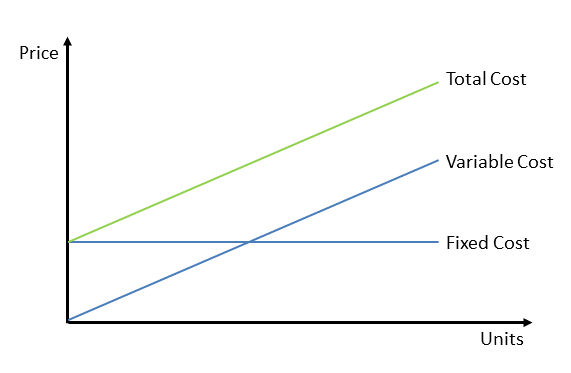
Variable Cost is costs vary depending on market fluctuations or heraffecting short-run production decisions that the business creates.
In this article, let's Bizzi find out information What is variable cost? How to calculate and the role of Variable Cost in production, helping businesses optimize financial decisions and operational efficiency.
What is variable cost in accounting?
Variable costs (VC) are costs that change in proportion to the quantity of products or services a business produces or sells. Basically, this type of cost will increase or decrease. depends on output of the business. Variable costs are also known as Variable Costs.
Examples of costs include variability:
- Raw materials in production (flour for bakeries, fabric for garment factories...)
- Wages are calculated by product or hour.
- Shipping costs are incurred based on the quantity of goods.
Variable costs include:
- Raw material cost.
- Direct labor costs.
- Energy costs for production.
- Packaging costs.
- Sales commission.
- Credit card transaction fees or shipping costs.
- Utilities such as electricity, gas, water.
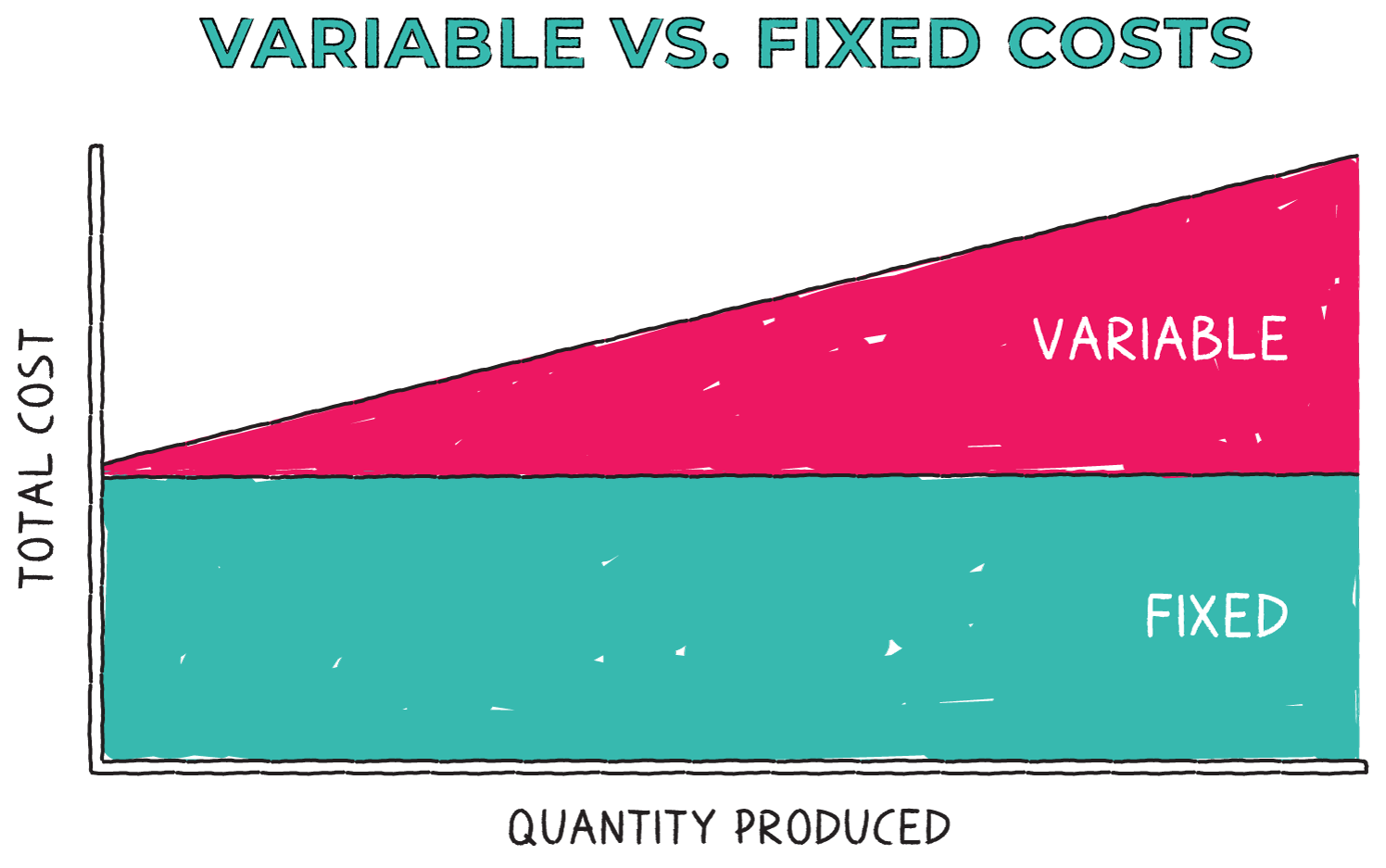
Characteristics and significance of variable costs
Characteristic:
- Total variable costs depend on the level of business activity; unlike fixed costs which exist whether there is production or not.
- Unit variable costs (variable to produce 1 unit of product) remain constant as the level of activity changes.
- Variable costs are zero if the business goes out of business.
- Direct impact on cost: Because variable costs account for a large part of product cost, businesses need to control them closely to optimize profits.
Meaning:
- Flexible in corporate financial management: When sales fall, businesses can cut back on production to reduce variable costs. When demand rises, they can increase production without making large investments in fixed costs.
- Support for pricing decisions & profit optimization: Variable costs is the basis for analyzing the relationship between costs, volume and profits, thereby accurately pricing products. Understanding variable costs helps businesses determine floor price (lowest selling price to avoid loss) and calculate, Break-Even Analysis more precise to determine when to start making a profit.
- Optimize production and operating costs: Businesses can seek to reduce variable costs by negotiating raw material prices, improving manufacturing efficiency, or automating.
- Support in business decision making, budgeting and planning: When considering expansion, businesses can predict variable costs to avoid financial risk. At the same time, understanding what variable costs are will help businesses compare in-house or outsourced production based on variable costs versus fixed costs.
Classification of variable costs
- Linear variable cost:
- Define: The variable costs varies by production activity in direct proportion.
- For example: Direct materials cost, direct labor, sales commission.
- Control: Control total costs and set variable costs per unit of activity.
- Level Conversion Cost:
- Define: Costs change only when activity levels change significantly.
- For example: Indirect labor costs, machinery maintenance costs.
- Control:
- Optimize the selection of the right personnel.
- Build appropriate variable costs for each level.
- Choose the appropriate activity level.
- Curved variable costs:
- Define: Costs do not have a clear linear relationship with production output.
- Characteristic: Difficult to identify and less common.
Variable selling costs
- Define: Costs that have characteristics of both fixed and variable costs.
- For example:
- Utility costs: Includes monthly subscription fees (fixed) and consumption-based costs (variable).
- Maintenance costs: Includes regular service contracts (fixed) and repair costs (variable).
- Telephone costs: Including line subscription fee (fixed) and call minute fee (variable).
- Transaction Fee: Varies by transaction quantity and value.
Variable cost in total cost
Variable cost in total cost shows the percentage of costs that vary with the level of activity of the business.
This ratio is calculated using the formula:
Variable cost ratio = (Total variable cost / Total cost) x 100%
This ratio helps businesses:
- Cost structure analysis.
- Risk assessment.
- Profit planning.
- Make business decisions.
Distinguish between variable costs and fixed costs
| Criteria | The variable costs | Fixed costs |
| Define | Expense attached attached to the product unit or sales activity. | Costs remain constant regardless of changes in output or sales activity. |
| Degree of change | Increases when output is higher, decreases when output is lower. | Unchanged regardless of increase or decrease in output |
| For example | Raw materials, direct labor wages, commissions. | Factory rent, machinery depreciation, insurance, administrative staff salaries. |
| Relationship with time | Changes by day, week, month, quantity… and only occurs when there is activity | Unchanged over a period of time. |
| Derivative | Only arises when the business carries out production activities. | No generation even if there is no production unit. |
| Change per unit | Constant. | Change. |
Real life example: Let's say you own a milk tea shop:
- Fixed costs: Rent is 10 million/month, regardless of how much you sell, you still have to pay.
- The variable costs: Cost of ingredients such as tea, milk, sugar – if you sell 100 cups, buy ingredients for 100 cups, if you sell 500 cups, buy ingredients for 500 cups.
How to calculate variable costs
Variable cost formulas
- Total variable costs:
- Recipe: Total variable cost = Number of output products x Variable cost per unit of product.
- Average variable cost:
- Recipe: Average variable cost = Total variable cost / Total output.
- Profit margin:
- Recipe: Profit Margin = Retail Price per Unit – Variable Cost per Unit.
- Break-even quantity:
- Recipe: Break-even quantity = Total fixed costs / (Retail price per unit – Variable costs per unit).
Illustrative example
- Example 1: Calculate total variable costs.
- A company produces 50 units of product, the variable cost per unit is $100.
- Total variable costs = $100 x 50 = $5,000.
- Example 2: Calculate average variable cost.
- The total variable cost to produce 80 shirts is $400.
- Average variable cost = $400 / 80 = $5/shirt.
- Example 3: Calculate profit margin.
- A company sells T-shirts for $20/piece, with variable costs of $12/piece.
- Profit margin = $20 – $12 = $8/shirt.
- Example 4: Calculate the break-even quantity.
- A T-shirt company has total monthly fixed costs of $1,200, a selling price of $20 per shirt, and variable costs of $12 per shirt.
- Break-even quantity = $1,200 / ($20 – $12) = 150 shirts.

How to optimize variable costs for businesses
Solution
- Save on direct material costs:
- Find new suppliers or negotiate better prices.
- Build strong relationships with suppliers.
- Buy raw materials in bulk.
- Partner with other businesses to buy together.
- Consider joint ventures with suppliers.
- Reduce direct labor costs:
- Replace full-time workers with seasonal labor when needed.
- Train staff to improve efficiency.
- Reduce commissions when possible.
- Build attractive bonus policies.
- Cut distribution costs:
- Find alternative shipping services at discounted rates.
- Reduce packaging costs.
- Use online shipping services.
- Switch to order fulfillment services.
- Other solutions:
- Plan and allocate specific variable and fixed costs.
- Control asset usage, avoid waste.
- Collect information on actual variable costs and establish standards.
- Periodic analysis of price fluctuations in the market.
- Analyze value-added processes to capture the effectiveness of each cost.
- Prepare variable cost estimates to easy to control in the short term.
- Propose measures to save variable costs.
- AI Applications: Read XML file, import invoice data automatically.
Financial management and variable cost optimization tools
Accounting and financial management software: Bizzi, QuickBooks, Xero, MISA, Odoo
- Helps track variable costs in real time, analyze cost trends and assist with budgeting
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) system: SAP, Oracle, Odoo
- Integrate accounting, financial, inventory management and manufacturing data to track variable costs more accurately.
- Support planning and cost forecasting based on actual production output.
Inventory Management Software: Zoho Inventory, Netsuite, KiotViet
- Helps optimize raw material costs (a major variable cost), reduce waste and ensure no excess inventory.
How does Bizzi help businesses manage variable costs?
Bizzi Built on in-depth analysis and tailored to every need cost management and control your business budget in the simplest way.
Send work/advance requests quickly
- Automatically calculate work norms
- Plan your budget clearly
- Easily request advances
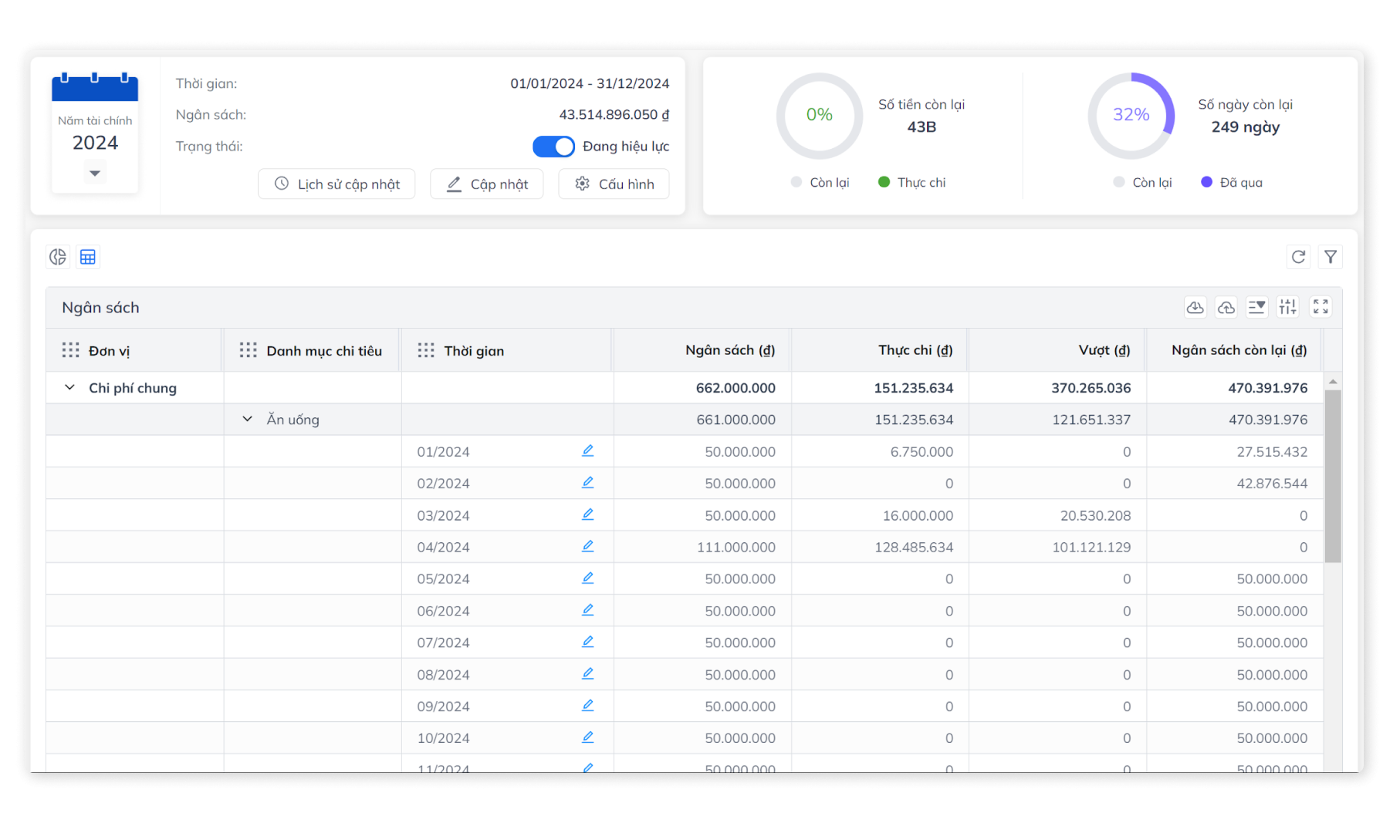
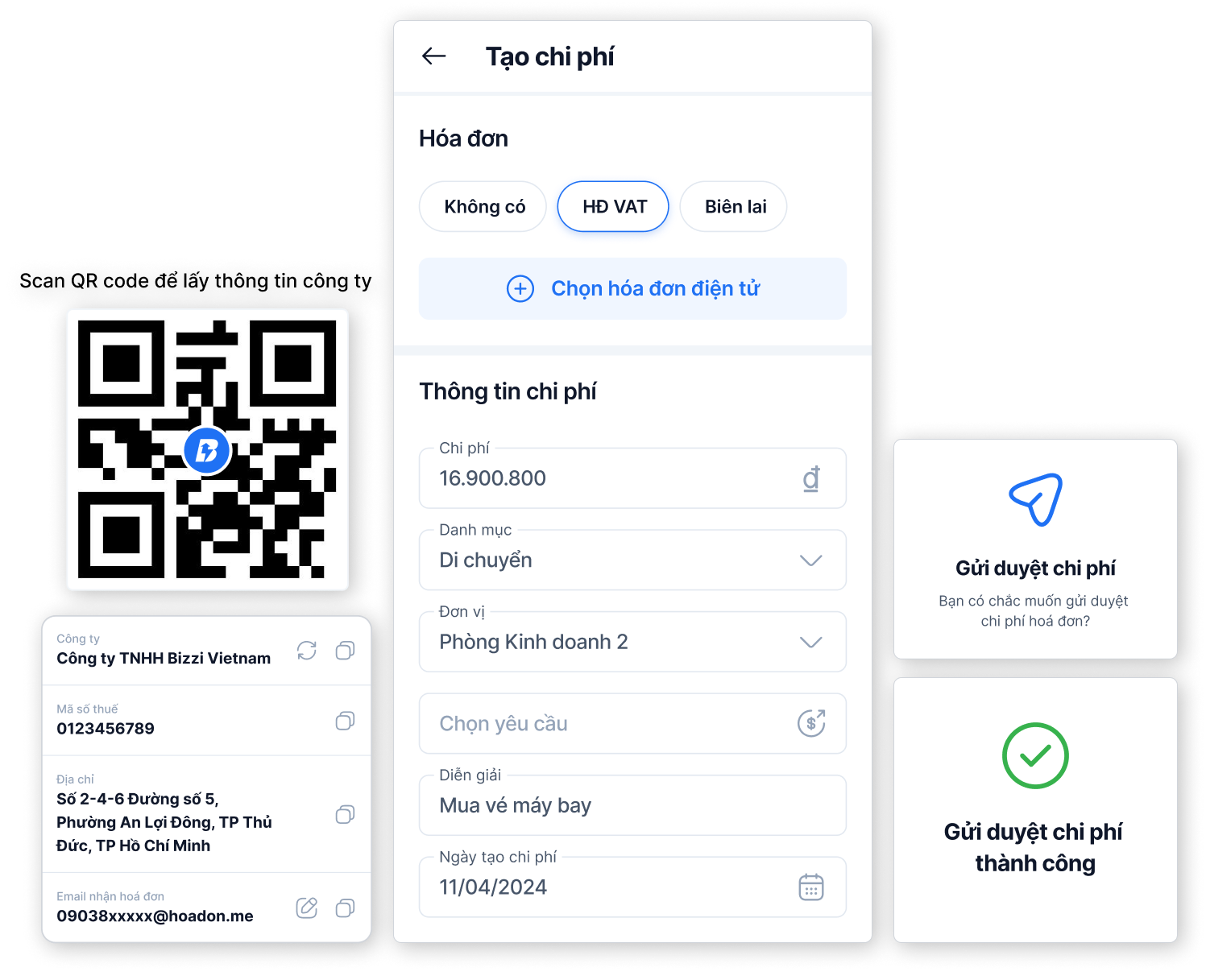
Simplify the process of collecting invoices – creating expenses
- Reduce receiving and checking time Electronic invoice – initiate payment in just 2 taps
- Proactive mass expense reporting helps streamline processes
- Automatically navigate the browsing flow according to established units, regulations, and decentralization
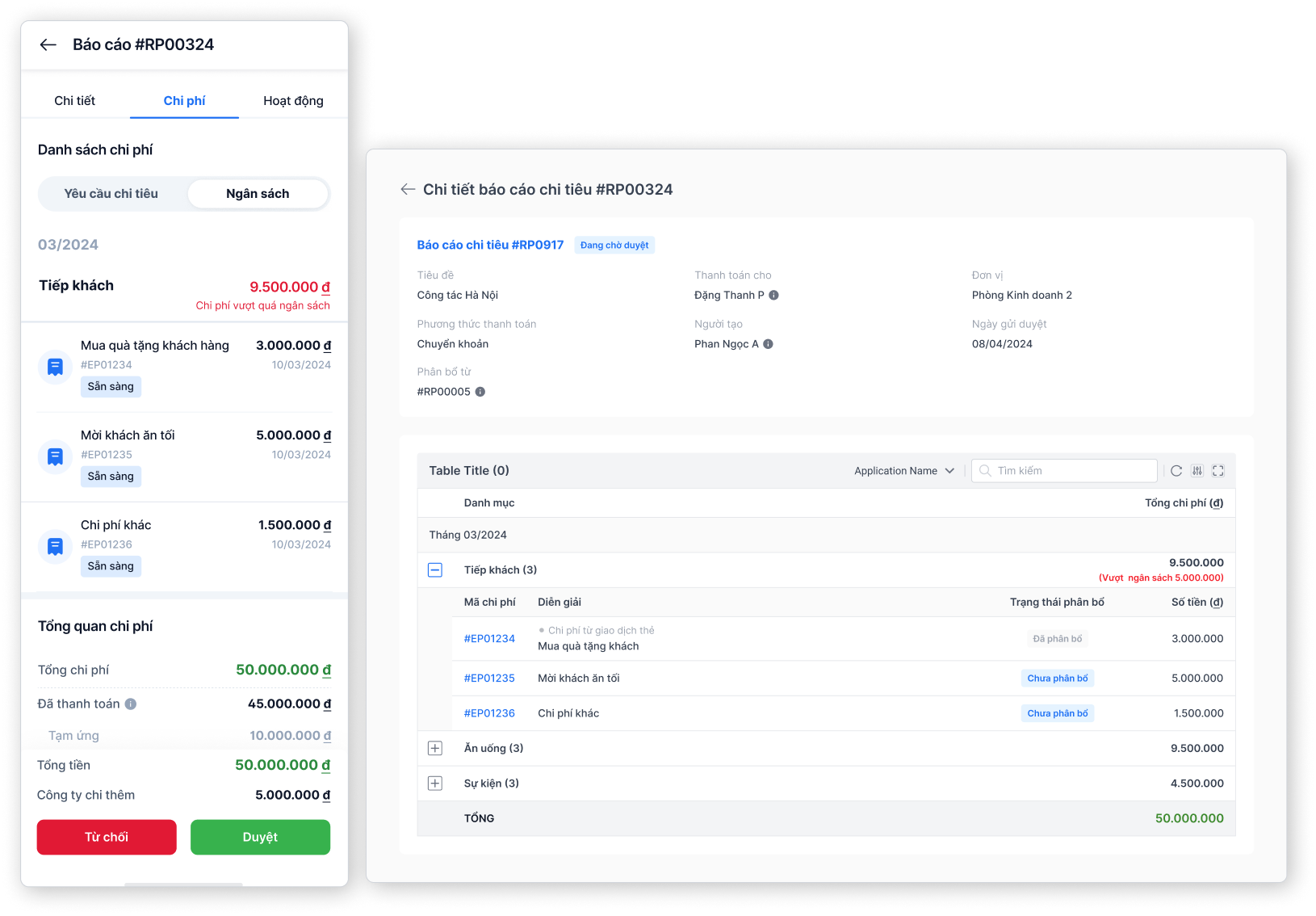
Approve documents conveniently and transparently
- Approve anytime, anywhere cross-platform
- Approval reminders to keep work from getting delayed
- Understand clearly the status of compliance with regulations and budget before making decisions
- Record approval/rejection history with valid reasons
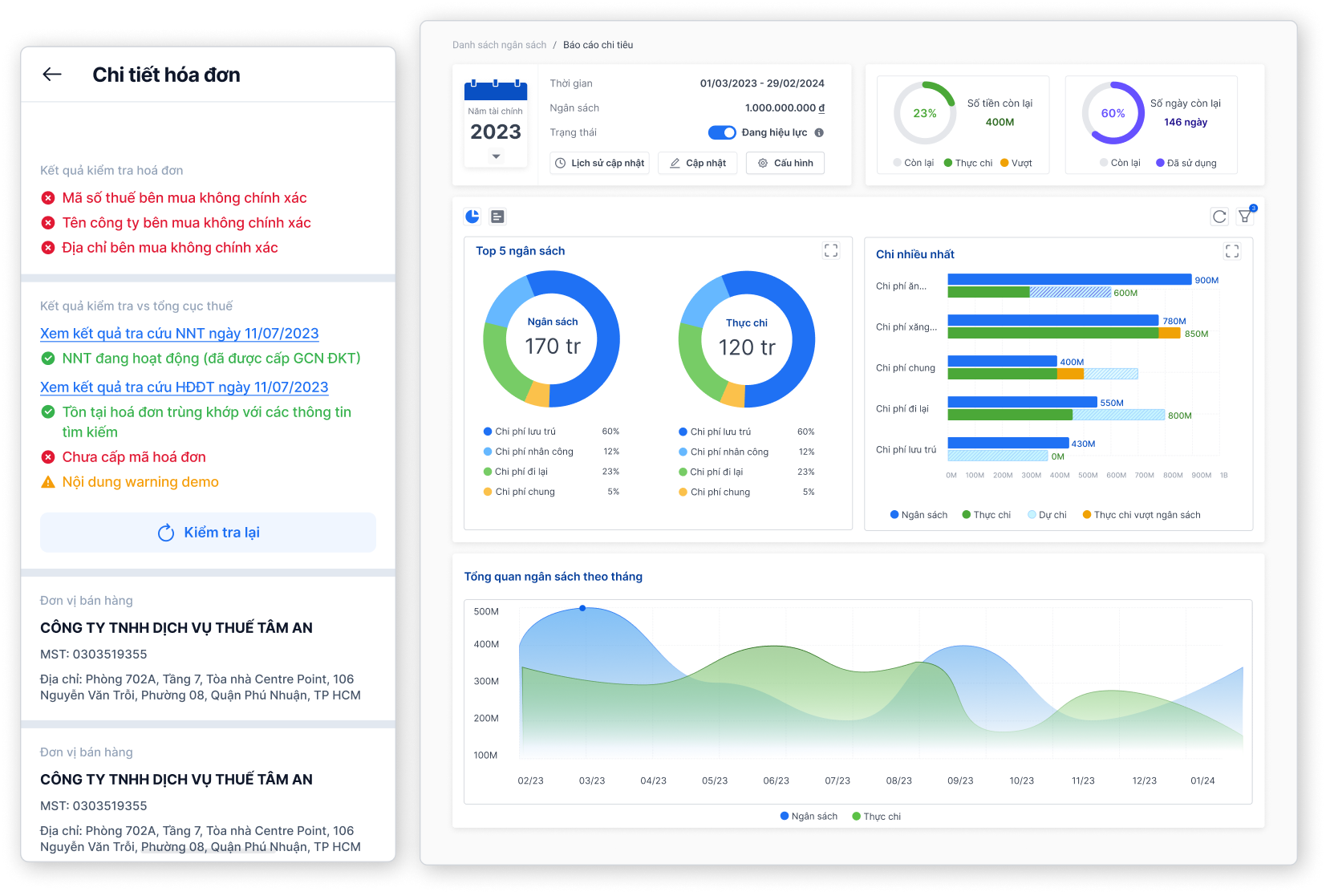
Control costs strictly according to policies and budget
- Complete and valid invoices and documents
- Prepare budgets by department, project and spending category
- Warning when costs and payment requests do not/do exceed the budget
- Display quick reports with detailed, up-to-date information on planned and actual expenditures
- Dashboard for intuitive, multi-dimensional cost management in real time across multiple platforms
Advantages of Bizzi – Optimal cost management solution for businesses
- Easy to use: Bizzi is designed with an intuitive and user-friendly interface, making it easy to record, track and manage expenses.
- Powerful Features: Bizzi offers a full suite of features for expense management, from recording invoices, categorizing expenses to creating and approving expenses online.
- Cost savings: Compared to other solutions, Bizzi has a reasonable price, suitable for many types of businesses, especially small and medium enterprises. small and medium enterprises
- Good support: Bizzi has a friendly and enthusiastic customer support team, always ready to answer all your questions.
Above is an article providing detailed information about What is variable cost? as well as how to calculate variable costs accurately. When managing variable costs effectively and optimally, businesses can reduce product costs, optimize cash flow, and avoid unnecessary costs. This creates the basis for increasing profits, improving competitiveness, and flexibly adjusting production according to the market.
In the era of rapid technological development, understanding what variable costs are and applying tools to management will contribute to increasing efficiency and optimizing resources for businesses. With Bizzi Expense – Comprehensive business expense managementAll business operations - revenue and expenditure will be digitized and automated intelligently.
Contact Bizzi now to experience specialized solutions specifically for your business!
- Link to register for a trial of Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/
Read more: