Ineffective debt management can cause many serious risks for businesses, directly affecting cash flow, reputation and long-term survival. Therefore, it is necessary to clearly understand what debt is and its nature in order to come up with appropriate management plans.
In this article, Bizzi will provide detailed information about the concept of debt so that managers have a clearer perspective on this concept in business.
What is the concept of Debt?
Definition of debt
Accounts receivable is the term used to describe the amounts receivable and payable arising from a business's operations. In other words, it is the amount of money that a business still has to collect from customers or pay to suppliers and partners at a given point in time.
Debt arises when there is a transaction of buying and selling, exchanging goods, services or financial obligations that are not paid or not fully paid at the time of the transaction, and is transferred to the next payment period.
Accounts receivable typically refers to short-term debts, expected to be paid within one year. Accounts receivable can be between businesses, individuals, or individuals.

Distinguish between Public Debt and Public Debt
Debt and public debt are two completely different concepts, belonging to two different fields (enterprises and the state). Debt is related to financial relationships in business operations (receivables, payables). Meanwhile, public debt is the total amount of money that the government borrows from domestic and foreign sources, which can affect the national economy if it exceeds the safety threshold.
| Criteria | Debt/Receivables in Business | Public Debt |
| Subject | Enterprises, economic organizations | State, central or local government |
| Nature | Receivables or payables to partners (customers, suppliers, etc.) | Loans that the State borrows for public spending |
| Purpose of origin | Businesses that have not yet paid, advanced, debited… | The government borrows to invest in infrastructure, pay off debt, and balance the budget. |
| Scope of management | Business accounting, business financial reporting | Ministry of Finance, Central Bank, National Assembly supervision |
What are the English terms related to debt?
- Receivable: Accounts receivable
- To pay debt: Debt to pay
- Accounting liabilities: Accounting liabilities
- Debt report: Debt report
- Debt confirmation: Debt confirmation
- Outstanding debt: Overdue debt
- Clearing debt: Debt offset
- Past due: Past due
- Aging report: Debt aging report
- Write-off: Write off debt
- Bad debt: Bad debt
- Debt collection: Debt collection
- Debt accounting: Debt accounting
- Debt comparison: Debt comparison
Common types of debt
Accounts receivable are usually divided into two main groups including Accounts receivable and Accounts payable.
Accounts receivable
Accounts receivable is the amount of money a business has not yet received from customers or partners after providing goods, products, or services. This item determines the business's rights to a sum of money, goods, or services that will be received in the future. Accountants need to closely monitor to collect on time.
Examples of accounts receivable:
- Sales of goods, products, and service revenue not yet collected.
- Financial investment.
- Internal collections, advances.
- Collect compensation, deduct employee salary due to loss or damage to goods.
Accounts Payable
Accounts payable are amounts that a business has not yet paid to suppliers or other parties involved in its business operations. These are current obligations of a business arising from past transactions or events.
Accountants need to regularly monitor, supervise, and reconcile to make payments on time, increasing credibility.
Examples of accounts payable:
- Payables to suppliers of tools, equipment, supplies, raw materials, services, and goods that have not been paid.
- Internal payables.
- Amount payable to employees (salaries, benefits).
- Amount payable to the state (tax).
- Cost to pay.
- Payable according to construction contract progress.
What are other related concepts related to debt?
Offsetting (Offset/Offset): Transaction between entities that are both buyers and sellers, paying by deducting each other's debts.
Closing debt: Accountants update, summarize, compare debt data between actual contracts/transactions and books, and check with related subjects.
What is the reason for the debt?
Accounts receivable arise from purchases, sales, payments, advances, or other financial obligations incurred during the course of a business's operations. Here are some common reasons why accounts receivable arise:
Unpaid sales transactions:
- Purchase on credit from suppliers.
- Sales on credit to customers, agents, and collaborators.
- Use the service and be allowed to pay in installments (eg shipping fees, COD collection fees for online shops).
Internal financial management is not tight:
- Lack of close monitoring of income and expenditure.
- There is no specific debt collection plan.

Changes from external factors:
- Market fluctuations or customers experiencing financial difficulties affect their ability to pay.
Other exceptional transactions:
- Overpayment to suppliers results in receivables.
- Received advance payment from customer, so it is recorded that must be returned to customer if not enough goods/services are provided
In short, accounts receivable mainly arise due to the time difference between delivery – receipt of goods – provision of services and payment. Therefore, closely monitoring accounts receivable will help businesses control cash flow, avoid loss and ensure business reputation.
What is the importance of accounts receivable in business?
Effective debt management plays a vital role for businesses. Here are the specific roles of debt:
Reflects financial health and operating performance:
- Debt is a key indicator of a company's financial health and operating performance.
- Accounts receivable analysis allows for assessing debt collection, cash flow forecasting, and evaluating customer and supplier quality.
- Provides a complete picture of working capital management and ability to meet financial obligations.
Optimize cash flow and financial flexibility:
- Allows businesses to use cash flexibly, delaying payments to suppliers to use capital for other purposes.
- Helps reduce initial financial burden and maintain positive cash flow.
- Accounts receivable can be converted into cash through specific financial instruments.
- Effective management helps maintain a stable cash flow and avoid financial shortages.
Support business expansion:
- Allows businesses to increase the size and scale of their business without using all of their equity.
- Create investment opportunities in new operations, purchases, facility expansion, product development.
- Flexible payment terms are helpful in attracting new customers and retaining old ones.
Risk management and relationship building:
- Help businesses manage cash flow effectively and proactively collect debts.
- Minimize financial risks such as insolvency, loss of reputation, bankruptcy.
- Contribute to building positive relationships with customers and suppliers.

What is the debt settlement process? Detailed instructions
The debt handling process is a series of steps that a business takes to record, monitor, reconcile, collect or pay receivables and payables. The goal is to ensure that debts are managed closely, on time, transparently and effectively.
General procedure
- Step 1: Update information and segment objects (customers/suppliers).
- Step 2: Record, control and notify periodic debt.
- Step 3: Debt collection (for receivables).
- Step 4: Handling bad or uncollectible debts (for receivables).
Accounts Payable Processing Procedure
- Step 1: Determine payables (review invoices, contracts, documents; determine amount, due date, payment terms; confirm validity).
- Step 2: Determine payment method (cash, bank transfer, check... based on contract, policy, supplier requirements).
- Step 3: Determine payment priority (based on importance, urgency, and ability to pay).
- Step 4: Prepare payment information (create payment slip/invoice with complete information).
- Step 5: Make payment (when due, record payment information into the system).
- Step 6: Monitor and update (ensure on-time payment, system updates).
- Step 7: Handle exceptions or issues that arise (dispute resolution, payment adjustments, negotiations).
- Step 8: Reconciliation and reporting (reconciliation with the financial system, reporting on debt status and payment progress).
Accounts Receivable Processing Procedure
- Step 1: Determine receivables (review invoices, contracts; determine amount and collection time).
- Step 2: Check and confirm validity (check accuracy, confirm not collected).
- Step 3: Send collection notice (official notice, reminder if overdue).
- Step 4: Track payment collection (ensure payment is made on time, in the correct amount, and by the correct method; record it in the system).
- Step 5: Handling exceptions and disputes (dispute resolution; consider flexible payment methods, debt repayment plans; if large/hard-to-collect debts require the participation of leaders, legal, debt collection agencies).
- Step 6: Reconciliation and reporting (reconciliation with the management system, reporting on debt status and collection progress).
Effective debt management methods and strategies
To effectively manage accounts receivable, businesses need to combine sound accounting practices with proactive cash flow control strategies. Below are the most important methods and strategies to optimize accounts receivable management.
| Accounts Receivable Management | Accounts Payable Management |
| Track specific objects, classify object groups.
Detailed accounting for each object and transaction to track payment deadlines and remind customers. Collect complete and carefully store documents. Timely grasp bad debt, overdue debt to come up with early solutions. Build customer classification table, evaluate and set debt policy for each group. Set up detailed customer management processes and specific goals. Clearly define who is responsible for working with each customer and how to contact them. Send invoices directly to customers to optimize collection time. Remind customers when payment is due, clearly stating terms and penalties. Develop a detailed collection plan, prioritizing large or potentially bad debts. Apply policies to encourage early payment (discounts) and penalize late payment (compensation fees, interest). Require customers to make a deposit. |
Track each object, continuously update and compare with books.
Consolidate data and periodically compare (end of month, quarter, year) with partners. Pay on time and in accordance with the Law for amounts payable to the state and employees. Track separately and update as soon as invoice arrives for items that do not have invoices. Develop supplier selection process and negotiate favorable payment terms. Establish a supplier information management process, ensure the system accurately records agreements and updates payment terms. Establish a process for reviewing supplier contracts, checking for accuracy, completeness, and legal compliance; include penalty/compensation provisions. Establish a strict internal purchasing process, require suppliers to issue purchase orders, compare with invoices upon receipt. Set up invoice processing procedures, reject incorrect invoices, process on time, pay on time (not early). |
Application of technology and software for debt management
Applying technology in debt management is necessary for the following important reasons:
Increase efficiency and accuracy
- Automating steps such as debt reminders, payment recording, and debt reconciliation helps reduce errors due to manual operations.
- Avoid confusion between receivables/payables, payment due dates and debt status of each partner.
Save time and money
- Technology systems help shorten debt processing.
- Reduce personnel costs for repetitive tasks such as updating books, calling, and sending debt reminder emails.
Centralized, transparent management
- Accounts receivable data is stored and processed on a single platform, making it easy to track and look up transaction history.
- Increase transparency within the business and with partners.
Reduce financial risk
- Debt management software can provide early warning of overdue debts, helping businesses proactively handle them.
- Avoid capital stagnation or loss due to loss of control.
Make decisions faster and more accurately
- Full reports and real-time data are available to support leaders in making timely financial decisions.
Enhance customer/partner experience
- Prompt, clear, and courteous debt reminders through the system help build a professional and trustworthy relationship.
Suggested tools to support modern debt management
| Demand | Recommendation Engine |
| Record – report debt | Accounting software (MISA, FAST, Bravo) |
| Automatically process input invoices, reconcile PO - GR - Invoice | Bizzi (AI + RPA) |
| Manage customers – orders – overall debts | ERP: Odoo, SAP, AMIS |
| Track debt through visual charts | Power BI, Google Data Studio, Excel Dashboard |
Bizzi – Technology solutions to help businesses overcome debt management challenges
Bizzi is a pioneering automatic invoice processing software in Vietnam, helping businesses optimize accounting and financial processes thanks to artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic automation (RPA) technology. Each electronic invoice is extracted and processed in less than 30 seconds, helping to reduce errors, increase work efficiency and save up to 80% of employee time.
With the motto "Effective assistant - Less stressful accounting", Bizzi has been trusted and chosen by more than 1000+ businesses, becoming the leading invoice digitalization solution, accompanying the digital transformation wave and global technology trends. With the challenge of debt management, Bizzi supports businesses in both aspects of receivables and payables.
Accounts Payable Management
Bizzi is a comprehensive solution that helps businesses control accounts payable and manage expenses accurately, transparently and economically. Bizzi supports automatic processing of input invoices and systematic management of business expenses.
- Bizzi Bot integrates RPA and AI technology to automatically upload, check and reconcile invoices, eliminating manual operations and minimizing errors.
- Reconcile invoices – purchase orders (PO) – warehouse receipts (GR) in real time to detect discrepancies or risks as soon as they arise.
- Automatically verify suppliers via tax code and operating status on the tax system, limiting the risk of working with invalid suppliers.
- Record and store electronic invoices for up to 10 years, meeting legal regulations and convenient for searching.
- Set up budgets by department, team or project, then allocate and monitor spending closely.
- Monitor spending in real time and alert when exceeding budget, helping businesses proactively control cash flow.
- Generate detailed expense reports by category, department or project – for analysis, auditing and financial decision making.
- Automated expense approval system with flexible approval flow by level, department or expense type, helping to speed up the approval process.
- Employees can submit expense requests before expenses are incurred, and track request status (pending approval, approved, rejected).
- Attach each expense to a specific task/project, making it easy to monitor and evaluate financial performance according to each business goal.
- Automatic alerts: Send notifications when there are new spending requests, expenses exceed the limit or unusual signs are detected.
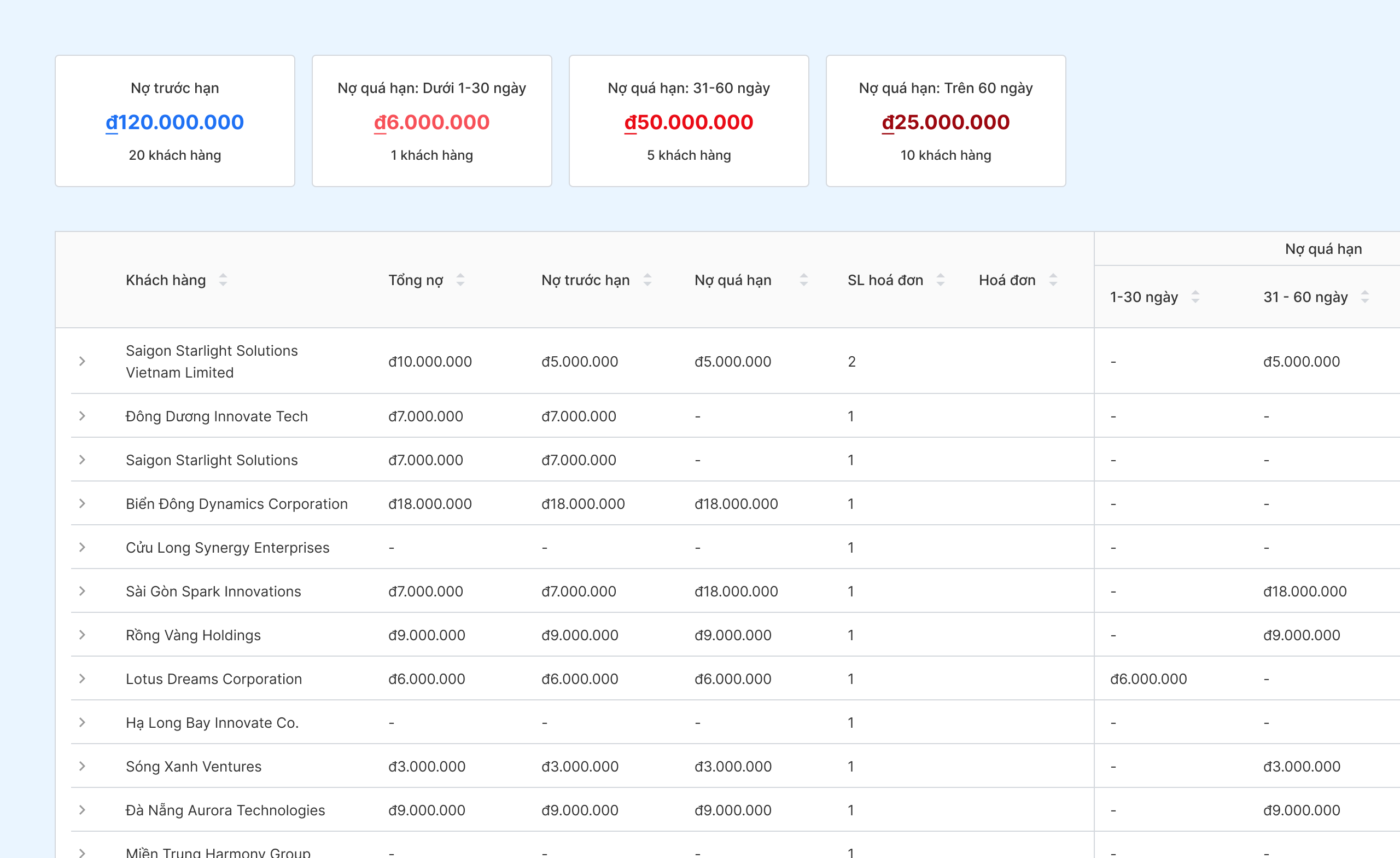
Accounts receivable management
Bizzi not only processes invoices automatically but is also a powerful tool in managing receivables and payables, helping businesses effectively control cash flow, improve financial capacity and reduce debt collection pressure.
- Automatic debt reminder: Set up flexible debt reminder processes according to customized scenarios. Bizzi automatically sends timely debt reminder emails or messages to customers, helping to limit overdue debt while still ensuring professionalism in communication.
- Overall debt management: Closely monitor and reconcile debt with important indicators such as DSO (Days Sales Outstanding) and debt aging report, helping businesses evaluate debt collection efficiency and control credit risk.
- Tracking debt for each partner: Bizzi automatically records and updates debt incurred with each customer and supplier, providing a clear and detailed view of the business's financial obligations.
- Warning of due and overdue debts: The system proactively warns of debts that are about to become due or are at risk of becoming overdue, helping businesses proactively plan for handling and protecting cash flow.
- Automatic debt reconciliation: Automatically compare and confirm debt balances between businesses and partners, minimizing errors and shortening dispute resolution time.
- Detailed debt report: Provide real-time reports on debt status, supporting management to make quick and accurate decisions in finance and debt collection.
Conclude
Above is all the information related to what debt is, the processing process as well as the method of debt management for efficiency and optimization. If your business is still having a headache about debt or cost management, please register to try Bizzi's solution package right away.
Bizzi supports businesses:
- Automatically receive, store and reconcile electronic invoices quickly and accurately.
- Simplify complex accounting operations, helping to reduce the burden on the accounting department.
- Optimize approval and cost management processes, enabling fast and transparent financial decision making.
Bizzi is not only an invoice processing tool but also an effective debt and cost management solution, supporting businesses to build a solid financial foundation and sustainable growth in the digital age.
- Link to register for a trial of Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/


