In today's volatile business environment, shocks in raw material costs, interest rates, exchange rates, or sudden changes in the supply chain have become the "new normal." Finance and Accounting departments, especially FP&A (Financial Planning & Analysis), face a major challenge: how to make timely decisions when past data no longer represents the future, and annual static budgets become almost completely outdated after only 3-6 months?
While budgeting at the beginning of the year is necessary, the underlying concern of CFOs and leaders is: "Not looking far enough ahead, 12–18 months into the future." and "I don't know what the worst-case scenario looks like." if the market reverses.
This is the time for businesses to shift to a more flexible and continuous financial forecasting approach: Rolling Forecast (Rotating forecast).
This article will help you:
- Explain clearly What is a Rolling Forecast? and the core difference from a static budget.
- Demonstrate how to design, implement, and operate an effective Rolling Forecast model in FP&A.
Why do businesses need rolling forecasts?
Financial forecasting and planning have changed significantly over the past decade. Traditional methods are no longer sufficient to keep pace with the rapid changes in the market.
1. Background and practical issues
To understand why Rolling Forecast is so crucial, we need to look at the pressures businesses are facing:
- Unpredictable fluctuations: Businesses are facing significant fluctuations in revenue (changing consumer habits), costs (inflation, energy prices), interest rates, exchange rates, and potential disruptions in the supply chain.
- Static budgets are "outdated": An annual budget (static budget) is built on initial assumptions and is typically only valid as a reference for 3–6 months. After that, it becomes a “dead target,” no longer reflecting the new market context.
- Making vague decisions: CFOs and FP&A departments are often forced to make major decisions based on past data (actuals) or outdated forecasts. This can easily lead to wasted costs, missed revenue opportunities, or sudden cash flow shortages.
2. What problem does a rolling forecast solve?
Rolling Forecast is the answer to these questions. Basically, Rolling Forecast is a continuous financial forecasting model. (continuous planning)
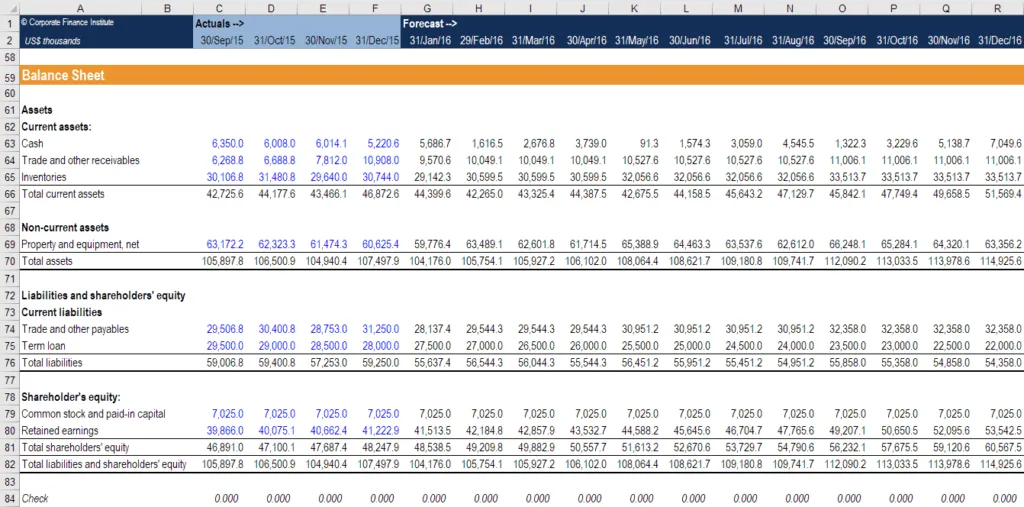
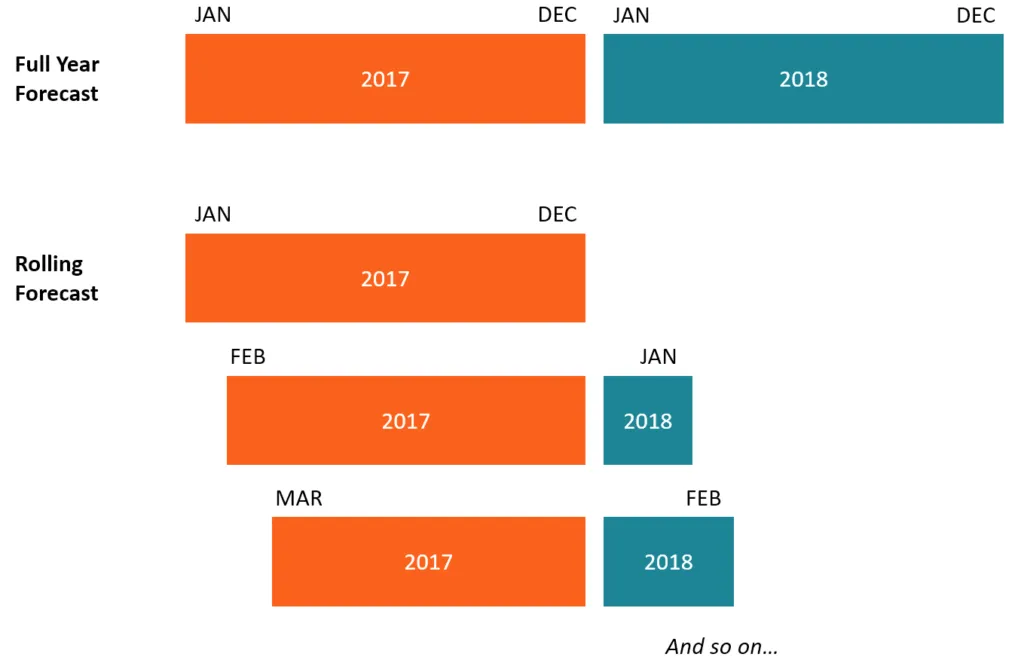
Instead of focusing solely on the current fiscal year (e.g., 2025), Rolling Forecast always maintains a fixed outlook extending 12, 18, or 24 months into the future.
Mechanism of action: Each update (usually monthly or quarterly) removes the previous period (Actuals) and automatically adds a new period to the end of the forecast window (Horizon). This ensures that management always has a view of the next 12 months, regardless of whether it is January or December of the fiscal year.
This method helps leaders:
- Decision-making is faster because data is tracked and updated to reflect the latest context.
- There is ample time to adjust long-term plans such as Capex (capital expenditure) or Funding Plan (capital raising plan).
II. What is a Rolling Forecast? How does it differ from a static forecast and a Rolling Budget?
For effective implementation, it is necessary to clearly distinguish Rolling Forecast from other financial planning concepts.
Definition of rolling forecast and rolling prediction
What is a Rolling Forecast? Rolling Forecast It is a financial forecasting method that is updated periodically (usually monthly or quarterly) to maintain a fixed forecasting "time window" into the future.
Key Features:
- Horizon is fixed: There is always a forecast for the next month (e.g., 12 months, 18 months), regardless of when the fiscal year ends.
- Continuously updated: The actual results of the past period will be included, and a new period will be added at the end of the model to maintain the $N$ monthly outlook.
What is a rolling budget and how does it differ from a rolling forecast?
| Characteristic | Rolling Forecast | Rolling Budget |
| Main objective | What will happen – Focuses on the accuracy of future predictions. | Spending goals and limits (What should happen) – Add layers of spending goals, authority, and responsibility. |
| Mechanism | Forecasts are based on the latest Assumptions and Driver data. | Updating spending limits may also require more complex approvals. |
| Role | Strategic forecasting tools. | Tools for managing expenses and responsibilities. |
In short: Rolling Forecast focuses on predicting the future, while Rolling Budget adds a layer of objectives and control. They can run in parallel, or Rolling Forecast can be used as input to update Rolling Budget.
Static forecast vs rolling forecast
| Characteristic | Static Forecast | Rolling Forecast |
| Frequency | Set up once a year, very few updates. | Regular updates (monthly/quarterly) according to schedule. |
| Flexibility | Inflexible, easily becomes outdated. | Highly adaptable, always reflecting the new context. |
| Scope | Usually linked to a fiscal year (e.g., forecast for Q3, Q4/2025). | Always maintain a fixed vision (e.g., the next 12 months, from December 2025 to November 2026). |
The role of rolling forecasts in FP&A and performance management.
In modern FP&A, rolling forecasts play the role of: continuous financial "radar" For the CFO, CEO, and Board of Directors.
- Data bridge: Connect Actuals (past data) – Budget (goals) – Forecast (future predictions) in a single view.
- The foundation of Planning: As a foundation for Continuity Planning (Continuous planning) Scenario Planning (Script planning), and Driver-Based Planning (Planning based on key variables).
- Measuring performance: Performance evaluation should be based not only on meeting budgets, but also on continuously adjusting forecasts to better reflect reality.
III. What are the structure and core components of a rolling forecast model?
Designing the model is the most important step. A good model should be simple, flexible, and driven by real-world business variables.
Forecast horizon
This involves deciding on the length of the forecast "time window": 12, 18, or 24 months.
- 12 months: Popular, flexible, and suitable for industries with short product/campaign cycles (FMCG, Retail, SaaS).
- 18-24 months: Suitable for long-cycle industries (Infrastructure, Real Estate, Large-scale Manufacturing) where Capex or R&D decisions need to be considered long-term.
This decision requires a balance between the need for foresight and the ability to make accurate predictions (the further into the future the prediction, the more difficult it is to be accurate).
Update frequency
The frequency of updates affects the workload and the timeliness of decisions.
- Monthly: Suitable for businesses that need tight control over cash flow and profits, or are in a phase of rapid growth/high volatility. Optimized when supported by an EPM platform.
- Quarterly: Suitable for businesses with low turnover or those that do not yet have an automated EPM system.
Each update needs to be Linked to the accounting closing schedule and executive meeting schedule (M-Review/Q-Review) To ensure that forecasts are used for immediate decision-making.
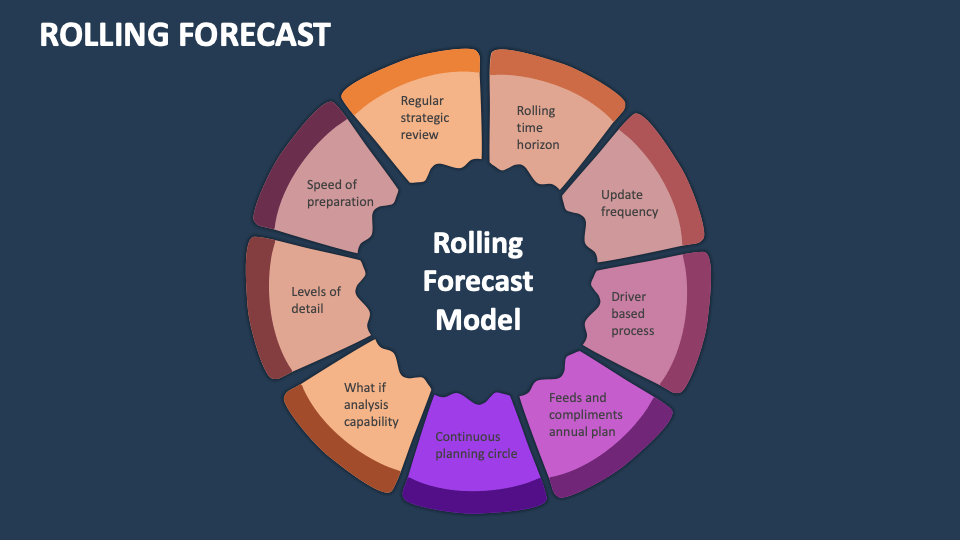
Key financial KPIs in rolling forecasts
The Rolling Forecast model should focus on the most critical KPIs, not on overly detailed forecasts like budgets. Core KPIs include:
- Revenue: By product, channel, region.
- Profit: Gross Margin, EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, and Depreciation), Profit Before Tax.
- Cash Flow: Operating Cash Flow, Ending Cash Position, and related indicators. Covenant Banking (if the business has bank loans).
- Expense: Capex (Capital Expenses), Opex (Operating Expenses), Headcount (Number of Personnel), Sales and Marketing Expenses.
Assumptions and driver-based forecasting
- Assumptions This forms the basis of all forecasts: revenue growth, cost ratios, exchange rates, interest rates, inflation, etc.
- Driver-based forecasting It is a forecasting method that uses key business variables (drivers) as a basis for prediction, rather than simply inputting detailed figures.
Benefit: This method reduces the level of "line-by-line manual input," instead FP&A focuses on managing and adjusting the data. Drivers truly drive financial results.This helps to improve the logic and scalability of the model and enhance the quality of dialogue with business units.
Scenario planning in rolling forecast
This is a key component for proactive leadership. Rolling Forecast allows for the parallel development of scenarios:
- Base case: Based on current market assumptions.
- Upside (Positive scenario): Higher revenue growth, more optimized costs.
- Downside (Negative Scenario): The negative impact of inflation/exchange rates/recession on revenue and costs.
FP&A only needs to adjust a few key drivers in each scenario, then assess the impact on P&L (Income Statement), Cash Flow, and Balance Sheet. This helps management prepare accordingly. "Options B and C" instead of just a single forecast number.
IV. The Rolling Forecast Implementation Process in Businesses
Implementing Rolling Forecast is a process-changing project, not just a financial undertaking.
Step 1 – Define objectives and scope
First, we need to answer the question: What is a rolling forecast used for?
- For example: Managing continuous cash flow, controlling gross profit by product line, or supporting growth strategies.
Next is scope: The entire corporation, individual Business Units (BUs), individual countries, or individual product lines. Start small and easily controllable (for example, forecast only P&L and Cash Flow for the largest BU) before expanding.
Step 2 – Design the driver-based model
As mentioned in section 11, this step involves selecting and standardizing the core drivers for Revenue, Expenses, Capex, and Headcount.
- Optimization: Reduce the number of detailed forecast lines but increase the logic based on the driver.
- Data source: Connect the driver to a specific data source (CRM for Sales Pipeline, ERP for Inventory, HRM for Headcount).
Step 3 – Connect actuals data
The accuracy of the Actuals is a crucial factor for Rolling Forecasts.
- Source: Actuals Retrieve Actuals from accounting systems, ERP, CRM, and expense management platforms like Bizzi.
- Standardization: Standardize account, unit, and product codes to Mount (Mapping) accurately with the forecast model.
- Timeliness: Ensure that each forecast period starts from the most recent, closed-end, or reconciled real number. Do not use "estimates". to reduce discrepancies.
Step 4 – Update the forecast periodically (rolling)
This is the core operational phase:
- Roll forward: Automatically remove the period that has passed from the horizon and add a new period at the end.
- Update Assumptions: Based on the actuals results and new market signals, the Assumptions and Drivers need to be adjusted (e.g., next month's growth rate, conversion rate, cost of goods sold).
Step 5 – Variance analysis
After each period, the FP&A needs to be compared: Actuals vs Budget vs Previous Forecast.
- Decomposition error: Analyze the discrepancies based on factors such as Volume (quantity), Price (selling price) Mix (product structure) Productivity (productivity).
- Identify the root cause: Identify the root cause in order to propose solutions. action (action), not just simply "recording discrepancies". For example: Revenue discrepancies due to decreased Volume (action: Marketing increased spending on the campaign), or due to a decrease in price.action: Sales should review the discount policy.
Step 6 – Adjust the plan, budget, and actions.
This is Rolling Forecast's ultimate goal: to turn insights into action.
- Adjust your financial plan: If the forecast indicates a cash flow deficit in the next six months, immediate adjustments to Capex, working capital, and the funding plan are necessary.
- Adjusting the strategy: If the forecast profit margin decreases, the cost structure, pricing plan, and product mix need to be reviewed.
- Action engagement: Integrate the Rolling Forecast directly into the action plan of each department (Sales, Marketing, Operations).
Rolling forecast workflow and departmental roles
Rolling forecasting is a job that requires collaboration across multiple departments:
- Sales and Marketing: Provide a sales pipeline forecast, campaign plan, and expenditure plan.
- Supply Chain and Operations: Provides Capacity (production capacity), Lead Time (delivery time), and production/inventory plans.
- HR: Headcount plan, compensation roadmap, and personnel costs.
- FP&A: Build models, gather data, analyze variance, and lead dialogue with businesses.
- CFO/CEO: Make decisions, validate scenarios, and determine course of action.
V. Application of Rolling Forecast in Financial and Cost Management
Rolling Forecast elevates financial management by... noted luxurious forecast and adjust.
Continuous Profit Management
Rolling Forecast allows you to track EBITDA, Gross Margin, and Net Profit continuously over the next 12–18 months. This helps:
- Early risk identification: Identify the downward trend in profit margins nine months before it becomes the Actuals, instead of waiting until the end of the year.
- Flexible adjustments: This creates space to adjust pricing strategies, optimize cost structures, or change the product mix in a timely manner.
Rolling cash flow forecast
This is one of the most important applications. Rolling Cash Flow Forecast helps predict cash inflows and outflows on a monthly/quarterly basis:
- Connecting P&L to the Balance Sheet: Connect the P&L forecast with Working Capital (AR, AP, Inventory) to get a comprehensive view of cash flow.
- Reduce risk: Reduce risk "Profits reported, but a lack of actual cash flow" due to poor management of accounts receivable/payable.
- Active capital plan: This allows the CFO to proactively plan fundraising, negotiate bank loans, or adjust the timing of Capex payments.
Agile budgeting
Rolling Forecast is used as input for mid-year budget updates (in-year budget updates). This helps shift the mindset from "fix budget" (fixed budget) to "budget + rolling view" (Budget included, with a rolling perspective).
It helps:
- Reduce the number of stressful and time-consuming negotiation cycles each year.
- Increase focus on execution by continuously adjusting spending targets to align with the latest revenue forecasts.
Financial risk management
Rolling Forecast, combined with Scenario Planning, allows for the implementation of... Stress Test (Endurance test).
- Impact assessment: Assess the impact of fluctuations in interest rates, exchange rates, or raw material prices on P&L and Cash Flow.
- Preparing for defensive decisions: If the Downside scenario indicates high risk, leaders can prepare defensive decisions such as: delaying the Capex payment schedule, restructuring debt, or optimizing operating costs early.
VI. Advantages, disadvantages, and conditions for successful Rolling Forecast
Rolling Forecast elevates financial management by... noted luxurious forecast and adjust.
Continuous Profit Management
Rolling Forecast allows you to track EBITDA, Gross Margin, and Net Profit continuously over the next 12–18 months. This helps:
- Early risk identification: Identify the downward trend in profit margins nine months before it becomes the Actuals, instead of waiting until the end of the year.
- Flexible adjustments: This creates space to adjust pricing strategies, optimize cost structures, or change the product mix in a timely manner.
Rolling cash flow forecast
This is one of the most important applications. Rolling Cash Flow Forecast helps predict cash inflows and outflows on a monthly/quarterly basis:
- Connecting P&L to the Balance Sheet: Connect the P&L forecast with Working Capital (AR, AP, Inventory) to get a comprehensive view of cash flow.
- Reduce risk: Reduce risk "Profits reported, but a lack of actual cash flow" due to poor management of accounts receivable/payable.
- Active capital plan: This allows the CFO to proactively plan fundraising, negotiate bank loans, or adjust the timing of Capex payments.
Agile budgeting
Rolling Forecast is used as input for mid-year budget updates (in-year budget updates). This helps shift the mindset from "fix budget" (fixed budget) to "budget + rolling view" (Budget included, with a rolling perspective).
It helps:
- Reduce the number of stressful and time-consuming negotiation cycles each year.
- Increase focus on execution by continuously adjusting spending targets to align with the latest revenue forecasts.
Financial risk management
Rolling Forecast, combined with Scenario Planning, allows for the implementation of... Stress Test (Endurance test).
- Impact assessment: Assess the impact of fluctuations in interest rates, exchange rates, or raw material prices on P&L and Cash Flow.
- Preparing for defensive decisions: If the Downside scenario indicates high risk, leaders can prepare defensive decisions such as: delaying the Capex payment schedule, restructuring debt, or optimizing operating costs early.
VII. What are EPM technologies and solutions that support rolling forecasting?
In reality, rolling forecasting is very difficult to succeed when relying solely on Excel and ERP systems.
The problem with creating rolling forecasts using pure Excel and ERP.
- The Actuals data is being retrieved slowly: It involves many steps: Export, Clean, and Import.
- Version control is difficult. Each business unit has its own file, making it difficult to consolidate and compare different forecast versions.
- It takes time to combine the numbers: Comparing Scenario and Variance Analysis is time-consuming, instead of focusing on the analysis itself.
EPM/FP&A Platform: The Role of Sactona (Bizzi Distribution)
The EPM (Enterprise Performance Management) platform is specifically designed to address the challenges of Rolling Forecast. SactonaThe powerful EPM platform (distributed in Vietnam by Bizzi) offers the following features:
- Centralized model: Allows for the design of a centralized driver-based forecast model, where all departments input data simultaneously.
- Automatic data connection: Connect directly to data from ERP systems, accounting systems, and expense management platforms such as Bizzi.
- Automatic winding: Automatically roll forward, keep the Horizon fixed, and save the version of each forecast for easy comparison of the current forecast with the previous forecast.
- Support for analysis: It supports visualization of Variance Analysis, Scenario Modeling, and provides a dashboard for CFO/CEO decision-making.
Bizzi Expense, Bizzi IPA + 3way are used as cost data sources for rolling forecasts.
The timeliness of the actuals data (especially in terms of cost) is a decisive factor in the quality of the forecast.
- Bizzi Expense: It helps track expenses by budget, department, and project in real time. When outsourcing, work, or marketing expenses arise, data is pushed to the financial system much sooner than with traditional processes.
- Bizzi IPA + 3way: Automatically process, reconcile, and account for input invoices.
This helps FP&A obtain cost actuals data. accurate and timely To update Assumptions in Rolling Forecast, instead of having to wait for the lengthy reconciliation and closing process.
Connecting Bizzi and Sactona in a modern FP&A architecture.
In modern FP&A architecture:
- Bizzi layer processing "Transactions and Documents" (Actual spending data).
- Sactona layer processing “Planning, Budgeting, Rolling Forecast, Scenario, Performance” (Planning data and analysis).
This combination creates a seamless chain from actual spending, processed automatically, to future planning and forecasting, enabling businesses to operate and manage financial performance continuously and effectively.
VIII. Frequently Asked Questions about Rolling Forecasts
- What is a rolling forecast in corporate finance? It is a continuous financial forecasting method that maintains a fixed view of the future (12-18-24 months), helping leaders make timely decisions.
- How often should rolling forecasts be updated? Monthly (if you have EPM) or quarterly (if you're just starting out or your business is relatively stable) is the most common frequency.
- Does rolling forecasting replace annual budgeting, or do they run in parallel? Rolling Forecast typically runs in parallel, acting as a “flexible forecasting tool.” The annual budget remains the “control target and spending limit.” However, Rolling Forecast can be used as input for mid-term annual budget updates (Agile Budgeting).
- Should small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) create rolling forecasts, and where should they start? Yes, you should start by forecasting P&L and Cash Flow for the next 12 months quarterly, focusing on 3-4 key drivers and using simple tools before investing in EPM.
- Which software effectively supports rolling forecasting in the context of Vietnamese businesses? EPM/FP&A platforms like Sactona (distributed by Bizzi) are the most effective solutions for automating processes, instead of using Excel.
- How does rolling forecasting work when integrated with EPM and Bizzi? Bizzi provides cost actuals that are processed automatically and promptly. EPM (Sactona) automatically retrieves these actuals, rolls up the forecast model, allows FP&A to adjust Assumptions/Drivers and run Scenarios, and then outputs the data to the dashboard for management.
IX. Conclusion
This article has explained in detail what Rolling Forecast is. Rolling Forecast It's not just a forecasting technique, but a flexible financial operating methods and proactive. It forces businesses to look beyond the current fiscal year, giving them ample time to adjust their strategies and resources.
In an uncertain economic environment, the ability to clearly see revenue, profits, and cash flow over the next 12–24 months is a vital competitive advantage.
When combined with a supporting technology platform:
- EPM platforms like Sacramento It helps automate scripting, script management, and analysis.
- Cost data platforms like Bizzi Provide Actuals clean and timely.
Rolling Forecast transformed from a “laborious Excel file” into a continuous financial performance management systemThis helps CFOs/CEOs make quick decisions based on the latest data.