Production management plays a key role, is the backbone for all activities of manufacturing enterprises. It not only ensures the efficient and stable operation of the chain but is also the key to optimizing costs, improving product quality and increasing competitive advantage. So what exactly is production management and how to implement it effectively?
Production management is the activity of planning, organizing, coordinating and controlling all factors related to the process of creating a product or service. It focuses on converting input factors (raw materials, labor, machinery, technology) into valuable products or services at the output, accurately meeting the needs of the market.
In this article, Bizzi will go deep with you to learn from the definition, role, common methods to how to apply digital transformation to build a comprehensive production management system, helping businesses break through in the modern context.
What is production management?
As defined above, production management can be understood as the art and science of systematically managing the entire production process. The core objective is to achieve maximum efficiency, through process standardization, optimizing resource utilization and minimizing costs per unit of product.
This activity is not only limited to the factory but also closely linked with other departments such as purchasing, logistics, finance and business to form a synchronized value chain.
The importance of production management in business
An effective production management system is not only desirable but also a requirement for business survival and development. If not managed well, businesses will face serious problems with costs, quality, and ultimately customer satisfaction.
- Ensuring operational efficiency: Standardize and optimize each step in production process, helping to improve labor productivity and reduce production time.
- Optimize costs and resources: Minimize waste (Muda) in Lean Manufacturing, from raw materials, waiting time, to labor. This directly affects the reduction of cost of goods sold (COGS), help increase profit margins.
- Improve and stabilize product quality: Establishing a strict quality control (QA/QC) process, such as applying ISO 9001 standards, helps reduce the rate of defective products to the lowest level.
- Supply and demand balance: Through accurate production capacity planning, businesses can respond promptly to market demand without causing excess inventory or shortages of goods.
- Increase profits and competitiveness: High quality products at reasonable prices and on-time delivery are the decisive factors that help businesses dominate the market.
- Strengthening reputation and sustainable development: A stable and efficient production process is the foundation for sustainable development and strong branding.
Production Management vs. Operations Management: What's the Difference?
Many people often confuse “Production Management” and “Operations Management”. Basically, production management is a subset of operations management.
- Production management: Focus mainly on the process convert tangible inputs into physical productsIts scope is limited to factories and enterprises.
- Operations Management: Has a broader scope, including produce products and provide services. It manages the entire chain of activities required to create and deliver value to customers, from design, manufacturing, logistics, to after-sales service.
Simply put, every business has “operational” activities, but only businesses that create physical goods have “production” activities.
Objectives of production management in business
To realize the above important roles, production management aims at specific and measurable goals, often called KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).
- Provide products with the right quality and quantity (Right Quality & Quantity): Ensure production of correct types and standards, reduce defect rate.
- Cost Optimization: Reduce costs per unit of product through waste elimination, process optimization and efficient use of resources.
- On-time Delivery: Shorten production cycle time and ensure on-time delivery, avoiding delays that affect customers.
- Increase Flexibility: Quickly adapt to market changes, from volume demands to product design requirements.
- Improve equipment effectiveness (OEE – Overall Equipment Effectiveness): Maximize machine uptime and performance, minimize downtime.
- Create sustainable competitive advantage: Through superior quality, price, and speed of delivery.
Basic functions of production management
Production management is a complex field, taking on many different functions to coordinate the smooth operation of the production machine.
- Production planning: Determine goals, forecast demand, plan output and master production schedules.
- Production organization: Design, arrange and allocate resources (personnel, machinery, production lines) reasonably.
- Production Management: Monitor, direct and adjust daily activities to ensure production is according to plan.
- Production control: Monitor, measure performance and compare against set goals. This function includes quality control, inventory management, and cost control.
- Supply chain and inventory management: Coordinate with suppliers to ensure raw materials are supplied on time, with the right quality, while controlling inventory at optimal levels.
- Human resource management in production: Recruit, train, assign work and motivate workers to maximize productivity.
8 core elements that create an effective production management model
An effective production management model is built on 8 fundamental elements, closely linked together.
- Market assessment and demand forecast: Grasp trends to forecast accurately, as a basis for production planning, avoiding surplus or shortage.
- Business positioning: Clearly identify competitive advantages (low cost, superior quality, or speed) to develop appropriate production strategies.
- Production capacity management: Evaluate and coordinate machine and labor capacity to meet production plans, minimize waste and optimize performance.
- Ensure output quality: Build a culture of quality throughout the organization, strictly adhere to standards to reduce errors and warranty costs.
- Facilities Management: Arrange the floor plan properly and maintain machinery regularly to ensure continuous production and reduce downtime.
- Planning and resource allocation: Allocate the right people, the right jobs, the right resources (finance, materials, technology) to increase efficiency and reduce pressure on each stage.
- Coordination of production activities: Link and balance stages in the production chain to ensure smooth operation and reduce waiting time.
- System operation control: Continuously monitor, measure and adjust processes to detect inadequacies and provide timely improvement solutions.
Popular production management methods in business
Depending on size, industry and strategy, businesses can apply one or a combination of different production management methods. Below are the most common and effective methods.
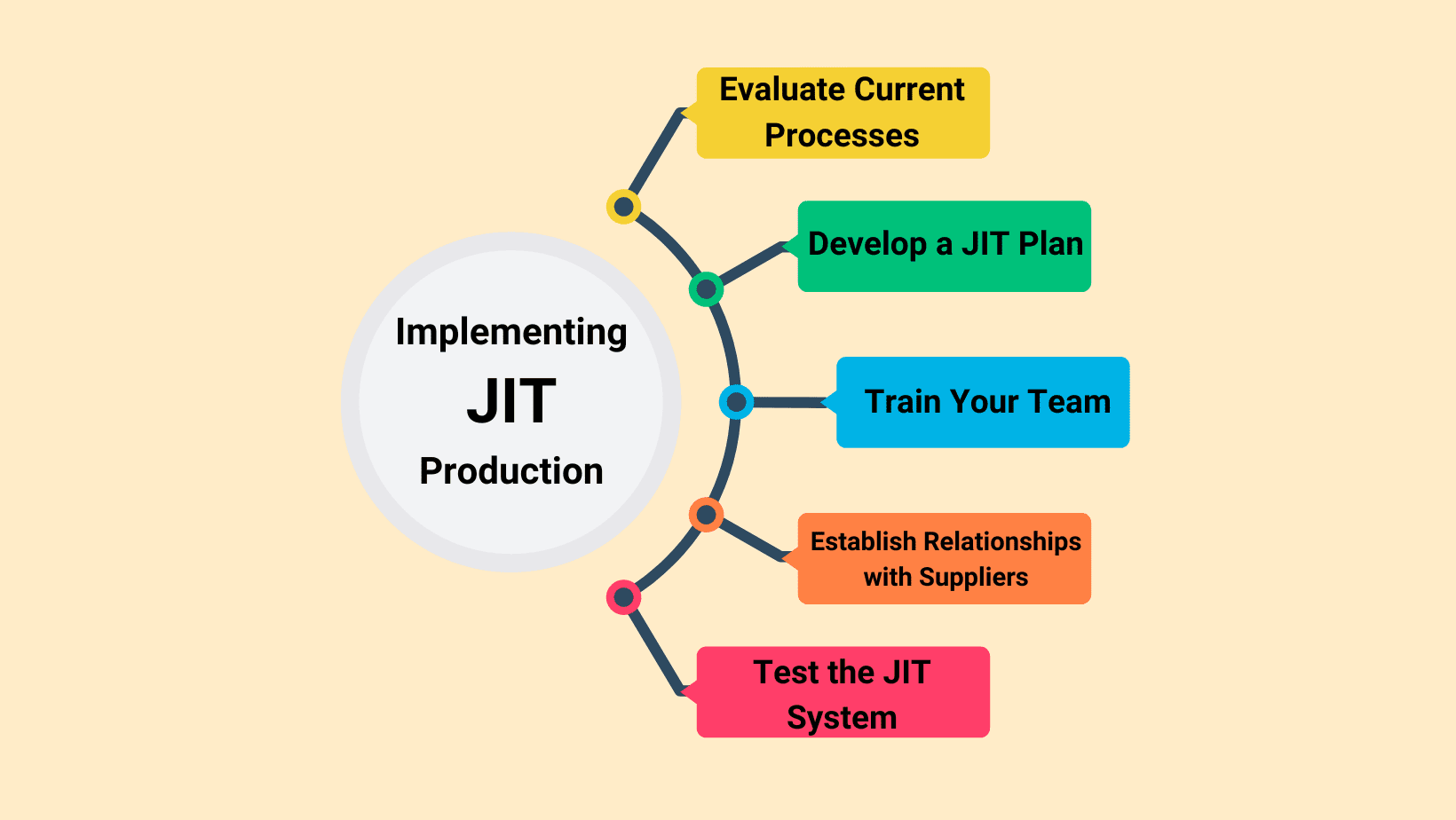
Just-in-Time (JIT) method
- Principle: “Right product – Right quantity – Right place – Right time”. JIT aims to produce and supply raw materials as needed, eliminating almost all inventory.
- Benefit: Dramatically reduce storage costs, increase flexibility, and reduce waste.
- When to apply: Suitable for businesses with a stable supply chain, relatively predictable market demand and highly repeatable production processes.
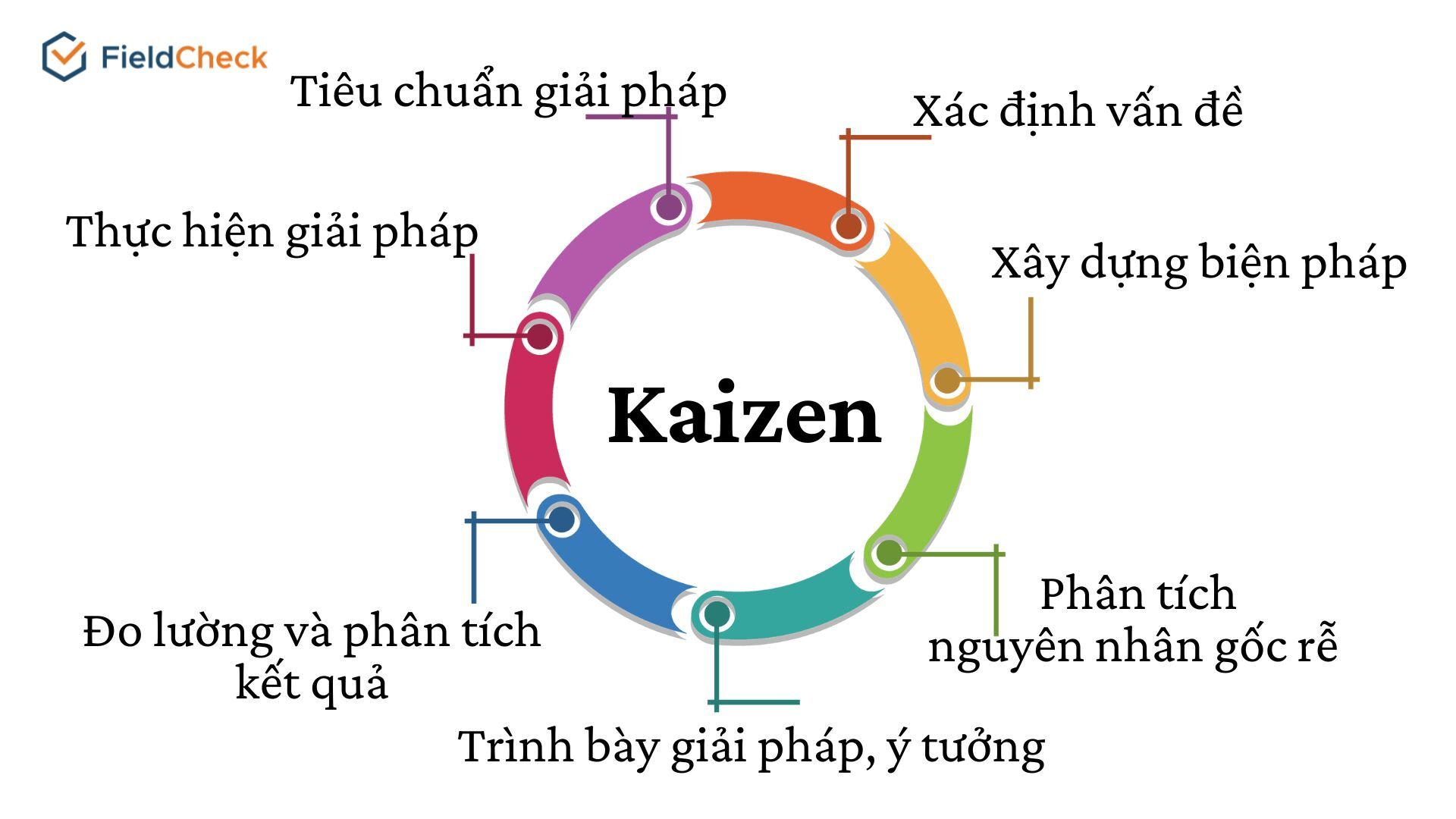
Kaizen Method (Continuous Improvement)
- Principle: “Change for the better”. Kaizen is a philosophy that encourages small, continuous, and frequent improvements from everyone in the organization, from leaders to workers.
- Benefit: Optimize processes, improve quality, increase productivity, build a proactive and united culture in the business.
- When to apply: Kaizen can be applied to any type of business, at any time, because the core philosophy is to constantly look for opportunities to do better.
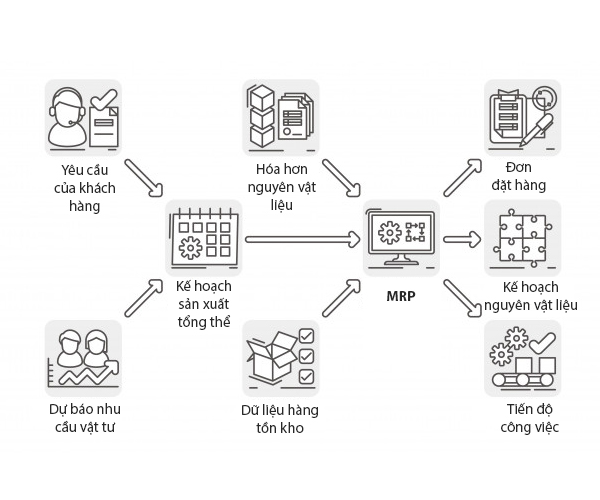
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Method
- Principle: Use computer systems to accurately calculate raw material requirements and when they are needed, based on the overall production plan.
- Benefit: Ensure raw materials are always available, avoid shortages or excess inventory, optimize purchasing costs and increase efficiency.
- When to apply: Most effective for businesses with complex production processes, many stages and using a variety of raw materials.
Kanban Method
- Principle: Use visual cues (cards, boards, lights) to manage workflow. One process only starts production when the next process signals a request.
- Benefit: Prevent overproduction, identify bottlenecks in the process, and maintain balance between stages.
- When to apply: Very effective when combined with JIT and Lean, suitable for manufacturing environments that require high flexibility and visualization.

Smart Manufacturing (Smart Manufacturing / Industry 4.0)
- Principle: Integrate digital technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), Big Data into the entire production process.
- Benefit: Automation, real-time data collection and analysis, rapid decision making, predictive maintenance and comprehensive optimization.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)
- Principle: Using a single software system to integrate and manage all aspects of business operations, from manufacturing, finance, human resources to supply chain. Manufacturing businesses account for the largest proportion of ERP adoption.
- Benefit: Synchronize data across the enterprise, providing a holistic view, improving decision making and enhancing collaboration between departments.
When integrated with specialized solutions such as Bizzi, system ERP integration Get closer control over manufacturing costs through automated invoice processing, approvals, and real-time budget tracking.
Steps to implement effective production management
To build a successful production management system, businesses need to follow a methodical roadmap.
- Define goals and strategies: Based on market analysis and business positioning, clearly define the production goals to be achieved (e.g. reduce 15% of costs, increase 10% of OEE).
- Building a management system: Choose the appropriate management method (JIT, Lean, Kaizen…), design the process and allocate the necessary resources for each stage.
- Human resource training and technology application: People are at the heart of every system. Employees need to be trained to understand the process and their roles. At the same time, apply appropriate technology and software to automate and optimize work.
- Evaluate, measure and continuously improve: Regularly monitor the production efficiency index (KPIs), analyze the results to find areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments. This is a never-ending cycle.
Digital transformation application helps comprehensive production management and cost optimization
Digital transformation is revolutionizing the manufacturing industry, helping businesses manage comprehensively and optimize costs in a superior way.
- Process automation: ERP and MES (Manufacturing Execution Systems) help coordinate, manage and track the entire process automatically, minimizing human error and increasing speed.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Big Data and AI help analyze huge volumes of data from manufacturing, thereby making accurate forecasts about demand, maintenance plans, and resource allocation decisions.
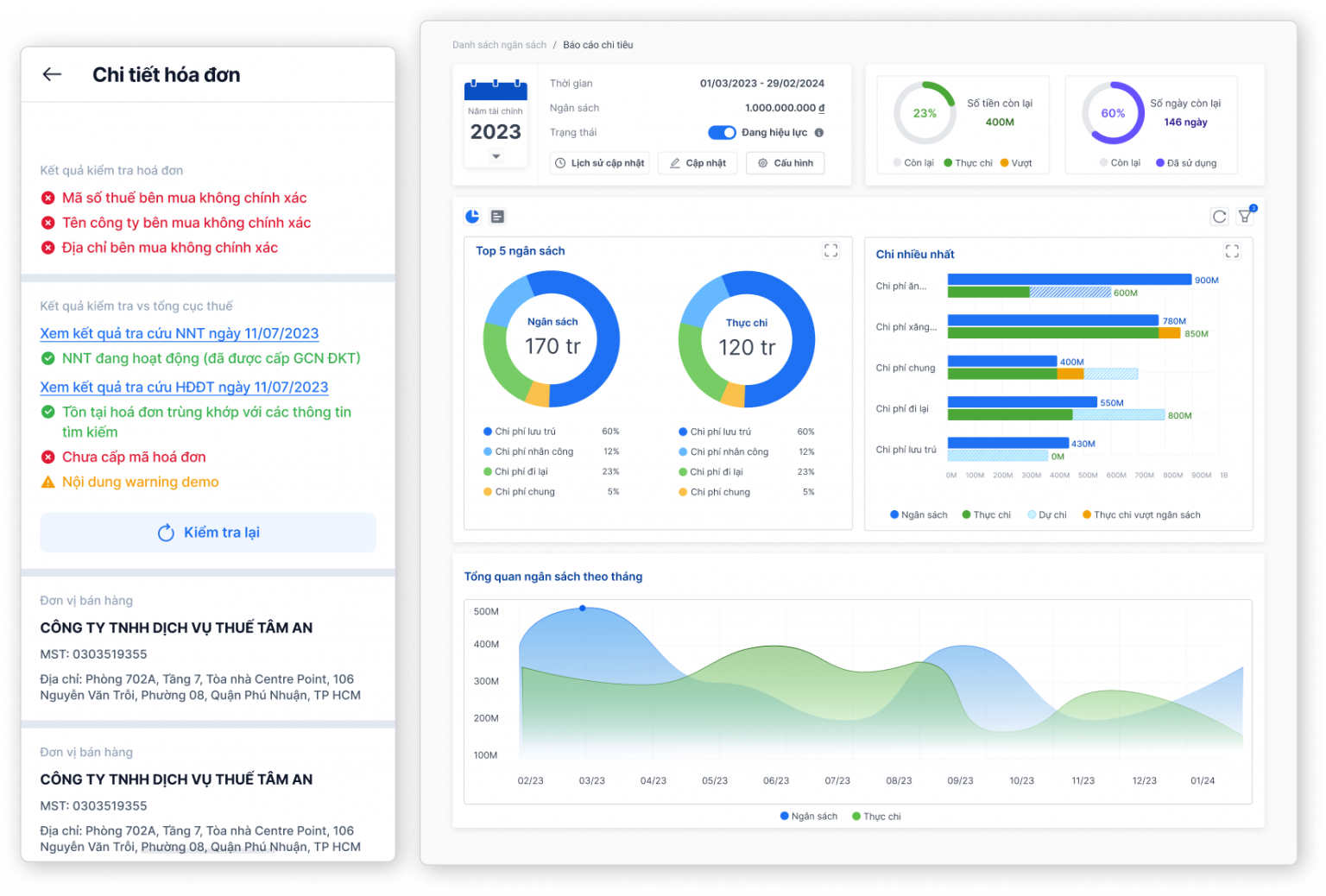
- Optimize inventory management: The software helps track inventory in real time, automatically alerts when raw materials are running low or in stock for too long, helping to reduce storage costs and ensure uninterrupted production.
- Comprehensive supply chain integration: Digital solutions seamlessly connect from supplier, manufacturing, to distributor, creating a Supply Chain transparent and efficient
In that context, automated cost management tools like Bizzi Plays an important role as a link, helping to optimize costs in production management:
- Automate invoice collection and processing: All input costs (raw materials, services, maintenance, etc.) are automatically collected and recorded, helping invoice processing automation, eliminating errors and saving hundreds of hours of manual work.
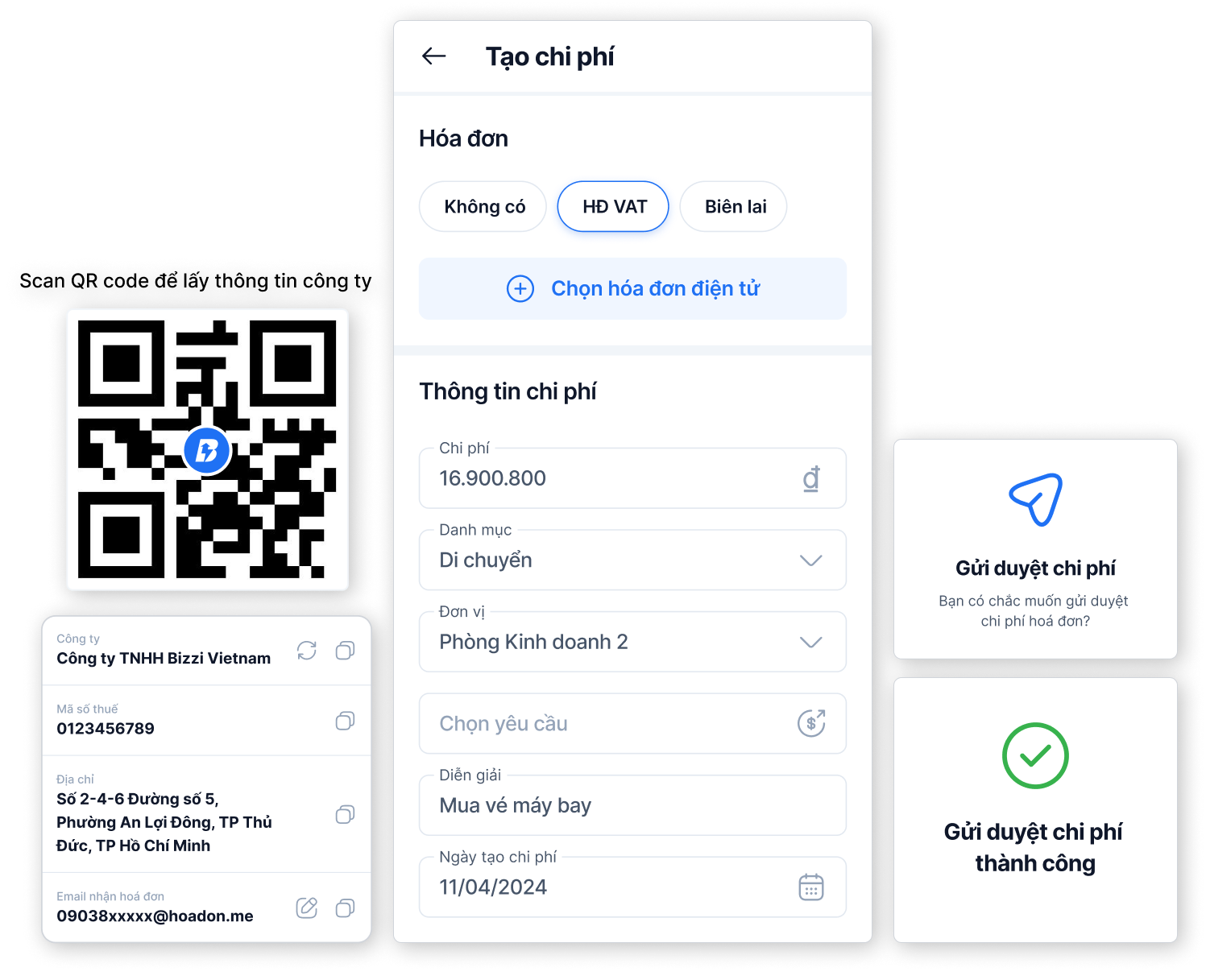
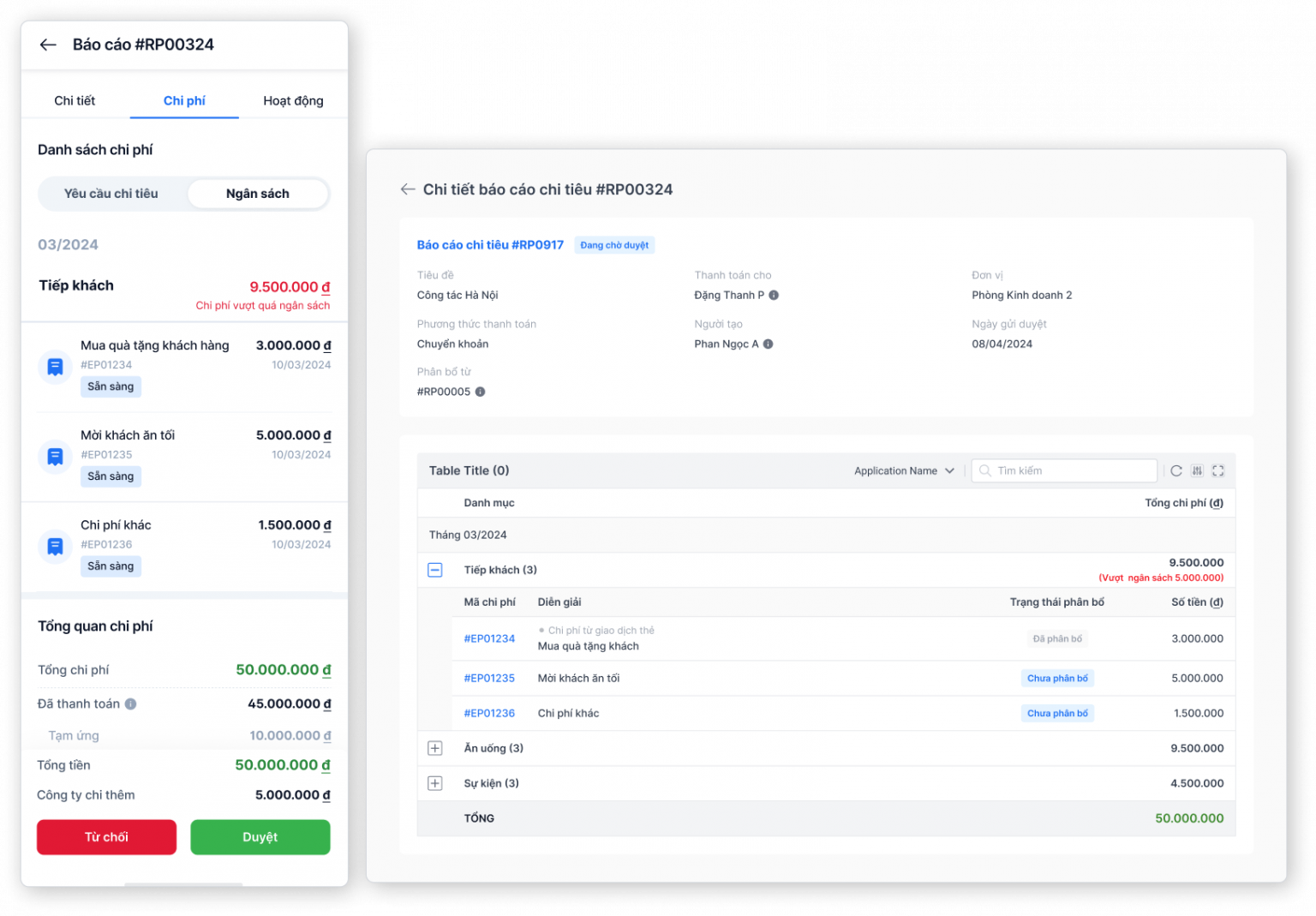
- Transparent cost approval and control: Bizzi offers flexible and transparent expense approval mechanisms. Managers can control budgets from the start, ensuring that all expenses are tracked and approved properly, avoiding cost overruns.
- Manage advance requests quickly and easily: Employees can easily create and submit advance requests for production activities. Detailed information and clear reasons help managers approve quickly, ensuring uninterrupted cash flow for production.
Practical example: Toyota Production System (TPS) – Lessons of success
Toyota is a global classic example of effective production management. The Toyota Production System (TPS), the foundation of Lean Manufacturing, has helped this giant achieve extraordinary results.
- Featured activities: Toyota was a pioneer in the application of Just-In-Time and Kaizen. They empowered workers, allowing them to stop the production line (Andon Cord) as soon as they detected a defect, ensuring that quality was “built in” to every step.
- Impressive results: The application of TPS has helped Toyota significantly reduce production time, increase productivity, and improve vehicle quality to the world's leading level. A study at the NUMMI joint venture plant (between GM and Toyota) showed that the rate of absenteeism decreased from 20% to only 2% and the labor cost to produce a vehicle decreased by nearly 50% after applying TPS.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Which KPI is most important in production management?
Important KPIs include Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE), First Pass Yield, Cycle Time, and Cost Per Unit. - Should small businesses invest in manufacturing management software?
Yes. There are many cost-effective software solutions (especially cloud-based SaaS solutions) that help small and medium-sized businesses standardize processes and manage effectively without large investments in infrastructure. - What is the biggest challenge when implementing production management?
The biggest challenge is often changing the culture and mindset of people. Implementation requires commitment from leadership, buy-in from all employees, and perseverance to get through the difficult initial stages.
Conclude
Production management is a continuous journey of planning, execution, measurement and improvement. In today's fiercely competitive environment, building an effective production management system, combined with the power of technology and digital transformation, is the most solid foundation for sustainable development and enhancing the competitiveness of enterprises.
To start your journey to cost optimization in manufacturing management, check out automation solutions from Bizzi.
- Sign up for a Bizzi product trial: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo for 1:1 consultation: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/
Read more:

