Marginal cost is an important indicator that helps businesses optimize production. Controlling and reducing marginal costs will help increase profits, improve performance and compete better in the market. In this article, Bizzi will provide you with full information related to what marginal costs are as well as how to optimize costs to maximize profits.
Definition and characteristics of marginal cost
Define
Marginal cost is the additional cost incurred to produce one more unit of a product or service. In Economics, it is the additional cost (∆C) to produce one more unit of output (∆Q).
Marginal cost shows the change in total cost when more product or service is produced, hence also known as marginal product cost or unit cost. In English, marginal cost is called Marginal Cost (MC).
Marginal cost characteristics
Measure only additional costs
- Marginal costing only accounts for the increase in cost when producing one more unit of product, not the total cost of production.
- Helps businesses focus on additional costs instead of overall costs.
Depends on production scale
- As output increases, marginal costs may fall due to economies of scale.
- But if production exceeds the optimal level, marginal costs may increase due to limitations in machinery, labor, and raw materials (Diseconomies of Scale).
May change over time
- Short run: Marginal costs can fluctuate widely due to raw materials, labor, and machine productivity.
- Long term: Businesses can invest in technology and optimize processes to reduce marginal costs.
Marginal cost formula
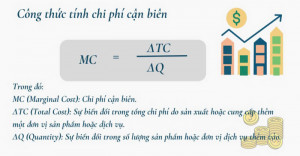
– General formula: MC = ∆C / ∆Q.
- In there:
- MC: Marginal Cost.
- ∆C (Change in cost): The change in total cost is calculated by subtracting the total cost of production from the old output from the new output.
- ∆Q (Change in output): Change in total quantity of products,is calculated by new total output minus original total output.
– Note: This formula only calculates additional cost per unit of product, not counting the total cost of the entire production.
For example:
- A lipstick factory has a total cost of 100 million VND for 1,000 lipsticks.
- If 100 more lipsticks are produced, the total cost increases to 105 million VND.
- Marginal cost = (105 million – 100 million) / (1,100 – 1,000) = 50,000 VND/lipstick.
Meaning and role of marginal cost
Marginal Cost (MC) plays an important role in many aspects of business, from production management, pricing, competitive strategy to financial decisions.
Below are the important meanings and roles of MC in each area of the business:
– In business management:
- Helps optimize production levels, thereby maximizing profits.
- Support making correct and optimal management decisions for pricing and business strategies.
- Helps managers compare results during plan implementation.
- Plays a role in assessing the quantity of goods and services provided to consumers.
- Support revenue comparison and make decisions to cut ineffective activities.
– Compare with Marginal Revenue (MR):
- If MR > MC: Profit is likely to increase, so increase output.
- If MR ≤ MC: Need to improve revenue and cost management, even stop production because it may be losing money.
– In Production:
- Helps determine optimal output levels for maximum profit.
- Help to adjust prices appropriately and evaluate production line efficiency, minimize risks and avoid capital losses.
– In Marketing:
- Is the foundation for determining the next marketing steps.
- If the marginal cost of increasing advertising spending is less than the additional revenue, increasing advertising spending is rational.
- Helps determine optimal pricing to maximize revenue.
– In Finance:
- Help investors evaluate the feasibility of the project and the profits it brings.
- Help managers develop policies to minimize risks and avoid financial losses if costs get out of control.
Relationship between Marginal Cost and Average Cost
Average Cost (AC) is the cost per unit of output, calculated by dividing total cost by the number of products.
The relationship between Marginal Cost (MC) and Average Cost (AC) is one of the important principles in microeconomics, especially in the theory of production costs. This relationship can be described as follows:
- As output increases, if MC < AC then AC will decrease.
When marginal cost is less than average cost, each additional unit of output costs less than average, causing average cost to fall. This is the stage where the firm is taking advantage of economies of scale.
- As output increases, if MC > AC then AC will increase.
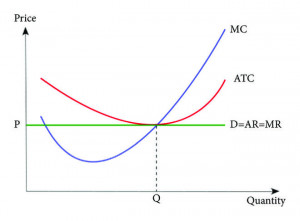
When marginal cost is greater than average cost, each additional unit of output costs more than the average, causing average cost to rise. This is the stage where diseconomies of scale appear.
- When MC = AC then AC is at minimum.
When MC = AC, average cost reaches its minimum. This is the point at which the firm is most cost efficient. At this point, if the firm produces less, average cost will still fall; if it produces more, average cost will begin to rise.
Marginal cost (MC) helps compare the results of implementing the plan, while average cost (AC) is used to evaluate the impact of changes in output on unit costs. This helps the business determine the optimal output level to minimize production costs.
The basic difference between these two types of costs is: MC is a cost increase per unit, AC is the cost on each unit.
Marginal cost curve
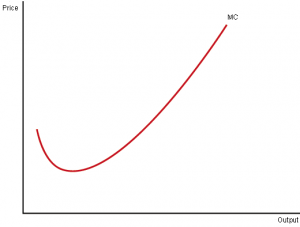
- For a typical business, it usually takes the form of an inverted parabola or a U-shape.
- Initially: MC value tends to decrease because costs (fixed + variable) per unit tend to decrease (economies of scale).
- Later stage: By mid-cycle, variable costs continue to increase, faster than the rate of decrease in fixed costs, causing MC to begin to increase.
- Turnaround point: The point at which the increase in variable costs equals the decrease in fixed costs.
- When output is low, MC can be high due to excess production capacity.
- As output increases to the optimal level, MC reaches a minimum value, then increases again if output exceeds the optimal level.
Notes when analyzing marginal costs
- Difficult to apply in some industries: Such as shipbuilding, airplanes, etc. with unfinished products having large value corresponding to revenue. Not calculating fixed costs into the final value of unfinished products can cause errors.
- Don't ignore exogenous factors and hidden costs: Raw material costs can change according to the market, labor costs can fluctuate due to wage increases or government policies, opportunity costs (can create higher profits if resources are used for other purposes).
- Pay attention to economies of scale: As production expands, marginal costs can decrease due to economies of scale (reduce average cost). However, if it exceeds the optimal level, marginal costs may increase due to the phenomenon of economies of scale.
- Caution should be exercised when applying: Must be presented and explained reasonably, accurately, and in relation to all variables in the particular situation.
- Identify variable costs clearly: To calculate accurately, it is necessary to determine which components of the total cost have variations and the specific amount of variation.
- Distinguish and understand the nature of marginal cost and average cost
- Determine calculation time and external factors: Costs can change over the short and long term, influenced by markets, technology, and policies.
- Avoid confusion with average cost.
How to reduce marginal costs effectively
– Leveraging economies of scale
- When producing in large quantities, marginal costs tend to decrease due to better utilization of resources.
- Solution: Increase production when marginal cost is lower than selling price to maximize profit.
– Reduce raw material and production costs
- Negotiate with suppliers to buy raw materials in bulk at better prices.
- Improve production processes to save materials and time.
– Technology application & automation
- Apply machinery and ERP software to reduce labor costs and increase efficiency.
- Technology helps reduce errors, avoid waste and improve productivity.
– Optimize human resources and work processes
- Train employees to improve performance and reduce errors in production.
- Arrange work properly to avoid wasting labor.
-
– Good control of fixed and variable costs
- Reduce fixed costs by optimizing rental space and warehouses.
- Consider outsourcing some services instead of doing them yourself if it's cheaper.
- Find suppliers with reasonable prices
– Leverage data to forecast demand
- Use data analysis to produce exactly what the market needs, avoiding overproduction and waste.
Evaluate a business based on marginal cost
Marginal cost (MC) provides important information about a business's performance, competitiveness, and long-term sustainability. More specifically, what does marginal cost say about a business's finances?
– Production efficiency
- If MC decreases as output increases → The firm is taking advantage of economies of scale, more efficient production.
- If MC increases rapidly when expanding production → The business may encounter economies of scale or the cost of raw materials and labor increased sharply.
– Pricing and profit potential
- If MC lower than selling price, businesses can continue production to maximize profits.
- If MC close to or above the selling price, profit margins fall, signaling that the business may be in financial trouble.
– Competitive strength
- Businesses have MC is lower than the opponent maybe sale price while still maintaining profits, creating competitive advantages in the market.
- Conversely, if MC is higher, the firm may experience price pressure and lose market share.
– Ability to expand business
- If MC slow increase in output, businesses are able to scale without incurring too much cost.
- If MC increase rapidly, expansion may be unsustainable or require technology investments to reduce costs.
– Financial risk
- If MC is consistently higher than selling price → The business may be selling at a loss, and needs to re-evaluate pricing strategy and optimize costs.
- If MC fluctuates strongly → Raw material or labor costs may be unstable, affecting long-term financial planning.
In short, it is possible to evaluate a business based on MC, but it needs to be combined with other indicators such as:
- Gross profit & net profit → See if the business is making a profit.
- Profit Margin → Assess profitability.
- Fixed costs & variable costs → Understand the cost structure.
- Brand strength & market share → MC is low but without a strong brand, it is still difficult for a business to succeed.
Conclude
The following article has answered the question of what is marginal cost and suggestions related to effective cost management. Marginal cost is an important concept in business and finance, helping businesses make effective production, pricing and cost management decisions. Understanding the concept, calculation formula and meaning of marginal cost will help build appropriate business or investment plans.
At the same time, businesses need to be careful when applying and analyzing marginal costs in specific situations; other factors need to be considered to make accurate decisions.
Expense management software is increasingly being adopted by businesses, especially in the e-commerce and shipping services sectors, to improve operational efficiency through process automation and effective budget management. Bizzi Expense is one of the leading cost management software solutions, trusted by large enterprises such as Masan Group, Mondelez International, Pierre Fabre,... thanks to its superior automation power and integration capabilities.
Not only simply supporting businesses in managing costs, Bizz Expense also helps optimize resources and increase efficiency through breakthrough features such as automatically navigating approval flows by unit, regulations, and established authorizations; analyzing costs and financial reports in real time; scanning data and checking the validity of invoices, etc.
With a user-friendly interface design, Bizzi Expense is the ideal solution for businesses that want to improve cost management, modernize processes and aim for sustainable development and long-term competitiveness.
- Link to register for a trial of Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/

