The nature of financial risk lies in the uncertainty and unpredictability, when even a small change in cash flow, interest rates or financial obligations can lead to major consequences for the business. To survive and develop, risk control is not only a management task but also a vital factor.
This article by Bizzi will analyze in detail the nature of financial risks, their classification and the most effective ways to prevent financial risks through the lens of modern management and automation technology.
Definition, nature and impact of financial risk
Financial risk is one of the major challenges that every business faces. Understanding the definition and impact of financial risk helps managers assess financial health and plan management more effectively.
What is Financial Risk?
Before going into details, it is important to understand the nature of financial risk. It is not just the numbers on the report but the possibility of a business losing capital, profits or solvency due to financial fluctuations.
Financial risk is the possibility that a business or individual will not be able to fully meet its financial obligations, resulting in capital loss, reduced profits or insolvency.
- For businesses: risks often come from debt, interest rate fluctuations, exchange rates, beyond capacity. business cash flow management.
- For investors: financial risks arise when investment value decreases or when the issuing company is unable to pay dividends and interest.
The main difference between financial risk and business risk
| Criteria | Financial risk | Business risks |
| Source | Due to capital structure (debt ratio) | Due to business operations and market environment |
| Scope of influence | Impact on solvency, financial pressure | Impact on operating profits |
| Level of control | Can be managed with financial strategy, debt optimization | More difficult to control because of the impact of external markets |
| For example | Businesses borrow too much, leading to inability to repay debts. | Sales plummeted due to changing customer tastes |
What is the impact of Financial Risk?
It can be said that financial risk is not only the "risk of losing money", but also directly affects the survival of the business, the interests of investors and the stability of the economy.
For businesses:
- Increased cost of capital: Interest rates, bond issuance costs, and opportunity costs are all higher.
- InsolvencyWhen cash flow is not enough to pay short-term debt → risk of bankruptcy.
- Reduced credibility and fundraising opportunities: Partners and banks are more cautious when granting credit.
For investors and the economy:
- Reduced expected profits: Due to fluctuations in stock prices, bonds or risk of corporate bankruptcy.
- Destabilizing the financial system: If many large businesses are at risk, it could lead to a widespread credit crisis.
5 common types of financial risks
Financial risk is not simply a loss figure but comes from many different sources. To manage effectively, especially in the digital age, businesses need to prioritize identifying the following 5 risk groups:
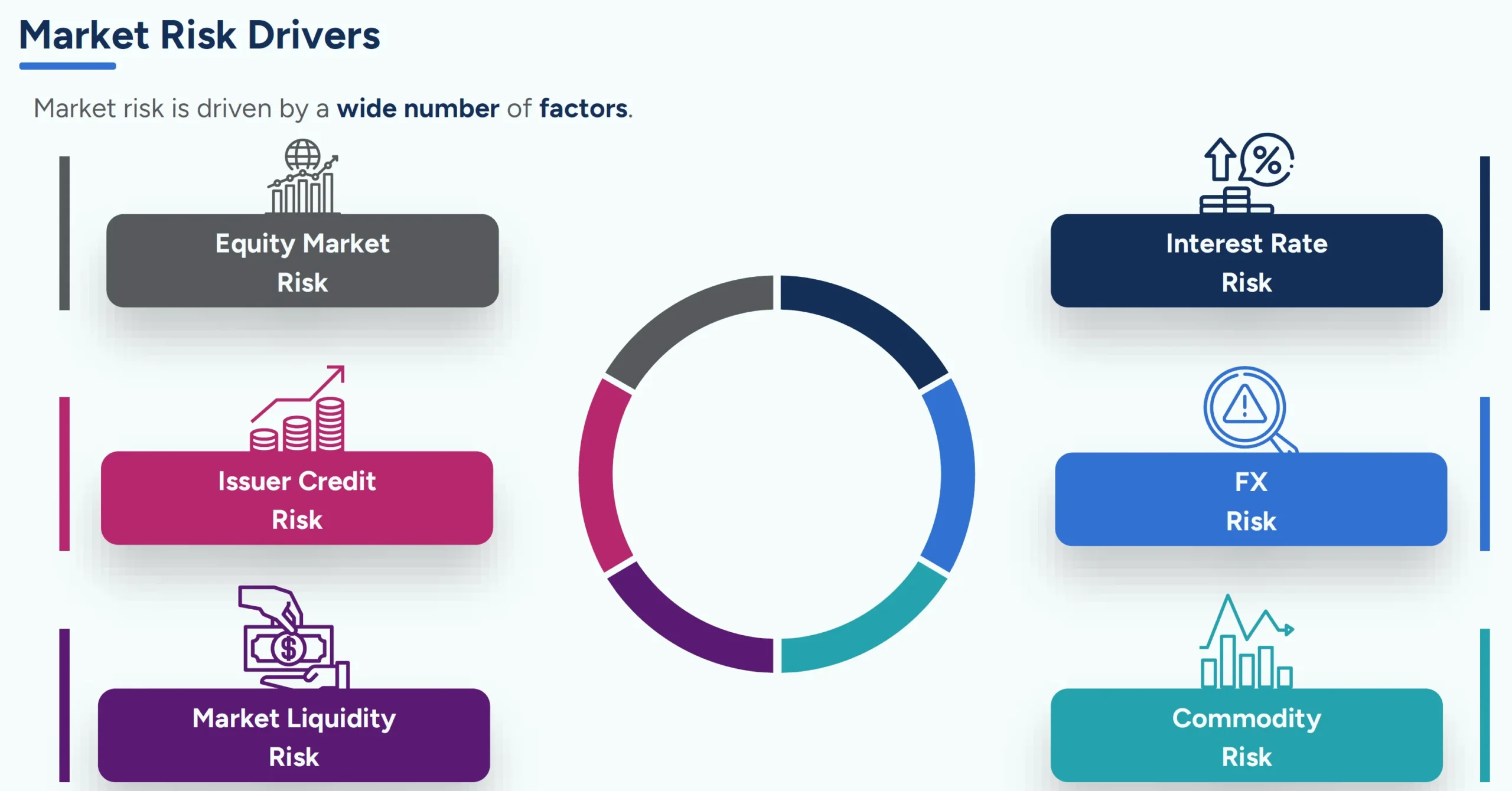
Market Risk
Market risk arises from fluctuations in the financial market, directly affecting the value of assets and investment portfolios of enterprises. Early identification of these fluctuations helps enterprises minimize unexpected losses.
- Risk of loss due to fluctuations in financial values in the market (stock prices, bonds, commodities, exchange rates).
For example: Exporting enterprises are at risk when the USD depreciates against the VND.
Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk occurs when a business does not have enough cash to meet short-term obligations, even though its total assets still have value.
- Lack of cash or the ability to convert assets into cash quickly.
- Is the main cause of bankruptcy risk, even when the business is profitable on paper (Insolvency).
- For example: A company has a lot of inventory but cannot sell it to pay interest on loans on time.
Credit Risk
Credit risk arises when counterparties fail to meet their financial obligations. This is a particular threat to the management of receivables and payables, and can have a serious impact on a company's short-term cash flow.
- DThe partner failed to fulfill his payment obligations on time.
- Related to:
- Accounts Receivable (Accounts Receivable – AR): Risk of customers paying late or not paying.
- Accounts Payable (AP): Risk of business losing reputation, being fined or losing discounts due to late payment.
For example: Customer bankruptcy makes the business unable to collect debt.

Market Risk
Arising from fluctuations in financial markets, including:
- Interest Rate Risk: Interest rate fluctuations increase borrowing costs, which is especially dangerous for businesses using high financial leverage.
- Exchange Rate Risk: Foreign currency fluctuations directly affect the profit margin of import-export enterprises.
Legal Risk & Systemic Risk
- Legal risks: Enterprises violate financial and accounting regulations. Especially in the context of digital transformation, compliance with regulations on e-Invoices and taxes is a vital factor to avoid heavy fines.
- Systemic risk: A problem that spreads from a financial institution or economy (e.g., 2008 crisis).
Causes: From macro fluctuations to internal governance loopholes
Understanding the causes helps businesses identify risks and prepare appropriate preventive measures.
Cause 1: From macroeconomic fluctuations
This is a group of factors that are difficult for businesses to control but have a strong impact:
- High inflation: Increases input costs (raw materials, labor), while currency value decreases → businesses find it difficult to balance costs and revenue.
- Economic crisis: Consumer demand decreases, customer cash flow is tightened → debt collection ability decreases → easy to lose the ability to pay off loans.
- Monetary policy: When interest rates increase, the cost of borrowing increases; when exchange rates fluctuate, businesses borrowing foreign currency or importing are susceptible to exchange rate risks.
Reason 2: Internal financial management
This is a group of factors caused by the business itself and can be completely overcome with technology:
- Poor governance: No financial planning, no clear capital strategy leads to inefficient use of capital.
- Financial leverage abuse: Businesses borrow too much compared to equity (D/E too high) to expand rapidly → debt repayment pressure increases sharply when revenue does not meet expectations.
- Lack of cash flow control: Not closely monitoring cash inflows and outflows, not forecasting cash flow, leading to short-term loss of liquidity.
Comprehensive risk management and prevention strategy
Finding a comprehensive and effective financial risk management solution is not just an option, but a mandatory factor to protect financial security; build reputation and trust, and maintain a sustainable competitive advantage in a volatile business environment.
Quantitative standards and forecasting models
Businesses need to establish a data-driven risk management framework:
- Monitor the following ratios: Debt/Equity Ratio (D/E), Current Ratio, Quick Ratio.
- Apply quantitative risk models such as Value at Risk (VaR) and comply with the international capital management framework Basel II/III to improve risk forecasting and tolerance capacity.
Traditional management solutions
- Manage cash flow closely and build up a reserve fund.
- Diversify capital sources to reduce dependence.
- Use hedging tools for interest rates and exchange rates.
The role of internal control system
Establish Process Controls and Audit Trails to prevent human errors and ensure compliance in all financial transactions.
Financial Automation: Operational Risk and Liquidity Control Strategies with Bizzi
Technology plays a key role as a “shield” to help businesses eliminate operational risks and increase liquidity. Bizzi provides a comprehensive cost management ecosystem:
- Automate Invoice Processing – Reduce Operational and Legal Risks: Bizzi Bot automatically collects and checks the validity of invoices with the Tax authorities, eliminating the risk of fake invoices or manual data entry errors.
- Cost and Budget Control – Preventing Losses: Set up spending policies and automated approval processes. The system will automatically warn or block overspending, ensuring absolute compliance.
- Effective debt management and collection – Liquidity risk prevention: The system provides real-time debt data, automatically sends payment reminders and bank reconciliation. This helps reduce DSO (Days Sales Outstanding) index and increases capital turnover speed.
- Enhance transparency and decision-making: Provides a real-time visual Dashboard, helping CFOs and business owners see the "financial health picture" immediately to respond promptly to fluctuations.
Frequently asked questions about what is financial risk?
Below are answers to frequently asked questions regarding financial risks:
When does financial risk arise?
Financial risks often arise when businesses or individuals use borrowed capital, depend on unstable cash flows, or are affected by macroeconomic fluctuations (interest rates, exchange rates, inflation). For example: a company borrows a large amount of money to expand production while revenue is uncertain → there is a risk of insolvency.
Can financial risk be measured?
Yes. Financial risk can be measured through financial indicators:
- Debt to Equity Ratio (D/E): Shows the degree of leverage.
- Debt Ratio: Shows the proportion of debt in total assets.
- Interest Coverage Ratio: Assesses the ability to pay interest.
These indicators help predict the level of risk and the ability of a business (or individual) to withstand financial fluctuations.
Conclude
Financial risks are an inevitable part of business. However, with the support of technology, businesses can completely switch from passive to proactive control. Instead of wasting resources on manual processes that are prone to errors, applying solutions like Bizzi helps businesses build a solid financial “immune system”: transparent, accurate and timely.
Let Bizzi help your business turn Operational Risk into an opportunity to optimize financial processes. Sign up for a Demo of our Risk Management Automation Solution today!
Register here to receive advice on solutions suitable for your business: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/


