Cost accounting is a basic and special step in accounting. If you do not understand the nature of cost accounting, it will easily affect the accuracy of financial reports, distort management information, affect operational decisions and even lead to legal violations and tax risks.
The following article by Bizzi will provide a comprehensive view of the cost accounting process and how to control costs in a business.
What is cost accounting? The foundation of cost accounting
Cost accounting is the process of collecting, recording, classifying and summarizing expenses incurred in the production and business activities of an enterprise, in accordance with current accounting regulations. This accounting helps to fully and accurately reflect costs to:
- Calculate the cost of products and services
- Business performance evaluation
Here are some basic concepts related to cost accounting, which are useful if you are preparing training materials, writing an accounting blog, or clarifying financial management processes:
- Cost: Is the total amount of resource expenditure (money, raw materials, labor, services, etc.) that a business spends to achieve a specific goal (product production, service provision, sales activities, management, etc.).
- Cost Classification:
By constituent elements: raw material costs, labor costs, outsourced service costs, etc.
By function: production costs, sales costs, business management costs
According to the relationship with output: fixed costs, variable costs, mixed costs
- Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): Is the total direct cost of producing a product or completing a service. Cost is the final result of the production cost accounting process.
- Cost norms: Is a standard cost level established for a unit of product/service to serve the purpose of control and comparison with actual costs.
- Direct and indirect costs
Direct costs: Directly associated with a product, service, or project (such as raw materials, direct labor)
Indirect costs: Cannot be directly attributed, need to be allocated (such as electricity, machine maintenance, ...)
- Accounting price: Product and material prices are calculated by the business. (Contact: Product prices include expenses).
- Accounting voucher: A form that records details of transactions (including expense transactions).
- Accounting date: Date of recording, statistics and calculation of cost transactions.
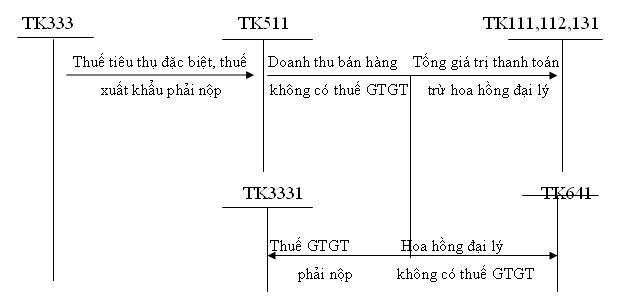
Classification of basic accounting types
Below is a classification of basic accounting types, divided by operations - statistics - accounting, to help you understand the role and method of recording economic - financial information in the enterprise:
| Accounting type | Concept | Characteristic | For example |
| Operational Accounting / Operational Recording | It is a form of primary, regular, quick accounting that directly records economic and technical operations during production and business activities. | Continuous, daily recording
No absolute accuracy required
Serve quick management, such as tracking raw materials, output, labor, etc. |
Track daily inventory, worker hours, volume of raw materials used, etc. |
| Statistical Accounting / Statistics Recording | It is a form of collecting, processing, and analyzing quantitative and qualitative indicators of socio-economic phenomena arising on a large scale in a certain period. | Recorded by synthesis and analysis
Use average, ratio, chart tools
Serves trend analysis, performance evaluation, macro decision making |
Labor productivity statistics, average material consumption, cost-to-revenue ratio, consumption trends by industry... |
| Financial & Managerial Accounting | It is a system for collecting, processing and providing financial and economic information in currency, according to accounting standards, serving financial reporting and business management. | Financial accounting: Record and reflect transactions that affect assets, liabilities, capital, revenue, and expenses. → Serving external parties: shareholders, banks, tax authorities... Managerial accounting: Cost analysis, budgeting, pricing to support internal management and operations. |
Financial accounting: Recording sales revenue, shipping costs, asset depreciation
Management accounting: Monthly production cost planning, break-even point analysis, etc. |
What are the characteristics of cost accounting?
Below are the basic characteristics of cost accounting in business - extremely important to understand the correct role, implementation and application in financial management:
Mandatory and compliant with accounting standards
- Cost accounting must comply with current accounting principles and regimes issued by the Ministry of Finance (for example: Circular 200/2014/TT-BTC or Circular 133/2016/TT-BTC).
- This is a mandatory activity for all businesses, to ensure transparency, accuracy and legality.
Expenses are recorded on an accrual basis.
- This means that costs are recorded when they are incurred, regardless of when the money is actually spent.
- For example, when a business receives advertising services in April, the expense is recorded in April, even though it is paid in May.
Recorded in currency
- Although costs may arise from materials, labor or services, when accounting, all are converted and recorded in monetary value (VND or accepted foreign currency).
Costs are classified according to several criteria for analysis purposes:
- By element: raw materials, labor, depreciation, outsourced services, other costs
- By purpose of use: production costs, sales costs, management costs
- By nature: fixed costs, variable costs, direct costs, indirect costs
Is the basis for cost calculation, budget control and decision making.
- Cost accounting helps determine the cost of products and services, serving the purpose of building selling prices and profit planning.
- Helps managers track actual costs against budget, make decisions to adjust or optimize cash flow.
Require valid documents to ensure legality
- All expenses when accounting must have full and valid accounting documents: invoices, payment vouchers, contracts, handover and liquidation minutes, etc.
- This ensures that costs are accepted when settling taxes, avoiding audit risks.
Accounting method
Cost accounting is the way businesses record, classify and track production and business costs. Choosing the right method will help businesses calculate costs accurately and control costs more effectively. Below are the common methods:
| Method | Characteristic | Advantage | Disadvantages |
| Direct costing method | Only include variable costs (costs that vary with output) in product cost. Fixed costs are not allocated to products but recorded separately in the period. |
Easy to control costs according to output fluctuations.
Suitable for businesses that need to analyze profits by product line. |
Does not fully reflect actual costs, especially fixed costs. |
| Full costing/Absorption costing | Include both fixed and variable costs in product cost. | Indicate full cost – required for selling price determination. Used in standard financial reporting. |
It is difficult to determine the real profit per product if the fixed costs are large. |
| Standard costing | Apply cost norms (materials, labor, production costs) to calculate the cost, then compare with reality. |
Helps businesses control costs and analyze variances easily.
Very suitable for mass production, processing industry. |
If the deviation is large, it may cause errors in the report. |
| Job order costing | If the deviation is large, it may cause errors in the report. | Very suitable for businesses that work on orders and do not produce in bulk (printing, interior design, construction, etc.). |
It is time consuming to track each order separately.
|
| Process costing | For continuous production, repetitive processes (eg food, chemicals). Calculate average cost by production stage. |
Suitable for mass production, helps simplify accounting.
|
No details on individual products.
|
Basic steps to cost accounting
Below are 6 basic steps to cost accounting in business - applicable to most types of business, especially important for financial accounting and management accounting:
- Collect expense documents: Purchase invoices, pay slips, service bills, etc.
- Identify cost objects: Costs related to which product, department, or activity.
- Identify the relevant expense accounts: Use the accounting system to record expenses.
- Record expenses in accounting books: Use accounting software or manual bookkeeping.
- Cost classification and synthesis: By cost element, cost item, cost department.
- Prepare expense report: Cost sheet, production cost report, etc.
- Cost analysis: Compare actual costs with plans, find out the causes of cost fluctuations.

Why do businesses need to perform cost accounting?
If you are working for a small business, startup, or scale up, starting to do proper accounting as soon as possible will help save a lot of risks and costs later. Businesses need to do cost accounting for the following extremely important reasons:
Effective cost control
- Helps businesses know what money has been spent on, where it is wasted, and from there have a basis for reduction and optimization.
- Avoid overspending and uncontrolled budget.
Make accurate business decisions
- When knowing clearly the costs of production - operation - marketing..., businesses can calculate: Product cost, Profit, Break-even point.
- From there, make decisions such as: whether to increase prices, cut any parts, invest more in where...
Financial planning – budget forecasting
- Cost accounting is important input data for building: Annual/quarterly financial plans, Product investment and development plans, Cash flow management

Calculate the correct cost of products/services
- If costs are not properly and sufficiently accounted for, businesses can easily: Sell at a loss without knowing it, and price incorrectly, causing products to lose competitiveness.
Meet legal and tax requirements
- Prepare financial statements in accordance with regulations
- Calculate and declare taxes accurately
- Avoid legal risks and tax penalties due to errors or fraud
Increase transparency and professionalism
- For Investors: They need to know what operating costs are to evaluate efficiency and profit potential.
- For Banks: When borrowing capital, banks will look at financial statements with clear accounting.
Bizzi – Comprehensive cost management solution for modern businesses
Bizzi Expense is not just a cost management tool, but a financial digital transformation platform that helps businesses control - optimize - make transparent the entire spending process. With outstanding advantages compared to other solutions on the market, Bizzi brings clear practical value:
Smart budget management – timely cost alerts
- Create flexible budget plans by year, department or specific project.
- Automatically reconcile incurred costs with established budgets, ensuring they do not exceed limits.
- Over budget warning immediately when: Create or approve spending requests – Submit expense report
- Intuitive budget dashboard helps track costs by multiple criteria: categories, employees, departments, projects…
Digital transformation of payment request process
- Completely replace manual paper documents, saving time and manpower.
- Quickly and accurately process all payment requests with just a few clicks.
- Data is securely stored, easy to look up and audit at any time.
Comprehensive management of all types of expenses
- The system supports all types of costs incurred: Business (airfare, hotel, meals), Purchasing (equipment, raw materials, stationery), Hospitality (Food, entertainment, gifts)
- Businesses can: Clear cost allocation by project, department, and personnel; Set up separate approval processes for each expense type
Automatically collect & aggregate cost data
- Automatically extract information from electronic invoices and receipts – reduce errors and increase processing speed.
- Aggregate data from various sources: Email, Mobile Apps, Accounting Software
- Helps businesses gain a comprehensive understanding of spending at all levels.
Support e-invoices & receipts – legal compliance
- The system allows simultaneous collection & storage of electronic invoices and paper receipts
- Automatically check invoice validity, reduce tax risks
- Fully comply with regulations on cost document management according to Vietnamese legal standards.
Conclude
Summary: Cost accounting is the basis for calculating product and service costs; it is the foundation for determining selling prices, profits, and market competition. Understanding what cost accounting is as well as knowing the correct cost accounting method will help businesses closely monitor spending, detect unreasonable spending, and thereby adjust the budget effectively.
In the process of operating and managing business costs, if we simply use traditional methods such as bookkeeping, Excel, etc., it will be difficult for accountants to control large amounts of paperwork and data.
Bizzi is proud to be the leading provider of comprehensive cost management solutions, helping Vietnamese businesses improve operational efficiency and optimize profits. With the ability to automate - flexibly - standardize comprehensively, Bizzi not only helps businesses control costs tightly but is also a powerful assistant in the journey of financial digitization, improving operational efficiency and long-term profits.
- Link to register for a trial of Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/


