Project management costs are not an additional cost but a core part of ensuring the success of the project. Investing properly and reasonably in management not only helps the project run smoothly but also saves costs in the long run.
This article by Bizzi will provide all the information related to the concept, how to plan project management costs as well as the most effective and optimal management methods.
What is project management cost? Meaning and role of project management cost
Project Management Cost are payments for project management personnel, software systems, facilities, equipment, administrative costs and other indirect costs serving project management from start to finish.
Project management costs typically include:
- Project Management Salary and Allowances
- Administrative costs: stationery, electricity, water, communication…
- Project management office/location rental costs
- Cost of training, meetings, testing, supervision
- Cost of using management software and support tools
Legal costs, consulting, reporting, completion documents...

Meaning and role of project management costs:
- Ensuring project progress and efficiency: The project is closely monitored and problems are quickly resolved thanks to an effective management team; helping to maintain this activity in a stable and organized manner.
- Increase transparency and financial control: Separating management costs helps businesses monitor and account clearly, without mixing them with construction or operating costs. At the same time, it is the basis for project settlement and auditing later.
- Contribute to improving project quality: Good management helps detect risks and errors promptly → improve the quality of construction and project output.
- Legal and financial basis when establishing and approving a project: In project establishment documents (especially public investment and construction), project management costs are mandatory items that require detailed estimates.
- Support for measuring project management effectiveness
- If management costs are low but the project is behind schedule and errors arise → management is not effective.
- If the management cost is reasonable and helps optimize the entire project → it creates much higher value than the cost.
Project management cost classification
Classifying project management costs helps businesses or investors easily plan, monitor, control and settle costs for each stage and each specific item. Below are common ways to classify project management costs:
Classification by cost content
Based on the content, project management costs include the following types:
- Management personnel costs: Salary, bonus, allowance, insurance of Project Manager, Coordinator, Project Accountant, Secretary, Assistant,... Quality Management Expert, Technical, Documentation...
- Office administration costs: Office rental, office equipment, Electricity, water, internet, stationery, Logistical costs for project management
- Operation and work organization costs: Internal meetings, technical seminars, Travel expenses, business expenses, Communication costs, mailing, printing documents
- Cost of management tools and software: Project management software (MS Project, Primavera, Jira…), Computers, management support equipment, Maintenance costs, software updates
- Consulting and legal fees: Bidding consultancy, preparing bidding documents; Audit consultancy, lawyers, legal support experts; Project completion consultancy, acceptance and settlement
- Inspection and monitoring costs: Internal inspection; Control progress, quality, labor safety; Risk assessment, periodic inspection
Classification by project phase
Classifying project management costs by stage helps businesses closely monitor budgets, effectively control spending, and accurately evaluate management efficiency according to progress. Below are common classifications by stage of the project life cycle:
| Stage | Cost Type |
| Investment preparation stage | – Cost of investment reporting
– Project planning – Legal advice |
| Investment implementation phase | – Management and operating costs
Construction supervision – Meeting |
| Project Completion Phase | – Prepare settlement documents
– Performance evaluation – Completion report |
Classification by cost nature
Classifying project management costs according to cost nature helps business accounting and finance record, account for and analyze costs effectively, while also serving budget control and strategic decision making.
Here are the most common classifications by nature:
- Direct Costs:
– Expenses directly related to project proposal, development and implementation (purchase of raw materials, equipment, hiring of labor, payment of suppliers).
– Varies according to project size or volume.
- Indirect Costs:
– Expenses that are not directly related to a specific cost object but still contribute to the success of the project (utilities, insurance, maintenance, benefits, taxes, marketing).
– Usually applies to both short-term and long-term, is mostly fixed and easy to predict and control.
- Fixed Costs:
– Unchanged throughout the project life cycle, regardless of size or output (software fees, vendor payments, administration, salaries, utilities, insurance).
– Important for long-term forecasting.
- Semi-Variable Costs:
– Combine fixed and variable costs, stable at a given output level but increasing above a threshold (logistics, facility rental, electricity, depreciation).
- Variable Costs:
– Varies by project volume or scope, directly related to cost objects (raw materials, packaging, logistics, labor, utilities, commissions).
– Comparison with fixed costs helps allocate resources reasonably.
- Sunk Costs:
– Expended in the past and irrecoverable, not affecting current or future decisions (machinery costs, rent paid).
- Total Project Costs:
– Includes all costs, fees and resources required to complete the project (fixed, variable, direct, indirect, risk management, design, development, operations, contingencies).
– Helps determine schedules and forecast feasibility.

05 steps to effective project cost management planning
Effective project cost management planning is one of the key factors in ensuring that the project stays on budget, uses the right resources, and meets financial goals. Here are the basic but comprehensive steps in this process:
Step 1: Determine the scope and basis of cost planning
- Define project objectives and scope of work to be performed.
- Identify related factors: implementation time, work scale, resources, human resources, technical requirements...
- Collect input documents: Feasibility study report; Project master plan; Technical specifications, design drawings; Contract (if any)
Step 2: Identify and analyze cost types
- Direct costs (construction, materials, labor, etc.)
- Indirect costs (management, office, outsourcing…)
- Contingency costs (for risks, price fluctuations…)
- Project management costs (mentioned above)
Step 3: Cost Estimating
- Estimate costs by item, phase or WBS (Work Breakdown Structure). Using the method:
– Analogous Estimating
– Bottom-Up Estimating
– Parametric Estimating
- Output: Detailed cost estimate table, can be attached with chart or Excel file.
Step 4: Cost Budgeting
- Summarize the estimated costs → to form the overall project budget.
- Cost allocation by: Phase (quarter/month) – Work item – Responsible department
- Ensure reasonable budget allocation and flexibility in adjustment.
Step 5: Establish a Cost Control Plan
- Set a Cost Baseline to track actual vs. planned.
- Building measurement indexes: CPI (Cost Performance Index) – cost efficiency index; CV (Cost Variance) – cost difference
- Establish reporting processes, change approvals, and cost risk management.
- Use tools: cost management software such as MS Project, Primavera, Excel…

Tips for effective project management cost control planning
Here are some extremely useful tips to help you plan project management cost control effectively, realistically, and easily implemented, even for non-finance teams:
| Tips | Explain |
| Clear scope – clear cost | Avoid uncontrolled expansion. |
| Reasonable risk provision | Always have a “buffer” cost for unexpected situations. |
| Regular monitoring | Create a budget vs. actual chart (Earned Value Chart). |
| Interdepartmental coordination | Helps estimate costs more accurately thanks to departmental expertise. |
| Archive and learn from old projects | Data from previous projects helps increase the accuracy of estimates. |
Project management cost calculation methods
Choosing the right project management costing method will help businesses easily estimate budgets, control expenses and optimize financial efficiency. Below are the most popular methods today, used depending on project type, complexity and available data:
| Method | Describe | Advantage | Disadvantages |
| Percentage (%) of total project cost | Calculate project management costs based on a fixed percentage or a prescribed framework compared to the total investment or total construction cost. | Easy to apply, fast, simple
Suitable for small or medium projects |
Does not fully reflect the complexity of the project
Can lead to under or over budget for management if not adjusted properly |
| Bottom-up Estimating | Identify each specific activity in project management, then calculate the cost according to the time and resources required for each activity.
Often associated with a work breakdown structure (WBS) |
Accurate, specific
Suitable for large, complex projects or those requiring high transparency |
Time consuming, requires data and planning experience |
| State norms/regulated unit prices | Apply legal documents or specialized norms that specifically regulate project management costs for each type (especially public investment and basic construction). | Suitable for government projects, easy to audit Have clear legal basis |
Lack of flexibility in the practical conditions of private enterprises May not reflect actual costs incurred. |
| Analogous Estimating | Use experience from previous similar projects to estimate new project management costs. | Fast, easy to do Suitable when quality historical data is available |
Accuracy is not high if the project has different characteristics. |
| Parametric Estimating | Use parameter indexes (such as management costs by number of employees, time, workload, etc.) to calculate. | Accurate if reliable data are available Can be automated with software |
Accurate statistical data is needed for modeling. |
Project management cost estimate
Project management cost estimation is an extremely important step to ensure that the project is implemented on budget and avoid uncontrolled cost loss. Below are detailed steps and notes to help you estimate project management costs scientifically and realistically:
- Cost estimate: Forecast the quantity and cost of all resources needed before the project begins.
- Note when estimating:
– Cost accuracy: Estimates are close to reality.
– Time accuracy: Based on experience.
– Be precise about requirements and constraints: Understand requirements clearly to avoid errors.
- Cost estimation methods:
– Expert review.
– Quality costs (risk prevention).
– Analysis of supplier bids (public projects).
– Use budgeting software.
– Reserve analysis (risk response).
– Three-point estimate (optimistic, pessimistic, most likely).
– Parameter estimation (statistical model).
– Top-down budgeting: Estimate total costs and allocate them.
– Bottom-up budgeting: Estimate the cost of each work package and then summarize.
Project management cost standards
Project management cost norms are rates or cost levels determined according to regulations of competent state agencies or internal enterprise standards, to serve the preparation, appraisal, approval and settlement of costs related to management work throughout the project life cycle.
Project management cost norms according to state regulations (for public investment and construction projects)
According to Circular 11/2021/TT-BXD issued by the Ministry of Construction, project management cost norms are prescribed as follows:
- For group A, B, C projects (according to investment scale)
| Total investment (TMTD) | Maximum project management cost ratio |
| Up to 15 billion VND | 2.5% TMTD |
| Over 15 billion to 100 billion VND | 2.0% TMTD |
| Over 100 billion to 500 billion VND | 1.5% TMTD |
| Over 500 billion VND | 1.0% TMTD |

- For projects using other budget capital:
Project management costs are still applied according to the above standards or according to the instructions of the industry's governing ministry, such as the Ministry of Transport, Ministry of Health, Ministry of Education and Training, etc.
Project management cost norms in private enterprises or other industries
For project types such as: Technology, software, marketing, startup projects; Internal implementation projects (no construction investment); Non-governmental or international funding projects (ODA, NGO...). Usually there will be no specific state regulations, but internal norms or international standards will be applied such as:
| Project Type | Suggested project management cost norms |
| IT Project | 5 – 15% total project budget |
| Marketing project | 7 – 12% campaign budget |
| Startup project | Calculated by number of employees × time |
| Aid project (ODA/NGO) | According to the instructions of the sponsoring organization (WB, ADB, UN...) |
Are project management costs taxable?
Whether project management costs are taxable or not depends on the regulations on value added tax (VAT) and corporate income tax (CIT) in each specific case. Specifically:
For value added tax (VAT)
- Project management costs may be subject to VAT if they relate to VAT-taxable services.
- Services such as consulting, planning, supervision or administrative services for projects may be subject to VAT at the rate of 10% (according to current regulations of Vietnam).
For corporate income tax (CIT)
- Project management costs are reasonable costs in determining taxable income of the enterprise. If these costs are reasonable and directly related to project implementation, they will be deducted when calculating corporate income tax.
- Specifically, when preparing financial statements and tax settlements, reasonable project management costs will be deducted from pre-tax income, helping to reduce the enterprise's corporate income tax obligations.
Cases not subject to tax
- Expenses related to non-commercial activities, such as internal business expenses that do not result in a purchase or sale transaction.
- Expenses related to tax-exempt services (such as certain educational, medical or charitable activities).
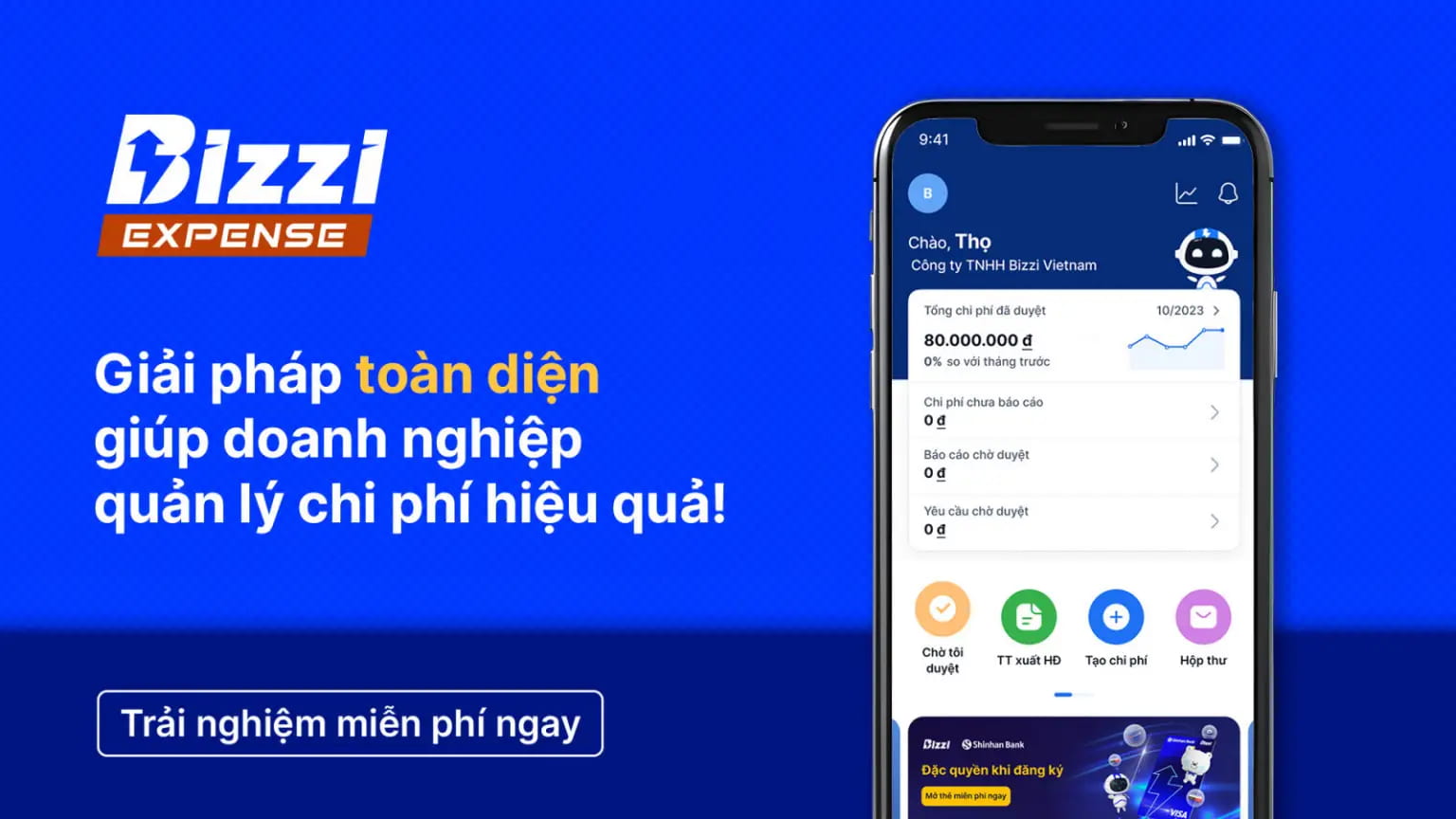
Bizzi Expense: Outstanding Project Expense Management Tool for Businesses
Bizzi Expense is a modern cost management tool that helps Vietnamese businesses optimize spending and improve financial efficiency. With its outstanding features, Bizzi Expense has helped many businesses reduce the burden of manual cost management.
Key features of Bizzi Expense:
- Spending control and irregularity alerts: Bizzi Expense allows businesses to declare spending categories and set up appropriate spending policies. The system will automatically detect and warn of unusual or over-budget spending, helping businesses control costs and avoid waste.
- Track and report expenses: Bizzi Expense's application supports multiple platforms such as web, smartphone and tablet, making it easy to collect invoices and create expense reports. In particular, the QR code scanning feature and individual email for each user help collect invoices quickly, ensuring accuracy and minimizing errors in expense recording.
- Flexible budget and spending policy management: Bizzi Expense allows you to set up budgets for each department, project and specific spending category in the fiscal year, helping businesses proactively manage and allocate financial resources appropriately. The intuitive management dashboard allows you to monitor the budget situation in real time, supporting quick decision making.
- Easily integrate and customize expense approval workflows: Bizzi Expense supports a flexible approval process, allowing you to configure different approval criteria and levels, allowing expense approvals to be done anytime, anywhere. This feature helps to reduce complex approval steps and save time on expense processing.
- Process automation and optimization: Bizzi Expense's automation feature saves businesses time, reduces manual work, and ensures high accuracy in expense management. This allows finance teams to focus on more strategic tasks instead of dealing with manual reports and paperwork.
Conclude
Technology is increasingly playing a key role in transforming the way businesses manage costs. Technology applications and cost management tools such as Bizzi Expenses play a key role in improving project cost management efficiency, optimizing workflows, and helping project managers achieve financial goals with accuracy and transparency.
Bizzi Expense Provides detailed analysis of cost types, cost trends over time, and comparisons with previous projects, helping to make strategic decisions to optimize costs. At the same time, detect financial risks at an early stage, so that early intervention measures can be taken to minimize losses.
Ready to take control of your business finances? Schedule a demo with Bizzi Expense today and discover how our innovative solutions can help you navigate the complexities of expense management with ease!


