Input invoices are important financial and accounting documents that help businesses calculate costs, deduct taxes and ensure transparency in all transactions. Good control of input invoices is the foundation for tax, financial and legal management.
Not only need to understand the nature of input invoices but also find a way to manage the huge amount of invoices effectively is also a headache for the Accounting and Finance department. Let's find the solution to this problem in the article below by Bizzi.
Overview of input invoices
Below is a complete and easy-to-understand overview of input invoices, helping you grasp the concept, role, classification and notes when using them:
What is input invoice?
Input invoice is the type of invoice that a business receives when purchasing goods, raw materials, or using services to serve the purpose of production, business, and maintaining the business's operations. It is a document proving the purchase of goods and services.
What is the role and meaning of input invoices??
Input invoices are the basis for accounting for expenses, tax deductions, and tax settlement with tax authorities; they are legal documents to prove the cost of purchasing goods and services of the enterprise.
Input invoices help businesses calculate business expenses production to make decisions on pricing, distribution, promotion, communication; control costs and manage finances transparently.
What are the documents that come with input invoices?
For an input invoice to be legally valid and serve accounting purposes, it must be accompanied by relevant documents:
- Contracts for the sale of goods, services, or fixed assets: Used to define the terms, rights, and obligations of the seller and buyer; an appendix is required if the contract does not list a detailed list of goods.
- Minutes of handover of goods, services, or fixed assets: Specify the time, place, quantity, quality, and delivery status.
- Receipt: Clearly state the origin, quantity, unit price, and total amount of goods, services, or fixed assets imported into the warehouse.
- Receipt, voucher, or non-cash payment voucher: Proof of payment and clearly state the amount, reason, and bank account.
- Contract liquidation minutes: Clearly state the time, results, and commitments of both parties related to the contract.
- Other documents: Transport contract, bill of lading, bill of lading, insurance contract, insurance certificate, documents proving the origin of goods (C/O, C/Q).

Distinguish between input invoices and output invoices
Input invoices and output invoices are two important types of invoices but have different roles and meanings in business operations and taxes of enterprises.
- Source: Input invoice is the invoice that the business receives when purchasing, and output invoice is the invoice that the business issues when selling.
- Tax implicationsInput invoices are the basis for accounting for costs, tax deductions, and input VAT settlement; output invoices are the basis for accounting for revenue, calculating taxes, and paying output VAT.
- Meaning to businessInput invoices are the basis for costs to make financial decisions; output invoices are the basis for determining revenue to evaluate business performance and plan strategies.
- Accompanying documents: The accompanying documents vary depending on the role of the buyer or seller.
Regulations on valid input invoices
In order for input invoices to be considered valid and legal, eligible for VAT deduction and included in deductible expenses when settling corporate income tax, enterprises need to comply with a number of mandatory regulations under current laws.
What is the mandatory content on input invoices?
According to Decree 123/2020/ND-CP, input invoices must have the following mandatory contents:
- Invoice name, invoice symbol, invoice template symbol, invoice number.
- Information about the name, address, and tax identification number of the seller and buyer.
- Invoice issue date/month/year.
- Name, unit, quantity, unit price, total amount of goods and services.
- Tax rate, tax amount, total payment, amount in words.
- Signature and seal of seller, signature of buyer (if any).
- Tax authority code (for Electronic invoice).
- Payment method (cash or bank transfer).
Time of input invoice issuance
The time for making and issuing input invoices must comply with the provisions of Clause 1 and Clause 2, Article 9 of Decree 123/2020/ND-CP:
- For the sale of goods: Is the time of transferring ownership or right to use goods to the buyer, regardless of whether the money has been collected or not.
- For service provision: Is the time when the service provision is completed, regardless of whether the payment has been collected or not. In case of payment collection before/during the service provision, the time of invoice issuance is the time of payment collection (except for some specific cases).
- For goods delivered multiple times or delivered by each project item: The time of invoice issuance corresponding to each delivery or handover.
What is an invalid input invoice?
Input invoices are considered invalid when they do not fully meet the required criteria regarding content, criteria or time of issuance.
- Requirements of a valid invoice: Must reflect the correct business, the content must not be edited/erased, the same type of indelible ink must be used, and the content on the copies must be consistent.
- Common errors: Missing required information, incorrect time of issue, no signature/stamp as prescribed, or incorrect format as prescribed. Invoices that do not fully contain required information may be subject to a fine of VND 4,000,000 to VND 8,000,000.

What are the legal issues and penalties associated with input invoices?
Legal issues and penalties related to input invoices often arise from the use of illegal invoices, false declarations, or violations of tax regulations. Below is a complete and clear summary of common legal risks and penalties that businesses need to pay special attention to:
What is the penalty for losing input invoices?
Enterprises that lose or damage input invoices may be subject to penalties according to the provisions of Clause 4, Article 26, Decree 125/2020/ND-CP (amended by Decree 102/2021/ND-CP):
- Warning penalty: For the act of losing, burning, or damaging an invoice that has been issued (except for the copy given to the customer) during use, has been declared and paid for tax, has documents proving the purchase and sale, and has mitigating circumstances; or the incorrect invoice has been deleted and the seller has issued a replacement invoice.
- Fine from 3,000,000 to 5,000,000 VND: For the act of losing, burning, or damaging an invoice that has been issued (copy given to the customer) during use, has been declared, and has paid taxes, has documents proving the purchase and sale, and has mitigating circumstances. In case the buyer loses the invoice, there must be a record of the incident between the seller and the buyer.
- Fine from 4,000,000 to 8,000,000 VND: For acts of losing, burning, or damaging issued but not yet created invoices; losing customer copies that have declared taxes but have no mitigating circumstances; losing invoices that have been created but not yet declared taxes.
- Fine from 5,000,000 to 10,000,000 VND: For the act of the buyer losing, burning, or damaging the input invoice during storage, except for the above cases.
- In case the third party loses the invoice: Any party transacting with a third party will be subject to penalties and must make a record of the incident.
Is there a penalty for issuing an output invoice without an input invoice?
According to the provisions of Decree 123/2020/ND-CP and related documents, enterprises unauthorized Issuing an output invoice without a corresponding input invoice. This is considered a violation of the law on the timing of invoice issuance.
- Consequences and penalties:
- Warning penalty: Invoicing is not done at the right time but does not lead to late tax payment and has mitigating circumstances.
- Fine from 3,000,000 to 5,000,000 VND: Invoicing at the wrong time but not leading to late tax payment (except in case of warning).
- Fine from 4,000,000 to 8,000,000 VND: Invoices are not issued at the correct time as prescribed by law (except in the above cases).
- Other risks: Unable to prove the origin of goods, not legalizing costs, increasing the amount of tax payable, may be subject to tax assessment or collection during inspection.
Is there a penalty for not declaring input invoices?
Declaring input invoices is the right of the enterprise, not a mandatory act.
- Affect: Enterprises will not be able to deduct input VAT, directly affecting the financial interests of the enterprise.
- Punishment: Failure to declare input invoices will not result in direct penalties unless there are signs of fraud or tax evasion. However, businesses must still fully store invoices to avoid penalties for losing invoices or tax evasion.
Manage and store input invoices effectively
Managing and storing input invoices is not only an accounting responsibility, but also helps protect businesses from tax and legal risks. With a clear process + suitable software, you can save a lot of time and effort when looking up or settling taxes.
How to check the validity of input invoices
To ensure validity, businesses can check input invoices in the following ways:
- Look up on the General Department of Taxation's invoice lookup page: Access the website http://tracuuhoadon.gdt.gov.vn/main.html, fill in information such as tax code, invoice symbol, invoice model number, invoice number, authentication code and click search.
- Use specialized website/software: Software such as iHOADON, MISA meInvoice, E-invoice have the feature of automatically checking the legal validity of electronic invoices.

What are the regulations for storing input invoices?
Input invoices must be preserved and stored according to the following regulations:
- Ensure safety, security, integrity, completeness, and no changes or deviations during storage.
- Store correctly and for the full period of time as prescribed by accounting law, minimum 10 years from the date of invoice.
- Electronic invoices must be stored electronically, accessible, usable, and have the ability to identify the origin/time of sending/receiving.
Traditional and limited methods of input invoice management
Accountants often use manual or semi-automated methods to manage input electronic invoices, but they have many limitations:
- Archive by email: Convenient for sorting and searching by sending date and supplier. However, not very professional, there is a risk of data loss when email is locked.
- Store on computer hard drive or cloud services (Google Drive, Dropbox): Easy to access and classify. The drawback is the risk of losing data when the computer crashes if not backed up, and the time consuming task of looking up each invoice one by one.
- Declaration on Excel: Convenient for statistics and lookup. But there is a risk of error in the process of manually entering data from invoices to Excel and from Excel to accounting software.
- Print out for storage: Helps avoid data loss when managing by email, but costs money in printing, storage, difficult to look up and check validity, still have to be accounted for manually.
- Image storage: Easy to implement and classify. However, database may be lost if storage device fails, management process is complicated and time consuming for large volume of invoices.
- Common disadvantages of manual management:
- Takes a long time: Manual data entry, classification, management, and checking reduce work efficiency.
- Difficulty in searching and explaining: Distributed data storage makes it difficult to find information when reporting or explaining taxes.
- Frequent errors: Manual data entry can easily lead to errors in data and information, causing tax penalties.
- Decentralized data: Leads to fragmented, inconsistent management, difficult for new staff to grasp.
- Difficult to summarize data for financial reporting: Data from many different sources makes checking and synthesizing reports complicated and prone to errors.
Applying technology solutions to manage input invoices
To optimize the input invoice management process, businesses are increasingly applying specialized software. Bizzi is a comprehensive cost control system and AI assistant for the finance and accounting department in automating the revenue and expenditure process.
Trusted by medium and large companies in many fields such as PNJ, GS25, MegaMarket, TIKI,... Bizzi provides a strict and modern cost management solution that has been researched and synthesized from the best practices of leading businesses:
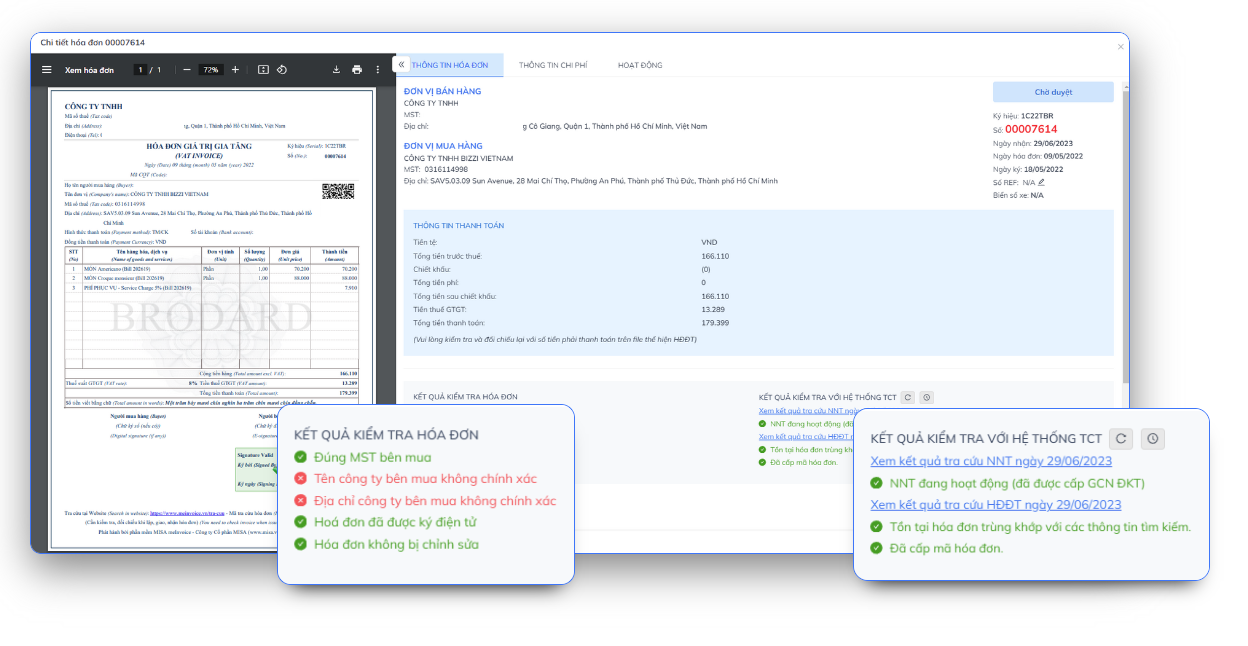
- Processing, reconciling and managing input invoices (IPA + 3way): Bizzi uses Bizzi Bot with RPA and AI technology to automatically upload, check and reconcile invoices. It automatically reconciles invoices with PO (purchase order) and GR (stock receipt) in real time to detect discrepancies.

- System helps verify valid suppliers by checking MST, operating status on the tax system. Automatically record and store input invoices with a storage period of 10 years. Warning of risky invoices from suppliers with unusual signs.

- Provide a separate email address for each business: Suppliers can send electronic invoices directly to the Bizzi system without manual operations.
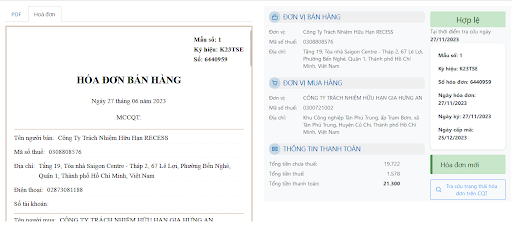
- Centralized storage – easy management: All electronic invoices are stored centrally on a single platform, with an intuitive list interface that helps users easily look up, track and control invoice status in real time.
- Automatically download original invoices from suppliers in PDF format from suppliers, guaranteed full information, include business logo, digital signature and necessary details.
- Extract data suitable for accounting software: The system allows exporting invoice data to Excel files in a format optimized for the accounting software that the business is using, helping to reduce data entry time and limit errors.
- Flexible configuration according to accounting needs: Bizzi is designed to be flexibly configured, easily customized according to each business's accounting processes and ERP system characteristics, ensuring quick deployment and smooth operation.
What are other frequently asked questions about input invoices?
Below is a summary of some questions related to input invoices:
Do businesses need input invoices?
Business households are not required to have input invoices in all cases (for example, if there are no sales activities). However, if there are transactions to purchase goods and services, they should have input invoices to record costs, prove the validity of the sales activities, serve as a basis for deducting VAT (if any), and serve as a basis when being inspected and settled by the tax authority.
How long is the input invoice declared?
Input invoices need to be stored for a minimum period of time. 10 years from the date of invoice, as prescribed by the law on accounting and invoices. This ensures that businesses can provide documents when necessary for tax inspection, reconciliation or explanation.
Conclude
Input invoices, if not managed properly, can cause serious damage to finances, taxes and business reputation, and even lead to criminal liability. Therefore, it is necessary to establish a strict invoice control process and continuously update legal regulations.
Hopefully through this article, readers will better understand the concept of input invoices, thereby drawing out optimal and effective methods of processing and managing input invoices. To receive advice and try a demo of Bizzi's solution, click to register here: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/