In many businesses, production planning is still simply understood as "the factory's work schedule." This understanding separates production from finance, leading to... production cost Out of control, inventory ballooned, and cash flow strained despite no decrease in revenue.
In fact, from the perspective of the CFO and the Finance department, The production plan is the central link connecting operations – costs – inventory – cash flow.When properly constructed, a production plan not only answers the question "how much to produce," but also determines how much capital the business needs, when to spend it, and where the financial risks lie.
This article analyzes What is production planning?nature production management Behind it lies the ability to create a feasible financial plan and control the Plan-Actual-Cash Flow in a volatile manufacturing environment.
What is a production plan and how is it different from a production schedule?
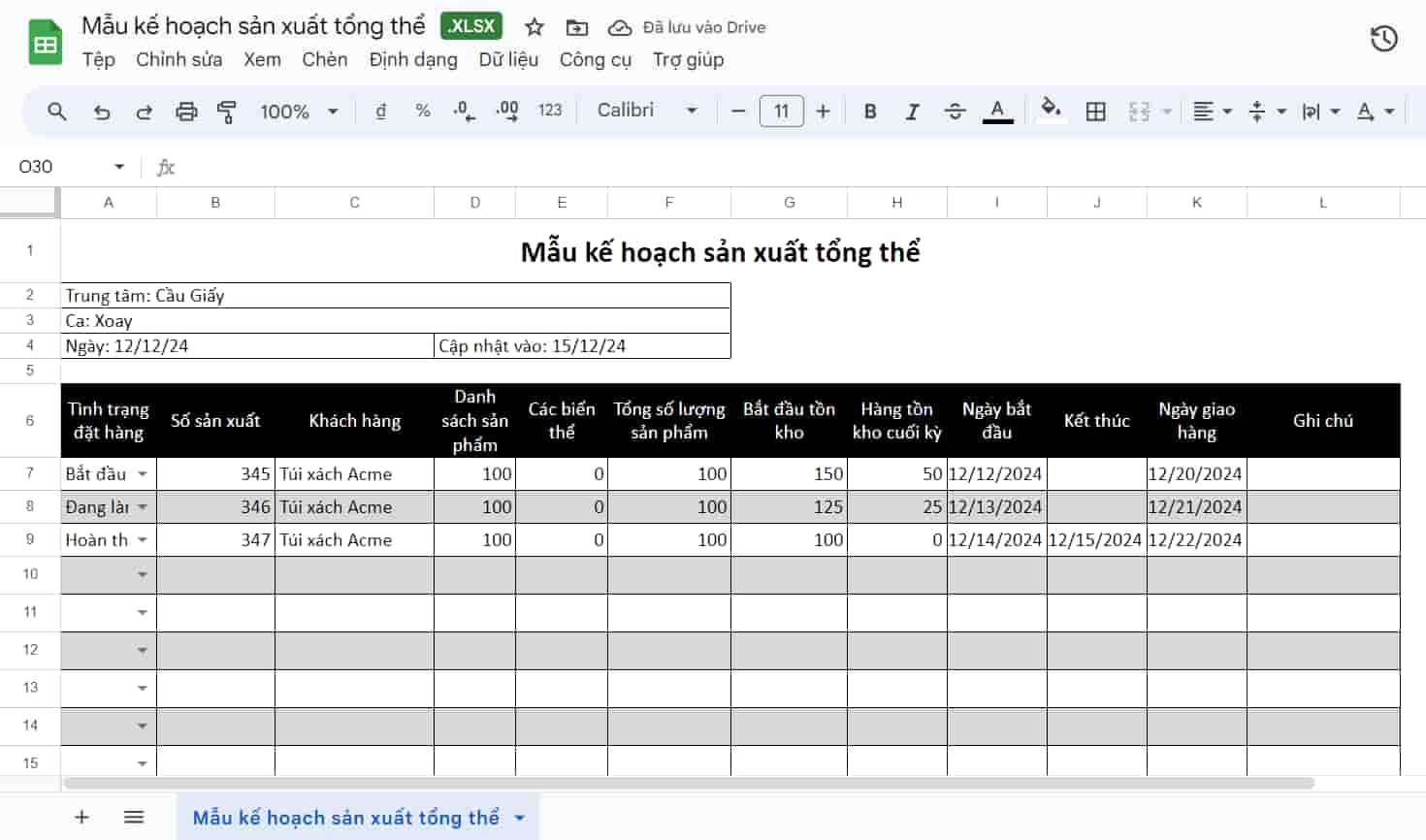
What is a production plan? A production plan is an overall plan that determines what products a business will produce, in what quantities, when, and with what resources, in order to meet market demand within its capacity and budget. A production schedule is simply a detailed implementation, broken down by day or shift, of that plan.
In essence, the production plan lies in the value of the fruit. tactical level, where decisions about output, product mix, and resource allocation are made. The production schedule is located at operational levelFocus on arranging machinery, shifts, and personnel to execute the plan.
Problems arise when businesses confuse these two concepts. A production schedule that is followed "correctly" can still lead to financial failure if The initial production plan was wrong.In that situation, COGS increases, inventory becomes excessive, working capital is locked up, and cash flow is strained. This is the point of greatest concern for CFOs when evaluating the quality of a production plan.
At the CFO level, the issue isn't about "whether the scheduling is right," but rather... Is the production plan being monitored using financial data?Bizzi was not involved in the production scheduling, but played a role. controlling the input layer of financial data (raw material costs, processing costs, operating costs) to ensure The production plan is based on actual costs, not estimates..
- Avoid this situation The production schedule is correct, but the financial plan is wrong.
- The CFO can trace back: Where does this production plan "eat up" the budget?
What core questions in business management does a production plan answer?
A proper production plan must simultaneously answer five core questions: what products will the business produce, how much will it produce, when, where, and with what resources? These five questions directly reflect decisions about product mix, capacity, plant allocation, and material usage.
From a financial perspective, the CFO doesn't stop at the question of "how much to produce," but expands to issues such as: how much money is locked in inventory, when cash flow for raw materials is incurred, and whether the revenue-expenditure cycle creates capital pressure. Therefore, What is production planning? It is inseparable from the problem of resource allocation and working capital management.
With 5 questions – What – How much – When – Where – With what – Bizzi provides direct support. "With what" and indirectly at "How much" & "When" through cost data. Specifically, the data invoice for purchasing raw materials, outsourcing costs, logistics costs Standardized by Bizzi to help CFOs:
- Accurate estimation The amount of money needed depends on how much is produced.
- See clearly Cash-out in stages according to the production plan.
Production planning is no longer just a matter for the factory; it has become a broader issue. capital utilization map.
What input data determines the quality of a production plan?
The quality of a production plan depends directly on the accuracy of the input data. Core data sets include demand or order forecasts, actual inventory, work-in-process (WIP), bill of materials (BOM), production standards, lead time, and capacity constraints.
In reality, many production plans fail not because of planning algorithms, but because of inaccurate input data. When the Bill of Materials (BOM) is incorrect, lead times are not updated, or inventory is misrecorded, the entire subsequent plan will suffer from skewed costs and cash flow. The "Garbage In – Garbage Out" principle is particularly true for production planning.
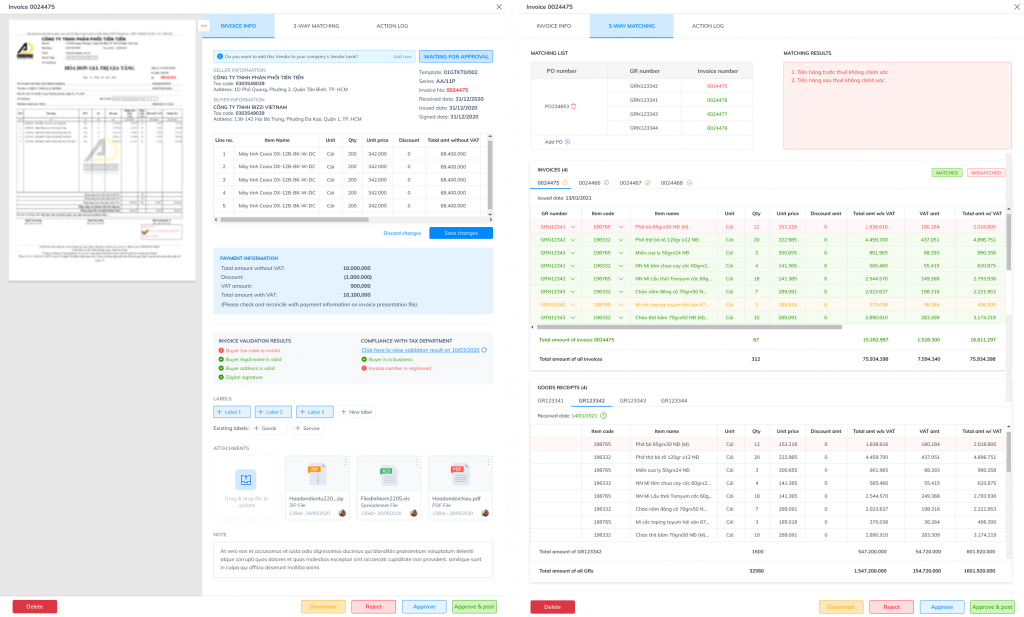
One often overlooked point is input invoice for raw materialsIf invoices are not closely reconciled with purchase orders (POs) and general merchandise prices (GRs), cost of goods sold and inventory will be inaccurate, leading to unrealistic production and purchasing planning. Standardizing invoice data, performing three-way reconciliation, and cleaning master data are fundamental to ensuring production plans accurately reflect the company's financial capabilities.
One of the common reasons for production planning deviations is Inventory data and cost of goods sold do not match., originating from:
- Incorrect input invoice
- No reconciliation of Invoice – Purchase Order – Grand Prize
- Raw material prices fluctuate, but the Bill of Materials (BOM) is not updated.
Bizzi addresses this point directly through:
- Bizzi Bot Automatically collect raw material invoices from suppliers.
- 3D verification Helps eliminate incorrect, duplicate, or invalid invoices.
- Standardize purchase prices → clean up Inventory value & COGS input
When the input data is clean, The new production plan has real financial value..
How do MPS and MRP translate production plans into material procurement requirements?
In the planning system, MPS determines production output for each period, while MRP translates this plan into specific material requirements based on the Bill of Materials (BOM) and lead time. The MPS-MRP logic chain is the bridge between them. production plan and purchasing plan.
From a CFO's perspective, Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is not just a technical problem but a tool for forecasting cash flow. Once material requirements are clearly defined, businesses can accurately estimate the timing and scale of cash outflows to suppliers. Without tight control over MRP, production plans can easily lead to over-purchasing, budget overruns, and liquidity pressures.
MRP stated What to buy – how much – when?, but did not reply:
- Did the purchase cost exceed the budget?
- Is there sufficient cash flow to make payments on time?
Bizzi adds a layer of financial control to the MRP by:
- Attach raw material procurement plan with cost budget on Bizzi Expense
- Alerts when purchase orders exceed limits or occur unexpectedly.
- Monitor Real-time actual spending, without waiting until the end of the term
The CFO has control. Production planning begins as soon as costs are incurred., not when the books have been "closed".
Which KPIs measure the effectiveness of production plans and have a direct impact on costs?
The effectiveness of the production plan is reflected in operational and financial KPIs such as OEE, OTIF, inventory turnover, and plan-actual deviation. These indicators are not only technical in nature but also directly impact unit costs and capital efficiency.
When OEE decreases, the cost per unit increases due to underutilized capacity. When inventory turnover slows, working capital is tied up and the cash cycle lengthens. Therefore, CFOs need to view production plan KPIs as early indicators of cost and cash flow risks, rather than just operational reports.
KPIs such as OEE, inventory turnover, and Plan-Actual are only valuable when:
- The actual data is reliable.
- The discrepancies were detected early.
Bizzi provided support by:
- Provide Actual costs have been invoiced.
- Use as input data for SACTONA (EPM) to:
- Analysis of discrepancies in production plans – costs – budget
- Simulate the financial impact if OEE decreases or inventory increases.
Production KPIs are "translated" into financial language which the CFO needs.
How does the production plan affect cash flow and working capital?
Production planning determines inventory levels, material purchasing schedules, and payment terms for suppliers. Inaccurate planning can lead to high inventory levels while lacking the cash to sustain production.
The common chain reaction is: a flawed production plan leads to over-purchasing of raw materials, increased inventory, and tied-up working capital. Conversely, a well-controlled production plan helps businesses balance safe inventory levels and cash flow, ensuring solvency without disrupting production.
Production plan decision:
- When should we spend money on raw materials?
- When is it necessary to collect money to continue production?
Bizzi was directly involved in two ends of the cash flow:
- Spend money: Control invoices, payment deadlines, avoid overspending – spending too early.
- Collect moneyBizzi ARM monitors accounts receivable and payable, ensuring payments are made on schedule.
Whether the production plan is feasible or not, look at it. cash flow, not just output.
Which is more suitable for creating and managing production plans: Excel, ERP, or EPM?
In practice, Excel is suitable for small businesses or environments with little change, but quickly reveals its limitations as data grows and needs to be controlled in terms of Plan-Actual data.RP in production Strong in recording real-world data, but often lacks the ability to simulate and analyze scenarios.
EPM is an additional toolkit that allows CFOs to connect production planning with budgets, analyze deviations, and make flexible forecasts. For manufacturing businesses with fluctuating demand, What is production planning? It's no longer just an Excel file, but a data-driven decision-making system.
| Criteria that CFOs care about | Excel | ERP | EPM / FP&A |
| Main role | Flexible calculation tool | Recording & Operation System | Planning, analysis & forecasting system |
| Production planning | ✔ Can be set manually | ⚠ Limitations, usually at the configuration level | ✔✔ Designed specifically for planning |
| Manage multiple plan versions | ✖ Easily duplicated, difficult to control | ✖ Inflexible | ✔✔ Clear version control |
| Record Actual (output, cost) | ✖ Not suitable | Strong | ✔ Receive data from ERP |
| Plan-Actual Analysis | ⚠ Manual, time-consuming | ⚠ Yes, but not deep. | ✔✔ Automatic, multi-directional |
| What-if scenario simulation | ⚠ It's possible, but easy to make mistakes. | ✖ Very limited | ✔✔ Pre-designed for simulation |
| Cost and cash flow linkage | No system | ⚠ Indirect | ✔✔ Closely aligned with budget and cash flow |
| Scalability as data grows | ✖ High risk | ✔ | ✔✔ |
| Suitable for CFOs in charge of financial control. | ✖ | ⚠ | ✔✔ |
| Level of human dependence | Very high | Medium | Low (based on rules & data) |
Bizzi doesn't replace Excel, ERP, or EPM, but rather acts as a clean financial data and cost control layer between ERP and EPM. Without Bizzi, CFOs would have to "clean data manually" before analysis.
Specifically:
- ERP records Actual
- Bizzi ensures that the Actual is accurate, complete, and under control.
- EPM (SACTONA) uses this data to:
- Plan-Actual Analysis
- Forecast costs and cash flow for the production plan.
What are the frequently asked questions about production planning? (FAQ)
Below are answers to frequently asked questions regarding production planning.
How does a production plan differ from a business plan?
A business plan sets revenue and market targets, while a production plan specifies those targets in terms of output, resources, and implementation costs.
Do small businesses need to create production plans?
Yes. Small scale does not exclude financial risk. Production planning helps small businesses control inventory and cash flow from the outset.
When should production plans be adjusted?
When demand forecasts change, capacity is disrupted, or input costs fluctuate significantly, production plans need to be updated promptly.
How does the production plan affect the cost of the product?
Incorrect planning increases unit costs due to inefficient resource utilization and excess inventory.
Is ERP sufficient for managing production planning?
ERP systems capture real-world data well, but for plan-actual analysis and forecasting, businesses often need an additional layer of EPM or FP&A.

Conclude
From a financial management perspective, What is production planning? It's not just about the factory's operations; it's a strategic decision that directly impacts costs, inventory, and cash flow. A production plan built on accurate data, measured by appropriate KPIs, and continuously monitored (Plan-Actual) will help businesses maintain operational efficiency in a volatile environment.
For the CFO, the focus isn't on one-time planning, but on capability. Control and adjust production plans based on actual data.When production plans are closely linked to invoicing, costs, accounts payable, and budgeting systems, businesses can proactively manage working capital, reduce financial risks, and make faster decisions.
Bizzi supported the entire journey by:
- Standardization and control input invoices
- Reduce the discrepancy between Plan – Actual
- Connect the production plan with budget and actual cash flow
To receive personalized solutions tailored specifically to your business, register here: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/