According to financial experts at Bizzi.vn – the leading B2B financial automation platform, Liquidity Ratio is an index that reflects the ability of a business to use short-term assets to pay short-term debts. This is a “health measure” that helps businesses assess their ability to maintain cash flow and prevent the risk of financial imbalance.
It is necessary to distinguish: Liquidity is related to short-term debt obligations, while solvency reflects long-term payment capacity. Therefore, this article by Bizzi will help you understand the concept clearly. What is the payment ratio?, how to calculate and the role of the payment ratio, thereby optimizing cash flow and making more effective financial decisions.
What is the payout ratio?
Payout coefficient is considered an important tool in the financial sector, helping to measure and evaluate the solvency of a business or organization. With another name is liquidity index, this is a tool that shows the ability of the business to repay short-term debts and ensure the balance between short-term assets and short-term debts. It is the ability to convert assets into cash to pay the debts of the business.
Liquidity ratios typically focus only on short-term debt-paying ability, since “liquidity” refers primarily to how quickly a business can convert assets into cash to pay debts due in less than 12 months.
Familiar coefficients: Current Ratio, Quick Ratio, Cash Ratio → compare Current assets with short term debt.
What is the data collected from the solvency ratios? These ratios provide important information for investors, banks and business managers to assess the business situation, ensuring the ability to meet financial obligations. The solvency ratio is divided into many different categories, corresponding to short-term debt and long-term debt.
What is the importance of liquidity ratio in financial analysis?
Solvency ratio is a core indicator in assessing financial health, especially in terms of short-term solvency and risk management.
- Short-term financial health assessment: This index plays an important role in assessing the financial health of a business in the short term. If the ratio < 1 → risk of insolvency. If the ratio is too high → it may show that capital is "frozen" in current assets and has not been used effectively.
- Measures short-term debt paying ability: Helps assess whether a business has the ability to pay short-term debts and payables within one year, ensuring financial stability and avoiding the risk of not being able to pay on time.
- Assess the balance between current assets and current liabilities: Allows assessment of the balance between short-term assets and short-term financial obligations, helping to maintain sustainable solvency and optimize the use of short-term assets.
- Financial risk forecasting and management: Assist in identifying potential future financial problems and taking preventive measures, adjusting financial plans accordingly.
- Support investment decisions and business expansion: Providing important information to investors, helping them to have more confidence in businesses with good liquidity ratios, thereby affecting their decisions to invest, borrow capital or expand business.
In general, to have a complete view, businesses need to combine other groups of indicators such as: profitability, operating efficiency, financial leverage.

What are the types of payout ratios?
Liquidity ratio is a core indicator in financial analysis because it reflects the ability of a business to maintain liquidity, manage short-term risks and ensure financial reputation. This is a key factor to maintain the trust of investors, banks and partners, and at the same time helps leaders make effective management decisions.
In addition to understanding the nature of the payment ratio, it is necessary to understand how many types of payment ratios are used for evaluation. Below are some payment ratios reflecting short-term debt, including:
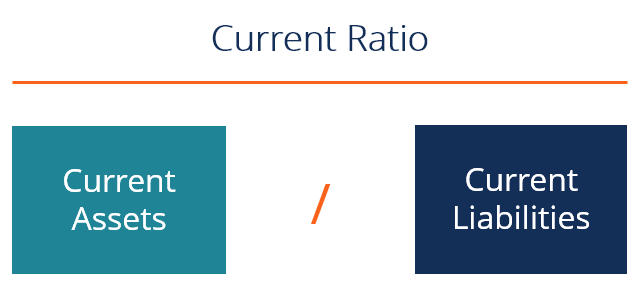
Current Ratio
- Concept: This is a useful tool to assess a business's short-term financial situation and short-term solvency (usually due within 1 year).
- Recipe: Current Ratio = Total Current Assets / Total Current Liabilities.
In there: Short-term assets include cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, short-term financial investments, inventories; Short-term liabilities include payables to suppliers, salaries, taxes, short-term loans.
- Meaning:
- > 1: Current assets exceed current liabilities, showing good debt servicing ability and stable financial situation.
- < 1: Short-term debt exceeds short-term assets, may have difficulty in paying debt, financial risk.
- Too high: May indicate inefficient use of short-term assets or liabilities, or failure to reinvest in production/business.
- Advantage: Easy to understand and calculate, forecast financial risks, measure solvency.
- Disadvantages:
- Does not provide details on the true liquidity of assets (inventory is difficult to convert).
- No consideration for profitability.
- Affected by depreciation.
- No distinction is made between combined and uncombined current assets.
- May not reflect properly if receivables are uncollectible or inventory is of poor quality.
- Can be formed from long-term debt or equity, not just short-term debt.
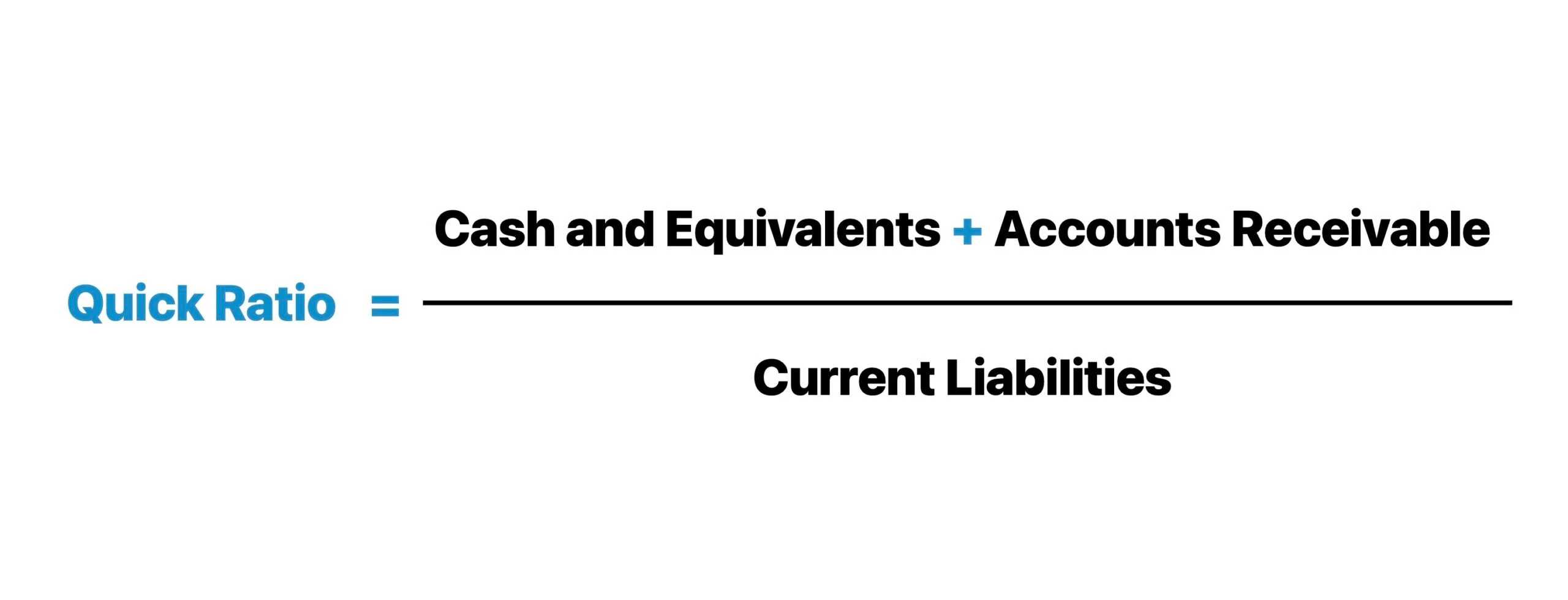
Quick Ratio / Acid-Test Ratio
- Concept: Measures the ability to immediately pay financial obligations without assistance from the sale of inventories.
- Recipe: Quick Ratio = (Total Current Assets – Assets Not Easily Converted to Cash (Inventories)) / Total Current Liabilities.
- Meaning:
- Measures immediate liquidity using only cash and cash equivalents.
- Reflects the ability to manage financial risks: Higher ratios indicate good financial management, maintaining liquidity.
- Important indicators for investors and borrowers.
- Optimal ratio: Usually 1:1.
- > 1: The business has the ability to quickly pay short-term obligations without using inventory, is flexible and stable.
- < 1: Businesses may encounter difficulties, risk having to sell inventory early, high financial risk.
- Too high: May indicate that the business is holding too much cash or liquid assets, not investing effectively in business operations.
- Advantage: Considers current assets that can be quickly converted into cash, a higher measure of liquidity.
- Disadvantages May be hampered by lack of quick assets, lack of overview of long-term financial situation.
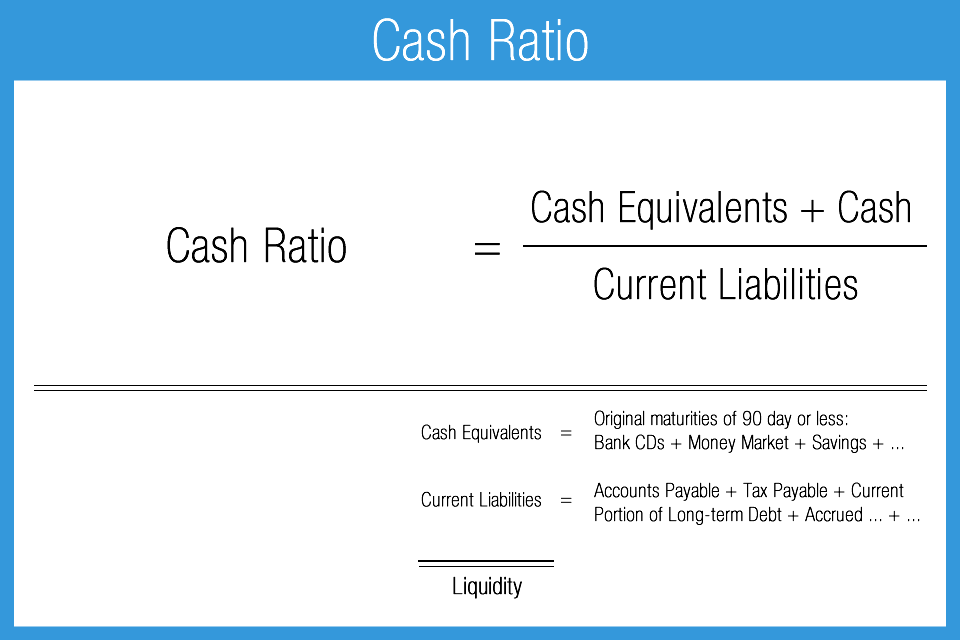
Cash Ratio
- Concept: Is a financial indicator that reflects the ability of a business to immediately use cash and cash equivalents (such as bank deposits, short-term highly liquid securities) to pay all short-term debts at a given time.
- Recipe: Cash Ratio = (Cash and cash equivalents) / Total current liabilities.
- Meaning: Indicates the ability to pay off debt immediately with cash only. The higher the ratio → the stronger the liquidity, but too high shows that capital has not been invested to generate profit.
- Advantage: Instant, simple and easy to understand credit assessment.
- Disadvantages: Does not consider other assets that can be converted to cash, does not reflect profitability.
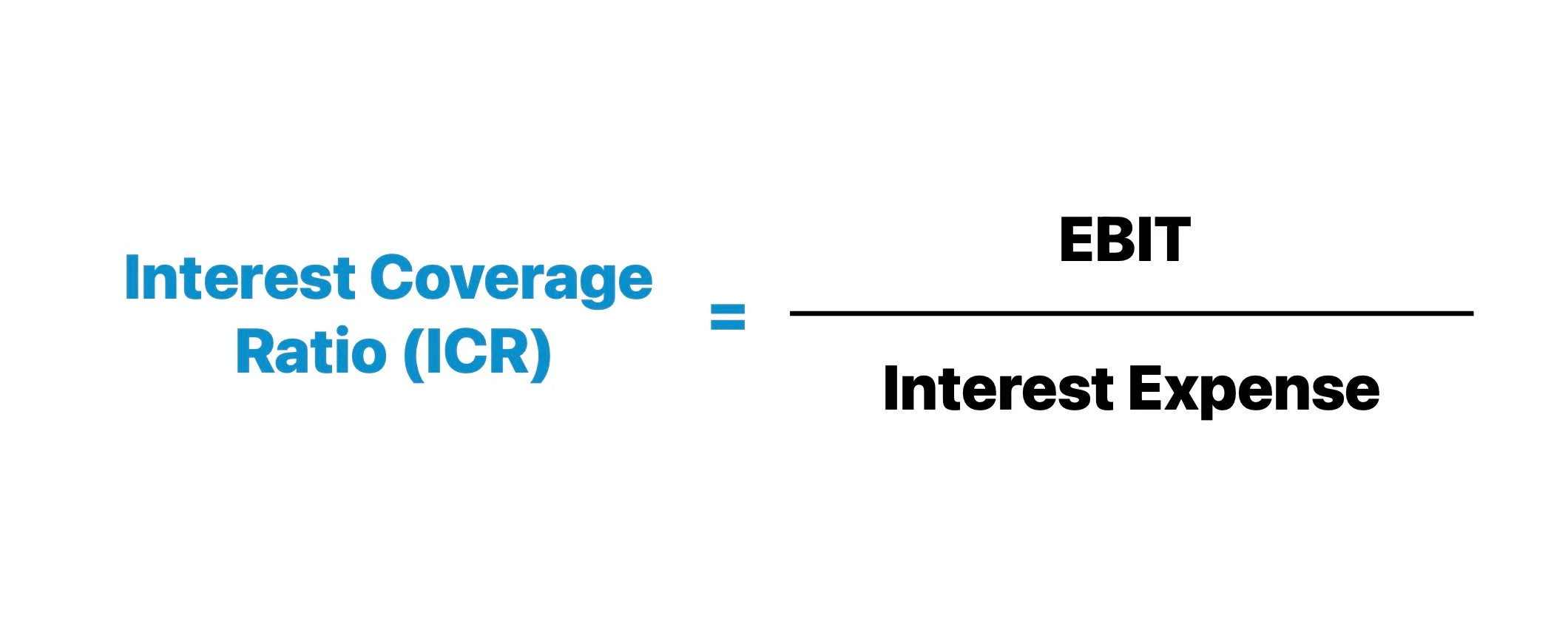
Interest Coverage Ratio
- Concept: Measures a company's ability to pay interest and annual debt payments from earnings or cash flow.
- Recipe: Interest Coverage Ratio = Earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) / Annual interest expense
- Meaning:
-
- > 1: The business generates enough income to pay interest expenses.
- < 1: The business does not generate enough income to pay interest on loans, the financial risk is great, and can lead to bankruptcy.
- Assess the safety level of the enterprise in meeting interest debt, measure financial stability and financial reserve level. This is an index that Banks/Credit Institutions are particularly interested in when evaluating loan applications.
- Aim to improve financial performance if the index is low.
- Limit: Does not consider changes in assets and liabilities, does not consider non-current assets that can be converted to cash.
Core Risks and Limitations: Why Can a Payout Ratio Look Good on Paper but Not in Real Money?
Although the payment ratio is an important tool to evaluate the financial health of a business, there are still misconceptions when analyzing the results. Many people often think that the payment ratio is "high is good, low is bad", but the reality is more complicated than that. Understanding the true nature of the payment ratio will help investors and managers more easily determine the financial capacity of the business.
Here are some of the challenges & opportunities when using payout ratios for valuation:
- Challenge:
- Short-term reflection only: Indexes such as Current Ratio, Quick Ratio... only measure the ability to pay. short term debt, does not fully reflect long-term financial health.
- Easy to be "deceived": Current assets may include bad receivables or illiquid inventory → make the ratio look good on paper but there is no real cash.
- Regardless of capital efficiency: Too high a ratio, for example a Current Ratio above 4, may signal Capital Tipping or Poor Inventory Turnover, indicating suboptimal asset utilization.
- Depends on the industry: Each industry has a different standard. A ratio of 1.1 may be acceptable for the Retail/Supermarket industry (due to fast cash flow) but is a big risk for the Industrial Manufacturing industry (requiring large working capital and inventories).
- Vulnerable to data manipulation: Businesses can “beautify” short-term financial reports (collect debts urgently, delay payments, etc.) to increase the coefficient at the time of reporting.
- Opportunity:
- Quick financial assessment tool: Just by looking at the coefficient, managers, investors, and creditors can immediately estimate the ability to pay.
- Early warning of risk: A persistently low ratio signals that the business is having cash flow difficulties → helping to detect problems early for handling.
- Build trust with investors & banks: A reasonable payment ratio proves that the business has a safe financial foundation, can easily raise capital or receive credit incentives.
- Management decision support: Help leaders consider increasing working capital, debt management, optimize inventory to improve cash flow.
- Combine with other indicators for comprehensive assessment: When combined with profitability, operating efficiency, and financial leverage, the liquidity ratio becomes an important piece in the overall financial health picture.
What is the accounting and management method for optimizing the payment ratio?
Optimizing and closely managing the payment ratio is a key factor to ensure financial sustainability, both maintaining reputation and creating a foundation for long-term growth. From the perspective of managers and accountants, below are some suggestions to contribute to optimizing these financial ratios:
For the Board of Directors, CFO or CEO
The board of directors, especially the CFO/CEO, not only plays the role of a supervisor but also a strategic decision maker, helping to improve the payment ratio proactively, sustainably, and in line with the development orientation of the business.
- Maintain a reasonable level of cash reserves:
- Do not let Cash Ratio get too low (risk of default).
- Not too high (idle money does not generate profit).
- Increase actual revenue and profit:
- Boost sales, expand market.
- Focus on products/services with fast cash flow.
- Restructuring short-term and long-term debt:
- Convert part of short-term debt into long-term debt to reduce immediate payment pressure.
- Use bank credit or credit lines to balance.
- Flexible investment:
- Deposit idle money into highly liquid channels (short-term deposits, certificates of deposit).
- Ensure liquidity and generate profits instead of leaving money lying around.
- Application of financial management technology:
- Use financial management software like Bizzi, Misa, Odoo for realtime monitoring.
Helps forecast cash flow and make quick decisions, reducing the risk of shortage.
- Use financial management software like Bizzi, Misa, Odoo for realtime monitoring.
For the accounting department
Accountants are considered the “keepers” of financial data, so they can:
- Tight cash flow management:
- Prepare cash flow statements regularly.
- Forecast short-term income and expenses to avoid shortages.
- Shorten time debt collection (Accounts Receivable):
- Track payment deadlines and remind customers.
- Apply early payment discount.
- Control expenses & accounts payable:
- Negotiate extended payment terms with suppliers.
- Classify your debts to prioritize paying off important ones.
- Accurately record and classify assets:
- Ensure cash and cash equivalents are accounted for correctly (not mixed with less liquid items).
- Monitor inventory to avoid capital being "dead" in poorly turned goods.
Optimize working capital and improve payment ratios with Bizzi.vn automation (Expertise Node)
Faced with the challenges of using payment ratios to assess the financial health of a business, applying cost and financial management automation solutions simultaneously is a smart choice to address the above limitations. Not only does it help businesses track financial data transparently and accurately, but technology software also plays a proactive role in improving payment indicators.
Among the current financial management software, Bizzi.vn is a prominent and powerful tool that helps businesses improve their financial health and optimize payment ratios through automating core processes, ensuring liquidity and maintaining competitive advantages. Bizzi provides solutions:
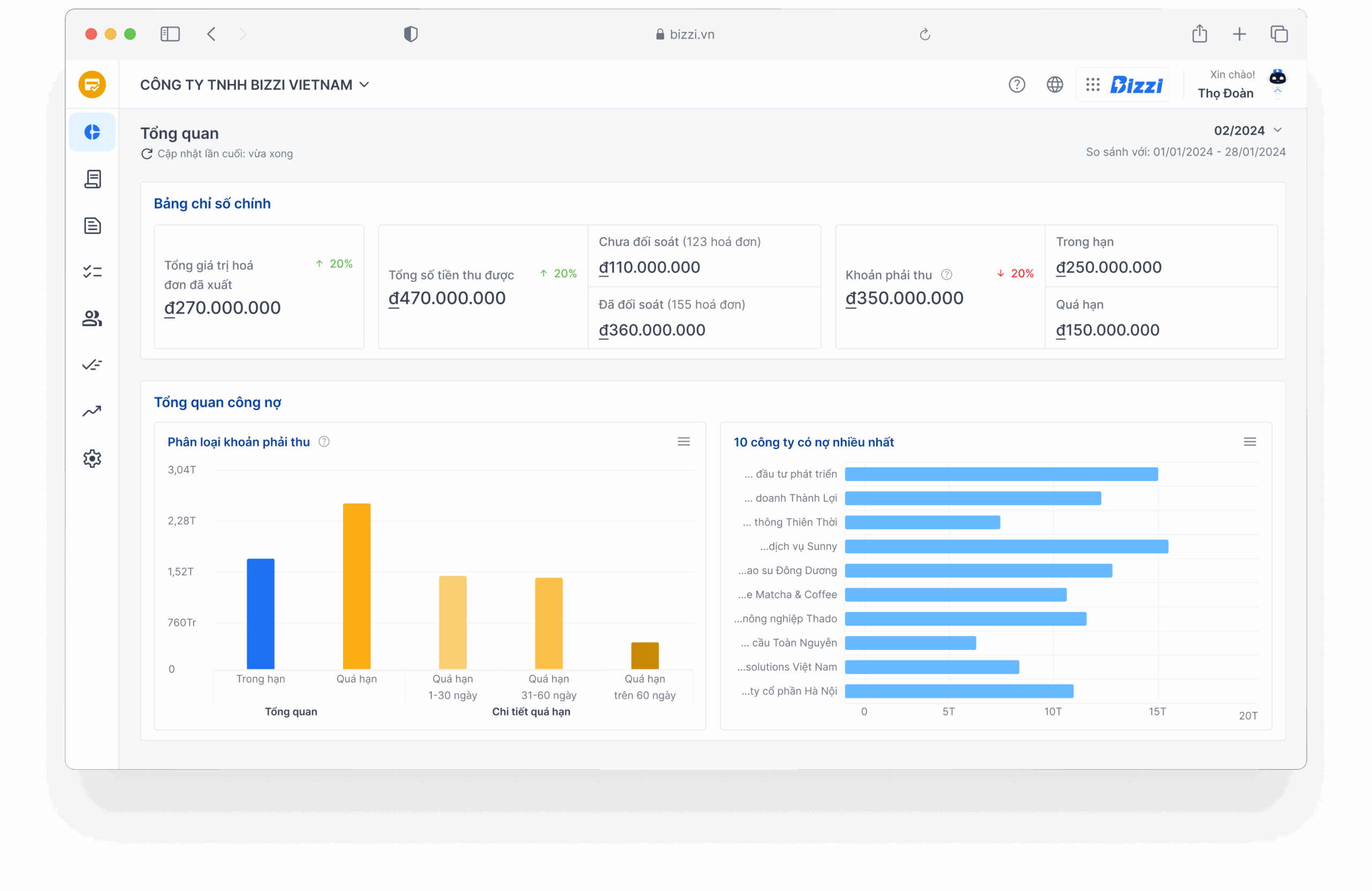
Among the current financial management software, Bizzi.vn is a prominent and powerful tool that helps businesses improve their financial health and optimize payment ratios through automating core processes, ensuring liquidity and maintaining competitive advantages. Bizzi provides solutions:
- Comprehensive cost control system: AI assistant for finance and accounting departments to automate revenue and expenditure processes and is a platform that integrates 30+ features to streamline and automate cost management, debt collection and B2B payments.
- Processing and managing input invoices (IPA + 3-way matching): Automatically process, check, reconcile invoices with PO and GR, verify suppliers, alert on risky invoices, integrate API with ERP & Accounting. This helps to tightly control payables, ensure accurate short-term debt figures, thereby helping to calculate payment indexes more effectively.
- Business expense management (Bizzi Expense): Set up budgets, monitor expenses, automatic approval systems, real-time expense tracking, expense reports, spending policies and over-budget alerts. Help businesses manage short-term expenses well, keep cash and highly liquid assets.
- Business Travel Management (Bizzi Travel): Automatic flight booking, business expense management, spending limits, approval process. Helps control unexpected expenses, directly affecting cash flow.
- Electronic invoice (B-invoice): Create, manage, store, and look up electronic invoices. Ensure transparency and accuracy of transactions, contributing to cash flow tracking.
Solutions like Bizzi help increase cash and cash equivalents (components of Cash Ratio) by automating Accounts Receivable (A/R) reconciliation and payments, shortening the collection cycle. At the same time, tight control input invoices and Accounts Payable (A/P) helps manage short-term debt accurately. Business expense management (Bizzi Expense) also helps businesses optimize short-term costs, ensuring cash flow is always at an optimal level.
Conclude
In short, if liquidity ratios are the Life and Death indicators of liquidity, then ignoring real-time data from automated platforms like Bizzi is the biggest cash flow management risk for CFOs in volatile markets. It is important to combine the analysis of these metrics with other financial metrics and the overall business context to get a comprehensive view and make accurate decisions.
Simultaneously applying cost and financial management automation solutions such as Bizzi.vn is a powerful tool that helps businesses not only monitor but also proactively improve payment indicators, optimize operational performance and minimize financial risks in an uncertain business environment.
To get advice on suitable solutions and experience all the features of Bizzi, register to make an appointment here: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/


