/delivery slip.
- Bank payment documents.
- Emails, text messages, and related business communications.
How to organize documents for quick explanations.
- Group by transaction (1 transaction = 1 set of documents).
- Sort by subwayContract → Execution → Invoice → Payment → Declaration.
- Please mark clearly:
- Which transactions involve a risk invoice?
- Supporting documents are required.
What should businesses do when the tax authorities notify them of a high-risk invoice?
When faced with risky invoices, businesses should respond quickly, with complete documentation, and to the point, avoiding being perceived as uncooperative.
1. Read and understand the content of the notification correctly (e.g., Form 01)
- Clearly define:
- Some bills
- Relevant filing period
- Content under suspicion, request from the tax authorities.
2. Internal review
- Comparison: Invoice – contract – warehouse receipt/delivery note – payment document
- Verify the legal status of the seller at the time the transaction occurs.
3. Prepare the explanatory document.
- Create a reconciliation table for each transaction.
- Gather all the necessary documents to prove the actual transaction.
4. Draft and send an explanatory letter.
- Please specify:
- Business information
- Billing information
- The nature of the transaction
- List of attached documents
- Commitment to accountability
- Submit on time to the correct tax authority as notified.
What are the ways to avoid risky invoices? The inspection and management process in businesses.
The core principle for avoiding risky invoices is control before deduction – before payment – before filing.
Step 1 – Check the supplier before making a transaction.
- Look up your tax identification number and business status on the tax authority's system.
- Check the change history:
- Legal status
- Representative
- Head office address
- Assess the level of risk before signing a contract.
Step 2 – Check the invoice before recording and paying.
- Check the invoice status on the electronic invoicing system.
- Compare:
- Invoice with Contract
- Invoice with Warehouse Receipt / Acceptance Report
- Check the non-cash payment conditions for large-value invoices.
Step 3 – Periodic reconciliation between accounting records and tax data
- Compare:
- Invoice data
- Tax return
- Invoice usage report
- Review:
- The supplier shows signs of risk.
- Unusual invoices generated periodically
Step 4 – Develop internal procedures for controlling invoice risks.
-
- Issue SOPs for:
- Reception
- Check
- Approve
- Store invoices
- Clear delegation of authority:
- Inspector
- Approver
- Issue SOPs for:
- The person ultimately responsible
The process of controlling invoices and expenses using the Bizzi system.
Bizzi is a powerful tool that helps businesses control invoice risks from the source – automating processes and thus preparing them for tax explanations. Bizzi solutions help control invoices, expenses, and avoid risks by automating the process from receipt to processing (OCR + AI), verifying invoice validity (digital signatures, tax status, PO/GR matching), providing early warnings of risky invoices (problematic suppliers/invoices), and offering a dashboard for expense management, thereby increasing transparency, reducing manual errors, and improving legal compliance.
1. Automatically receive and classify input invoices (Bizzi IPA)
- Automatically receive electronic invoices from:
- Invoice portal
- Supplier
- Automatically extract invoice data.
- Categorize invoices by:
- Supplier
- Department
- Project
- Cost Type
2. Real-time invoice risk monitoring and alerts.
- Automatic check:
- Tax code
- Supplier operational status
- Compare the invoice criteria according to regulations.
- Early warning:
- Invoices from high-risk businesses
- Unusual invoices in terms of value and frequency.
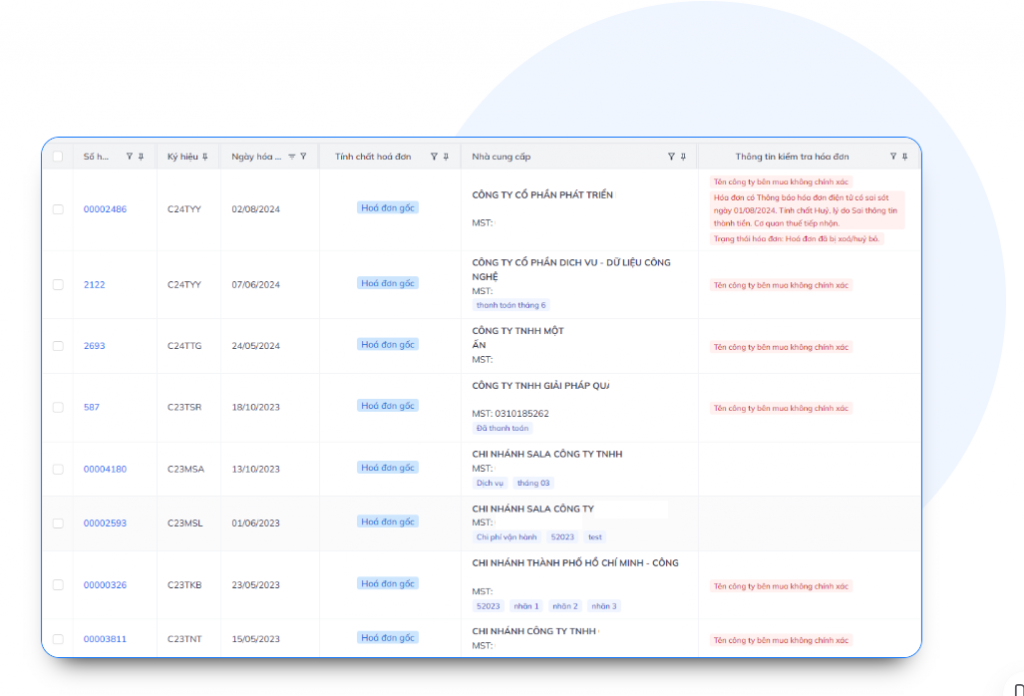
3. Three-way matching: PO – GR – Invoice
- Automatic matching:
- Purchase Order (PO)
- Warehouse receipt (GR)
- Bill
- Error detected:
- Quantity
- Unit price
- Types of goods/services
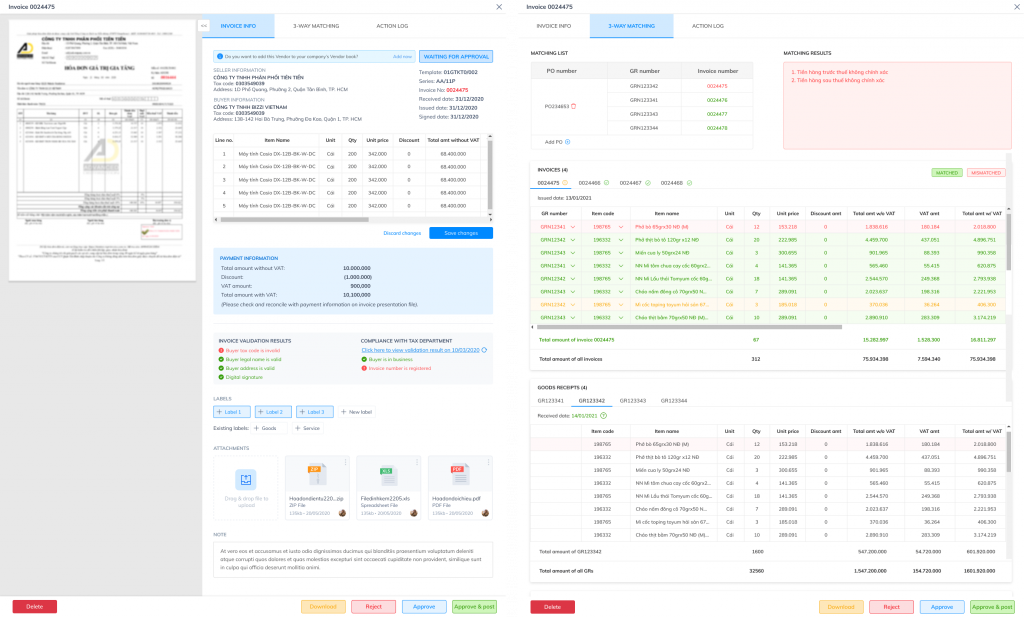
4. Centralized document storage for inspection and explanation purposes.
- Centralized storage: Invoices, Contracts, Inventory slips, Payment documents
- Quick access to one transaction equals one complete set of documents when requested by the tax authorities.
5. Cost Control & Budgeting Link (Bizzi Expense)
-
- Attach each invoice to:
- Expenditure
- Departmental budget
- Project budget
- Monitor expenses in real time.
- Budget overrun warning.
- Attach each invoice to:
- Automate the expense approval process based on risk-controlled invoices.
In summary, Bizzi transforms the manual and risky invoice control process into an automated, transparent, and efficient one, helping businesses reduce operating costs, avoid financial errors, and better comply with tax laws.
What are some frequently asked questions about risk invoices?
Risk invoices aren't scary if a business has control procedures and complete documentation. Here are some questions related to risk invoices.
1. How can I tell if the invoice I receive is a high-risk invoice?
- Check the invoice status and supplier tax identification number on the tax authority's system.
- Check the invoice for any unusual signs:
- High value, high frequency
- New supplier, limited information.
- Receive notifications/alerts from tax authorities or internal control systems.
2. Are risk-related invoices eligible for VAT deduction?
- It may be deductible if the business can demonstrate:
- Real deal
- A legitimate and valid invoice.
- No deduction is allowed if the nature of the transaction cannot be proven or if the invoice is determined to be illegal.
3. How long does it take to respond to a notification from the tax authorities regarding a high-risk invoice?
- The deadline for responding is specified in each notification from the tax authority.
- Businesses need to respond promptly to avoid being perceived as uncooperative or facing further action.
4. What should I do if I receive an invoice from a business that has then absconded?
- Proactively review all related transactions.
- Prepare documentation to prove the actual transaction.
- Provide a full explanation as requested by the tax authorities.
Businesses do not automatically lose their right to deductions if they can prove that the transaction was genuine and valid at the time it occurred.
5. What documents are most important to prove that a transaction is genuine?
- Contracts, appendices, purchase orders.
- Delivery and receipt records, warehouse entry and exit slips, acceptance certificates.
- Bank payment documents.
- Business communication records (emails, confirmations).
Conclude
The above information covers what constitutes a risky invoice and how to handle it legally while avoiding risks for businesses. It's clear that invoice management is not just about compliance, but also about protecting the company's finances and reputation. Proactive control from the outset is always much cheaper than paying the price later. invoice risk indicators.
The application of modern cost management solutions, especially process automation, helps businesses increase cash flow transparency, reduce errors, and improve overall financial control. This is a necessary step to optimize resources and ensure long-term growth.
Bizzi's cost management and invoice processing solution provides a comprehensive cost management solution, helping businesses standardize processes, save processing time, and effectively control expenses in real time. Trusted and implemented by many businesses, Bizzi is a powerful tool that helps businesses proactively protect their financial interests and improve cost management.
- Sign up here to try Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/