In the digital age, running a business effectively requires close coordination between departments through a modern management system. This is where ERP – enterprise resource planning system – plays a key role. However, to maximize the power of ERP, businesses need to understand each What is ERP subsystem? and how they support specific functions such as finance, human resources, manufacturing or logistics. The following article will help you clarify the concept of ERP subsystems and introduce the core subsystems that are indispensable in any ERP system.
1. Definition and role of ERP subsystems
In an ERP system, subsystems act as specialized “links”, linked together to create a unified operating platform. Instead of using separate software for each department, businesses can integrate the entire management process – from accounting, human resources, sales to production – on the same smart system. This not only increases operational efficiency, but also helps synchronize data, make it transparent and support quick and accurate decision making.
1.1. What is ERP subsystem?
ERP subsystems are independent functional components in the enterprise resource planning system (ERP), each subsystem is responsible for a specific area of business such as finance, human resources, sales or warehouse management. Although separate in function, these subsystems are integrated into a single software platform, helping data between departments to always be updated synchronously, consistently and easily retrieved.
Through the subsystems, businesses can control and automate the entire operating process — from production to consumption, from human resources to finance — without using separate, disconnected software. The high flexibility of each module also allows businesses to deploy each part according to their needs, while easily expanding the system's scale as they grow.
1.2. The role of ERP subsystems
Implementing ERP subsystems is not only a technological solution, but also a strategy to improve long-term business management efficiency. Each subsystem undertakes a key business function, and connects with other departments to create a continuous and accurate data flow. When properly integrated, ERP subsystems will help businesses operate lean, make quick decisions and adapt flexibly to market changes.
- Optimize internal operating processes: Each subsystem handles a separate business — for example, the accounting subsystem handles finances, the human resources subsystem tracks attendance, and the sales subsystem manages orders and customers. Thanks to the instant connection between subsystems, the entire process is digitized and coordinated effectively, reducing manual errors and improving efficiency.
- Data Linking on a Unified Platform: Subsystems do not operate separately but share data through the same ERP system. This helps the flow of information between departments to be seamless, transparent and fast, supporting administrators to make decisions based on immediate and accurate data.
- Cost optimization, flexible expansion: Enterprises can choose to deploy subsystems in order of priority or budget, instead of having to invest all at once from the beginning. Expanding new subsystems later does not affect the system structure, helping to optimize costs and grow flexibly according to actual needs.
- Replace traditional standalone software: The ERP system integrates all necessary management functions into a single platform, eliminating the situation of “each person using their own software”, which leads to fragmented, difficult to control and unintegrated data. This creates a seamless, easy-to-control, and comprehensive reporting ecosystem.

2. Key subsystems in the ERP system
An ERP system is a collection of integrated subsystems (modules) that help businesses comprehensively manage all operational activities. Among them, some subsystems are considered key - almost mandatory in any business, regardless of size or field. Below are popular ERP subsystems that play a fundamental role in the system:
2.1. Accounting - Finance subsystem
Is the core subsystem in every ERP system, helping businesses control finances closely and transparently. This subsystem tracks cash flow, revenue, expenses, manages invoices, assets, budgets and financial reports. Automating accounting operations helps reduce errors, save time and make quick decisions based on real-time data. Includes subsystems such as general accounting, accounts receivable, banking, fixed assets, budgets, cost centers and internal transactions.
2.2. Sales Subsystem
Manage the entire sales cycle – from receiving customer requests, quoting, creating orders, tracking shipments to issuing invoices and managing business performance. This subsystem helps optimize inventory, coordinate resources effectively and increase the ability to respond to market demand. At the same time, integrate reports analyzing revenue and profit by each sales channel or employee.
2.3. Purchasing Subsystem
Support businesses to control the purchasing process: from making requests, sending orders, checking the quality and quantity of imported goods, verifying invoices to evaluating supplier performance. The feature of analyzing transaction history, prices and delivery times helps to optimize purchasing costs and ensure a stable supply for production and business activities.

2.4. Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Subsystem
Store comprehensive customer information – from potential customers to existing customers. The CRM subsystem supports tracking transaction history, feedback, consumer behavior, thereby helping to build personalized approach and care strategies. In addition, it also supports activities such as email marketing, campaign management, and customer journey analysis.
2.5. Warehouse Subsystem (Inventory Management)
Allows businesses to monitor inventory in real time, control quantity, location and status of goods. Integrates technologies such as barcodes and QR Codes to perform fast and accurate import and export of goods. Helps businesses avoid excess or shortage of inventory, and accurately calculates cost of goods sold.
2.6. Production Subsystem
Especially important for manufacturing enterprises, this subsystem allows planning and monitoring of the production process from raw materials to finished products. Automatically calculates the demand for raw materials, machinery, and labor according to standards, supports production coordination and controls progress, productivity, and quality.
2.7. Project Subsystem
Often used in the construction industry, technical services, information technology... The Project subsystem helps businesses manage the entire life cycle of a project: from planning, allocating resources, monitoring progress to controlling costs and profits. The early warning system helps handle arising risks and ensures the project is on schedule and on budget.
2.8. Human Resource Management Subsystem
Manage employee records, contracts, insurance, compensation, timekeeping, training and performance evaluation. This subsystem helps the HR department operate efficiently, automate payroll processes and comply with legal, insurance and personal income tax requirements.
3. Overall benefits of implementing an ERP system
Understanding What is ERP subsystem? will help businesses fully realize the overall benefits that this system brings. An ERP system is structured from many subsystems such as finance - accounting, purchasing, sales, warehouse, production, human resources, ... to help manage more comprehensively and effectively. Below are the Outstanding benefits of ERP system:
- Effective control of financial information: The accounting and financial subsystem in ERP helps businesses consolidate data at a single source. This not only ensures accuracy and consistency but also supports the creation of quick, transparent and timely financial reports.
- Speed up your workflow: ERP subsystems automate processes and connect data between departments. As a result, businesses can eliminate repetitive operations, reduce processing time and speed up work progress.
- Minimize data errors: When using ERP, information is entered once and synchronized across subsystems. This helps to minimize errors due to manual data entry and ensures data reliability throughout the system.
- Easily control employee work process: ERP allows managers to monitor the activities of each department through functional subsystems. Each task, status and result are recorded and clearly displayed on the system.
- Professionalize the management process: ERP implementation means standardizing processes according to international standards. The subsystems operate flexibly but are closely linked, helping to increase management efficiency and create a professional image for the business in the eyes of partners and customers.

4. How to choose the right ERP subsystem for your business
To effectively deploy an ERP system, businesses need to clearly understand What is ERP subsystem? and choose the subsystems that truly meet operational needs. Choosing the right subsystem not only helps optimize costs but also improves overall performance.
- Identify business goals and operational needs: Businesses should start by analyzing their current processes, operational bottlenecks, and long-term strategic goals. From there, identify essential subsystems such as accounting - finance, sales, logistics, human resources or production.
- Prioritize core subsystem first – expand later: Instead of deploying the entire system at once, businesses can choose core subsystems that bring immediate value, then gradually expand according to growth needs.
- Consider the cost – overall budget: In addition to the cost of purchasing software licenses, businesses need to evaluate all the hidden costs that come with it, such as deployment, training, maintenance, upgrades, and long-term technical support. Some ERP solutions based on the SaaS (subscription) model can be flexible and save initial costs.
- Compare features between popular ERP subsystems: Depending on the field of operation, businesses should compare the subsystems on each ERP system to evaluate the customization capabilities, compatibility with the current industry and scale. For example, the manufacturing industry needs the production management and BOM subsystem, while service businesses need to prioritize the CRM and human resource management subsystem.
- Choose a reputable supplier with industry experience: An ERP vendor with experience in a specific industry will help businesses configure the system as realistically as possible. At the same time, it is necessary to evaluate after-sales service, technical response time, and the ability to expand the solution as the business grows.
Choosing the right ERP subsystem from the start will create a solid foundation for future digitalization and business expansion.
5. Bizzi's role in optimizing financial processes and integrating with ERP
In the context of businesses increasingly prioritizing digital transformation and process streamlining, ERP subsystem plays a central role in connecting and optimizing all operations. However, many businesses face difficulties when the financial accounting subsystem in ERP is not deep enough to handle complex financial processes. This is where Bizzi comes into play as a strategic supporting platform, helping to automate finances and integrate smoothly into existing ERP systems.
5.1. What is Bizzi?
Bizzi is a specialized platform for financial automation, acts as a AI assistant for finance and accounting departments. The platform integrates more than 30 features to help businesses automate cost management, debt collection, and B2B payment processes.
Bizzi is designed to in-depth supplement for the ERP subsystem, especially in the financial accounting aspect – helps process data faster, reduces manual errors and improves cash flow management efficiency. 
5.2. Core features of Bizzi related to finance
Bizzi provides a comprehensive toolkit to help businesses automate financial and accounting operations, from invoice processing to cost and debt management, helping to optimize cash flow and minimize operational risks.
- Automatic Invoice Processing (IPA + 3-Way Matching): Upload, check and reconcile invoices in just 30 seconds with AI & RPA; automatically reconcile with purchase orders (POs) and warehouse receipts (GRs); alert on risks and archive valid invoices.
- Business Expense Management (Bizzi Expense): Allocate budgets by department/project, monitor in real time, automatically approve expenses and provide detailed cost reports as required.
- Manage worki (Bizzi Travel): Comprehensively manage business travel expenses such as airfare, hotels, transfers, set limits and control pre-approvals.
- Electronic bill (B-invoice): Issue standard invoices, support mass creation, customize templates and store electronically for at least 10 years.
- Accounts Receivable Management (ARM): Automatic debt reminders via email/SMS according to scenarios, DSO reports, real-time debt reconciliation and debt due warnings.
- Bizzi Business Credit Card: Support spend first - pay later with interest rate 0% within 45 days; directly integrated with internal cost management system.
- Connecting capital sources: Help businesses access flexible and fast forms of funding, integrated into operating cash flow.
- Automatic order processing: Support receiving and processing orders from customers quickly, shortening the sales cycle.
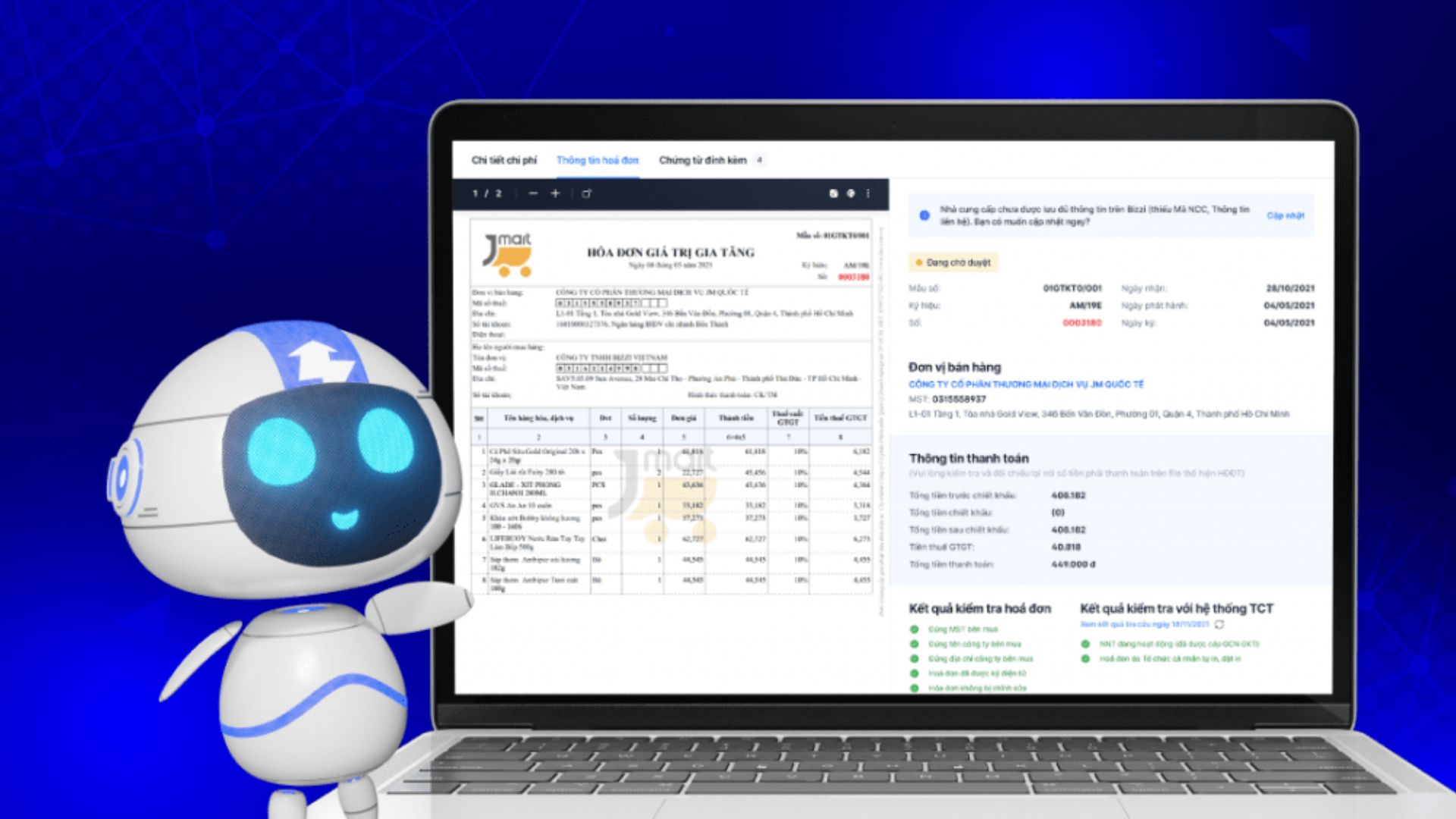
5.3. Bizzi as a complementary solution to ERP systems
No replacement increase efficiency For existing ERP modules, Bizzi offers a flexible integration layer:
- Open API Integration: Synchronize data with accounting software and ERP systems such as SAP, Oracle, Microsoft Dynamics… via Open API or custom API.
- Compatible with multiple systems: Easily integrate with cloud, hybrid or on-premises systems thanks to flexible connectivity models like file-based or REST API.
- Optimize ERP financial subsystems: Focus on specialized financial processes such as invoice reconciliation, expense control, accounts receivable, etc. that many ERP systems do not specialize in.
With deep integration and financial expertise, Bizzi helps businesses ERP system optimization, while enhancing flexibility and the ability to make quick decisions in the modern financial environment.
Learn more at: https://bizzi.vn/tich-hop-erp/
To improve the efficiency of invoice management as well as automate the financial and accounting processes of the business. Register to experience Bizzi's comprehensive solution suite today!
- Link to register for a trial of Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/
6. Conclusion
Understanding each ERP subsystem not only helps businesses choose the right solution but also optimizes internal operational efficiency. From finance - accounting, warehouse management, to human resources or sales, each subsystem plays a strategic role in improving productivity and making accurate decisions. If you are looking for a solution that supports flexible automation of financial - accounting processes, Bizzi is the ideal choice to seamlessly connect with existing ERP systems, promoting effective digital transformation.


