In the era of digital business growth, the amount of data - documents - transactions generated every day increases exponentially. This puts departments such as accounting, human resources, and operations under constant pressure to process information quickly, accurately, and consistently.
Automation is therefore no longer an “option”, but has become the operating standard of modern businesses.
Let's learn about Automation with Bizzi in this article!
“Automation” is no longer an option, but the standard of modern business
In the context of businesses entering the stage of accelerating digital transformation, the need to search for keywords “What is automation” increased dramatically as most organizations began to see the limits of manual operations. Each month, departments such as finance - accounting, human resources, and operations spend hundreds of hours entering, checking, approving, and reconciling documents.
As the size of the business increases, the number of documents also increases, leading to more errors, delayed approvals and untimely reporting. These manual processes create major operational bottlenecks, reducing growth and financial transparency. Therefore, more and more businesses are turning to automation as a mandatory solution to save 30-60% in operating costs and shorten work processing time.
Because of this, users began to delve deeper into “What is automation”: they want to know the exact definition, the types of automation that exist, the real benefits that automation brings, and which tools can be deployed quickly and at a reasonable cost. A large group of people are particularly interested in Finance Automation, as this is the area that has the most obvious impact on costs, cash flow and operating performance.
This article is built with three main goals in mind:
(1) Clearly and easily explain “What is Automation?” in a way that is suitable for non-tech people.
(2) Clarify the common types of automation that businesses are applying in practice.
(3) Analyze each specific application in operation, especially finance - accounting - costs

What is Automation?
In its most basic definition, Automation is the use of technology to perform repetitive processes and tasks that were previously handled manually by humans – with the goal of reducing time, reducing errors and increasing operational efficiency. This is not a passing trend, but the core foundation that helps businesses move towards a smart operating model.
1. Short and easy to understand definition
Automation is simply let machines do things humans don't need to do, especially repetitive tasks such as data entry, reconciliation, sending emails, and summarizing reports. What businesses get is faster processing speed, higher accuracy, and the ability to expand operations regardless of the number of employees.
2. Understand the true nature of Automation
One of the biggest misconceptions is that “automation will replace humans”. In fact, automation no replacement, but human support Work faster, smarter, to focus on strategic work.
Automation takes place in 3 levels:
- Task Automation: Automate small, repetitive tasks
For example: Excel data entry, email notification, create advance payment voucher. - Process Automation: Automate a multi-step process
For example: approve expenses, process input invoices, generate debt reports. - End-to-end Automation: Automate the entire process chain
For example: from purchase request → receiving goods → comparing PO/GR/Invoice → recording costs → financial reporting.
The more mature a business becomes in terms of data and processes, the more end-to-end automation becomes.
3. Distinguish between Automation – RPA – AI (to avoid using the wrong concept)
Although often used interchangeably, automation, RPA, and AI are not the same thing. The following table helps you visualize clearly:
| Concept | Describe | Key Differences |
| Automation | Automate tasks with fixed processes | Rule-based |
| RPA (Robotic Process Automation) | Software robot simulates user operations | No programming required, simulates hand movements |
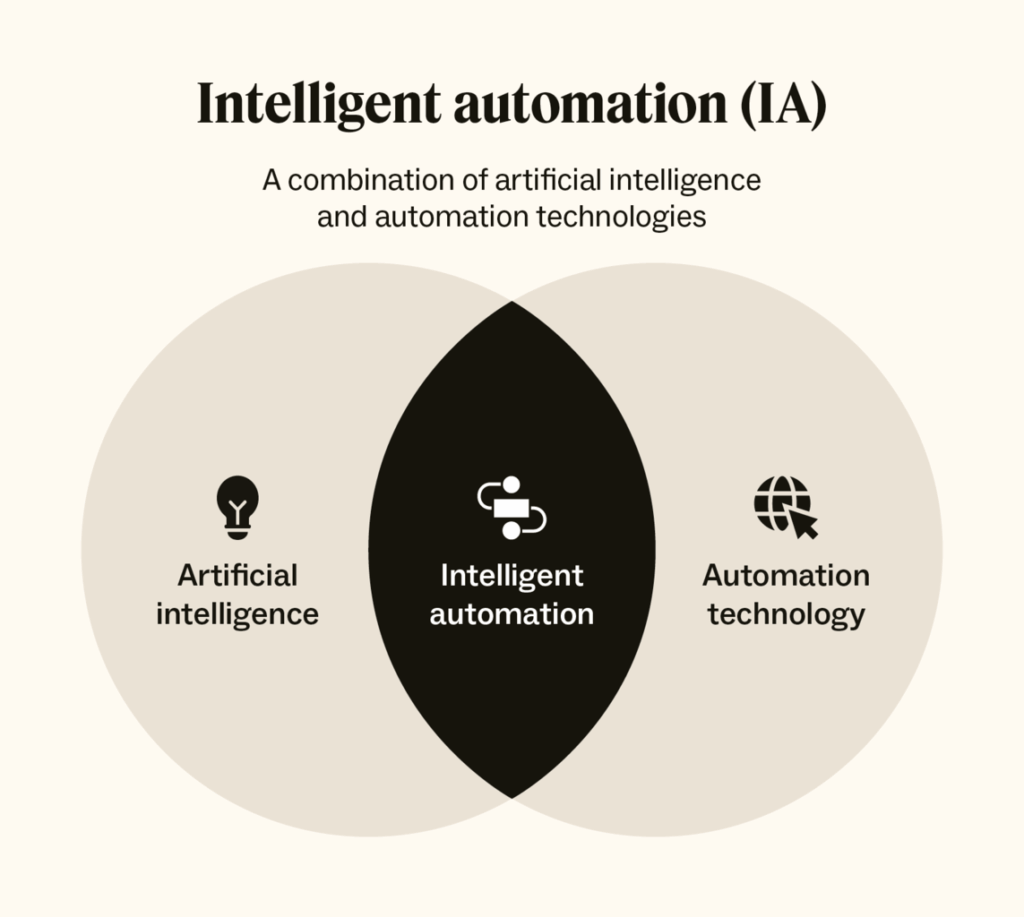
| Intelligent Automation (IA) | RPA + AI + ML to “understand” data and make decisions | Ability to learn and adapt |
| Hyperautomation | Combine multiple technologies for complete automation | Highest level of automation |
Understanding the differences helps businesses choose the right solution instead of making the wrong investments or buying technology beyond their needs.
- History and development trends of Automation
Automation is not new; it has been around for nearly a century:
- 1940s: Automation appears in industrial production.
- 2000s: Spread to IT, office, business services.
- 2020s: Exploding thanks to the combination of Cloud – AI – RPA – Low-code.
- 2024-2027: Gartner forecasts “90% businesses will use at least one automation platform”.
The difference of the current stage is that automation no longer only appears in production, but has become the operating platform in every department: finance - human resources - marketing - supply chain - customer care.
5 popular types of Automation in businesses
Once you understand “what is automation,” it’s important to understand what automation options are available to businesses. Here are the five most common automation groups, focusing on office, operations, and financial environments – not including industrial automation.
1. Business Process Automation (BPA)
Business Process Automation is a form of comprehensive automation of a multi-step, multi-person, and highly repetitive internal process. Businesses use BPA to reduce costs, shorten processing times, and eliminate manual errors in core processes such as accounting, expense approval, invoice reconciliation, and reporting.
A typical example in the Vietnamese market is Bizzi – a financial process automation platform that helps businesses process invoices, reconcile PO-GR-Invoice and approve expenses in real time.
2. Office Automation
Office Automation focuses on automating administrative and office tasks such as sending emails, creating documents, managing forms, scheduling meetings, or storing data. Toolkits such as Google Workspace, Microsoft 365, Notion, or Zoho help businesses standardize documents, synchronize departmental data, and reduce time spent on paperwork.
3. Workflow Automation
Workflow Automation allows businesses to design standard process flows, in which each step (submit - approve - process - summarize - report) is automatically triggered based on rules. This type of automation is very suitable for businesses that are operating many inter-departmental processes such as: purchasing, advance payment, contract approval, expense request... Low-code platforms such as Power Automate, Workato, Make or Zapier help to deploy quickly without the need for a large IT team.
4. RPA – Robotic Process Automation
RPA is a “software robot” that simulates human operations on a computer: click – copy – paste – enter data – download files. RPA is suitable for processes with large amounts of data, clear structures and little change. Large enterprises often use RPA to automate ERP data entry, bank data reconciliation, document verification or report standardization.
5. AI Automation / Intelligent Automation
This is a smarter level of automation, combining RPA and AI to process unstructured data such as PDF invoices, emails, images or text. AI Automation helps the system "understand - learn - recognize" to automatically classify documents, extract data, identify fraud or make decision suggestions. This is an important foundation for businesses that want to build a smart operating system.
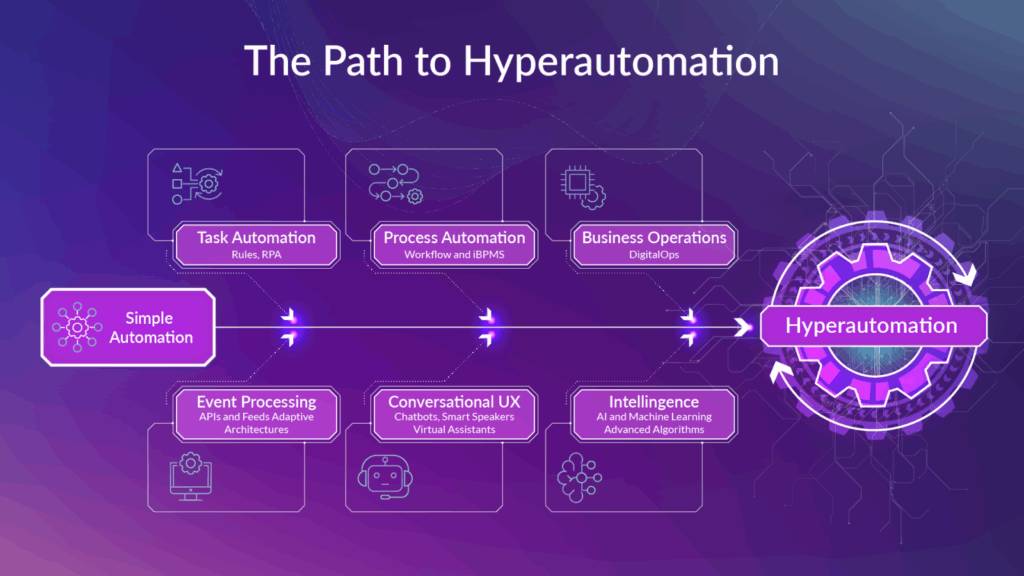
6. Hyperautomation – The highest level of automation
Hyperautomation is a trend defined by Gartner: combining many technologies such as AI, RPA, BPA, workflow automation and API integration to create a business that operates almost entirely automatically. The goal is to create a “digital workforce” – a virtual force that works 24/7 and connects all processes from operations – finance – customers.
Practical applications of Automation in business
Below are detailed applications by department – how businesses are applying automation every day to optimize operations.
1. Automation in finance and accounting (Finance Automation)
This is the segment with the strongest demand for automation because of the large volume of data, high error rate and requirement for financial transparency.
Businesses can automate:
- Processing input invoices: The system automatically downloads invoices, reads data, checks validity, and compares PO – GR – Invoice.
- Approve expenses: automatically suggest remaining budget, route requests to the correct approval level.
- Debt & Cash Flow Management: automatically aggregate costs by department, project, warn of budget overruns and warn of due debts.
The strongest point is the model real-time finance: all costs, cash flow, invoices are updated instantly → helping CFOs make decisions earlier instead of waiting for the reporting period.
2. Automation in human resources (HR Automation)
HR departments have a huge number of repetitive tasks. Automation helps:
- Automatically filter CVs and send email responses to candidates.
- Automatically generate contracts and enter personnel data.
- Automatically check attendance, approve leave, calculate salary.
→ Reduce administrative burden and improve employee experience.
3. Automation in operations & supply chain
Automation helps synchronize data between warehouse - accounting - purchasing - sales:
- Auto update inventory.
- Automatically create import/export vouchers based on orders.
- Automatically circulate documents to relevant departments.
This reduces the risk of data corruption and speeds up delivery.
4. Automation in marketing & sales
Automation helps businesses reach customers smarter:
- Email automation, multi-channel remarketing.
- Send personalized messages based on behavior.
- Chatbot supports customers 24/7.
- Combine marketing spend data to measure ROI by campaign.
Automation not only helps marketing save time but also improves conversion efficiency.
5. Automation in customer care
Businesses are applying:
- Chatbot takes common questions.
- Automatically classify tickets and assign them to the correct department.
- Automatically generate SLA reports to monitor service quality.
Thanks to that, businesses maintain stable services, regardless of employee working hours.
Benefits of Automation – from data and reality
When businesses ask “what is automation”, the next question is always: How does automation clearly benefit? Beyond just saving time, automation creates a dramatic shift in cost, accuracy, and speed. Here are the two most important benefit groups – quantitative (measurable) and strategic (long-term impact).
1. Quantitative benefits (can be clearly measured)
The numbers below are compiled from market benchmarks and actual data from businesses that have implemented self-service automation:
| Category | Before automation | After automation |
| Invoice processing time | 3-5 days | < 4 hours |
| Data entry error rate | 10-15% | < 1% |
| Monthly accounting operating costs | 100% baseline | Discount 30-60% |
| Expense approval speed | Slow, via email | Real-time on the system |
These numbers prove that automation not only “reduces work” but also completely solves bottlenecks – from data entry to approval, reconciliation and reporting.
2. Strategic benefits (long-term impact)
In addition to direct measurements, automation also creates a series of strategic benefits that help businesses improve operational capacity:
- Reduce costs – increase productivity: Human resources reduce time doing repetitive tasks, focus on analysis, decision making, and strategy optimization.
- Increased financial transparency – audit support: All transactions are tracked and automatically reconciled → reducing fraud and standardizing data according to accounting standards.
- Increased scalability: When a business opens more branches or doubles sales, the automation system still handles the volume of data without requiring a corresponding increase in the number of employees.
- Creating a “digital workforce”: The system works 24/7, no breaks, no errors, no overload.
This is the key value for businesses to enter the intelligent operations phase.
Challenges & risks when implementing automation
While automation offers great benefits, businesses can still run into risks if implemented incorrectly. Here are some common risks – their causes – and their solutions.
| Risk | Reason | Solution |
| High initial investment cost | Businesses don't evaluate ROI, start with projects that are too big. | Start small (pilot), choose processes that are easy to measure effectively: invoices, expense approvals, data reconciliation. |
| Difficult to integrate legacy systems | Old, closed, difficult to connect ERP/CRM. | Choose a platform with open APIs that can integrate with many systems – like Bizzi, Make, Workato. |
| Changing HR habits | Fear of being "replaced" | Training, internal communication, and automation clarification help HR… reduce work, not eliminate jobs. |
| Data Security | Poor data governance, misaligned sharing of authority. | Choose a platform that meets ISO 27001 security standards and has strict role-based authorization. |
| Discrete Automation | Automate piecemeal, without an overall roadmap. | Build an enterprise-wide automation strategy (Enterprise Automation Roadmap). |
Automation & Digital Transformation
Automation does not stand alone – it is an important layer in Digital Transformation. Understanding this relationship helps businesses deploy in the right order, avoiding waste.
1. Automation is the second layer in the digital transformation roadmap
- Digitization: Convert paper documents → PDF files, Excel, digital data.
- Automation: The system automatically processes data and the operating process does not require manual human processing.
- Intelligence (smart optimization): Data is analyzed, forecasted, and decisions are suggested using AI.
→ Automation is the transition from “having data” → “data is processed automatically”.
2. Difference between Automation and AI
- WHO make data-driven decisions
- Automation enforce that decision
- Intelligent Automation = AI + RPA + Workflow → the system makes decisions and executes itself
3. The role of RPA & Automation in digital strategy
RPA and automation help businesses:
- Retain the old system while increasing operational capacity
- Automate critical processes without replacing ERP
- Cost optimization in the digital transformation phase
Automation is the “bridge” between old infrastructure and future smart operating systems.
Popular automation tools & platforms
Below are the automation tools most used by Vietnamese and international businesses – divided by functional groups so you can choose the right one for your needs.
| Tools | Group | Main features | Fit |
| UiPath, Blue Prism, Automation Anywhere | RPA | Handling large, complex processes | Large corporations |
| Power Automate, Workato, Make, Zapier | Workflow / BPA | Easy to use, cross-platform integration | SMEs, Startups |
| HubSpot, ActiveCampaign | Marketing Automation | Email, CRM, nurturing | Marketing Team |
| Bizzi Automation | Finance Automation | Financial and accounting automation: invoices, expenses, debts | Vietnamese businesses |
Bizzi – A Prime Example of Finance Process Automation
Bizzi Automation offers comprehensive financial process automation:
- Automatically download and reconcile invoices with PO/GR
- Multi-level spending approval, budget transparency
- Over budget warning – debt due warning
- Support standardization of financial processes according to auditing standards
- Flexible integration with ERP/Accounting
Bizzi helps Vietnamese businesses move towards the model Finance Automation international standards at optimal cost.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is Automation?
Automation is the use of technology to automatically perform repetitive tasks, reducing time and errors.
How is Automation different from AI and RPA?
- Automation: automate work according to rules
- RPA: robots simulate human operations
- AI: helps automation become smarter, able to read and understand data
Can small businesses use automation?
Absolutely. Low-code platforms like Bizzi, Make, Zapier help SMEs deploy quickly and at low cost.
Where to start automation?
Let's start with the process that generates the most cost and is easiest to measure ROI:
→ process invoices, approve expenses, reconcile debts.
Automation not only saves money, but also redefines how businesses operate.
In the context of businesses having to expand rapidly while still ensuring cost control, automation is no longer an upgrade option – but a mandatory operating platform. Automation helps businesses reduce manual processing costs, eliminate operational errors and increase response speed throughout the entire financial – accounting – operations cycle. This is also the first step to building a transparent, unified and scalable data system when businesses enter the growth phase.
The article cover has provided full information about what automation is to help you understand the benefits and applications of automation. Not only does it bring short-term benefits, automation is an important piece in Finance Transformation and Digital Transformation. When data is digitized and automated, businesses can move from a “manual reporting” model to “real-time data-driven decision-making.” This gives CFOs, CEOs, and management teams the confidence to make strategies based on accurate insights instead of gut feelings.
“Automation does not replace humans – it frees them from repetitive tasks to focus on analysis, innovation and strategy. And Bizzi is the clearest example of how automation is changing the finance department of Vietnamese enterprises: faster, more transparent and more efficient.”
👉 Explore Bizzi Automation – Solution to automate financial processes, approve spending and control budgets in real time, suitable for Vietnamese businesses in all stages of growth: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/


