Electronic invoices are becoming an inevitable trend in the digital transformation process of enterprises. To ensure transparency and efficiency in tax management, the Ministry of Finance has issued Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC, detailing the use of electronic invoices, methods of transferring data to tax authorities, as well as criteria for service providers.
So, what should businesses pay attention to in order to comply with the regulations? In the article, Bizzi below will help you understand the important content of Circular 78, how to implement it and the optimal solutions to apply electronic invoices in the most convenient way.
1. Overview of Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC
On September 17, 2021, the Ministry of Finance issued a Circular to guide the implementation of a number of articles of the Law on Tax Administration and Decree 123/2020/ND-CP related to invoices and documents. This Circular officially takes effect from July 1, 2022, creating an important legal basis for organizations and individuals to properly apply regulations in tax administration.
The highlight of this document is the encouragement to apply electronic invoices, especially for units with sufficient IT infrastructure conditions, to promote digital transformation and modernize financial management.

2. New and noteworthy points in Circular 78 on electronic invoices
2.1 Compulsory application of electronic invoices
According to Decree 123/2020/ND-CP and Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC of the Ministry of Finance, all enterprises, economic organizations, business households and individual businesses are required to switch from paper invoices to electronic invoices from the date of 07/01/2022.
The implementation roadmap is divided into two phases:
Phase 1 (from November 2021 - March 2022)
Pilot implementation in 06 key provinces and cities: Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, Phu Tho, Binh Dinh, Hai Phong, Quang Ninh.
The goal of this phase is to test the system, ensure that businesses and tax authorities can adapt to the use of electronic invoices, and detect and fix any technical issues that arise.
Phase 2 (from April 2022 – July 2022)
After completing the trial phase, from April 2022, the application of electronic invoices will be expanded to all remaining provinces and cities across the country. All enterprises, organizations, and business households must complete the conversion to electronic invoices before the date of 07/01/2022.
2.2 Electronic invoice template
Electronic invoices in Vietnam are managed under the Law on Tax Administration and Decree 123/2020/ND-CP, with specific regulations on electronic invoice forms and symbols for standardization and classification.
Electronic invoice symbol
The symbol consists of 6 characters:
- “T”: Regular electronic invoice.
- “D”: Special electronic invoices (used in some specific industries).
- “L”: Electronic invoices for retail activities.
- “M”: Electronic invoice for cash register.
- “N”: Electronic invoices used in the energy sector.
- “B”: Electronic invoices in the insurance sector.
- “G”: Electronic invoices in the field of transportation.
- “H”: Electronic invoices in the aviation sector.
For example: C25TAA is an invoice with code, issued in 2025, regular type.
Electronic invoice sample number symbol
The denominator is a digit from 1-6:
- No.1: Electronic value added tax (VAT) invoice - the most common type of invoice, used in transactions of buying and selling goods and services subject to VAT.
- Number 2: Electronic sales invoice - applicable to organizations and individuals trading in goods and services not subject to VAT.
- No.3: Electronic public property sale invoice - used in transactions related to public property according to the provisions of law.
- Number 4: Electronic national reserve sales invoice – for the sale of goods in the national reserve list.
- Number 5: Other types of electronic documents such as electronic stamps, electronic tickets, electronic cards, electronic receipts or documents with content equivalent to invoices, depending on the field of operation.
- Number 6: Electronic internal delivery and transportation note or electronic delivery note for goods sent to agents for sale – often used internally within a business or with distribution agents.

2.3 Authorization to create electronic invoices
Authorizing the creation of electronic invoices is when a business or economic organization authorizes a third party (the authorized party) to create electronic invoices on its behalf when providing goods or services. This authorization is intended to support businesses in their business activities, reduce the process of creating invoices, and ensure legality.
The proxy invoice must meet the following requirements:
- Fully display the name, address, and tax identification number of both the principal and the agent.
- There must be clear information about the electronic invoice, including: invoice type, invoice symbol, invoice number symbol.
- The delegation must be made in writing between the two parties in the form of a specific contract or agreement.
The authorization document for electronic invoice issuance must include the following important contents:
(1) Information about the principal and the authorized party
- Company/Organization Name
- Business registration address
- Tax Identification Number (MST)
- Information about digital certificates
(2) Information about authorized electronic invoices
- Invoice type (VAT invoice, sales invoice…)
- Invoice symbol
- Invoice number symbol
(3) Purpose of authorization
- Identify the reasons why a business needs to outsource e-invoicing, such as reducing workload, optimizing accounting processes, or assisting in business operations.
(4) Term of authorization
- Determine the validity period of the contract/agreement, which can be monthly, yearly or indefinitely depending on the agreement between the two parties.
(5) Payment method of authorized invoice
- Regulations on payment methods between related parties, including bank transfer, cash or other forms in accordance with law.
Authorizing the issuance of electronic invoices is considered a change in the registration information for using electronic invoices. Therefore, both the authorizing party and the authorized party are obliged to notify the direct tax authority. This notification is to ensure that the use of electronic invoices is carried out in accordance with legal regulations and avoid unwanted violations.

2.4 Handling of Incorrect Invoices
According to Circular 78 on electronic invoices (Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC), the handling of electronic invoices sent to tax authorities when errors are detected is specifically guided as follows:
Use Form No. 04/SS-HĐĐT to notify error correction.
Sellers can use Form No. 04/SS-HDDT to notify the adjustment for each invoice or multiple invoices with errors. This notification must be sent to the tax authority no later than the last day of the VAT declaration period in which the adjusted electronic invoice is generated.
Processing invoices when service is canceled
If the seller issues an invoice when collecting money in advance or while providing a service, but the service is later canceled, the seller must cancel the issued electronic invoice and notify the tax authority using Form No. 04/SS-HDDT.
Handling errors that arise after adjustment or replacement
If an erroneous electronic invoice has been processed by adjustment or replacement, but additional errors are later discovered, subsequent processing will be carried out in the same manner as the first time.
In case the invoice lacks the sample number symbol, invoice symbol, invoice number
In case the electronic invoice is created without the invoice number symbol, the invoice symbol, or the invoice number is incorrect, the seller only needs to make adjustments without canceling or replacing it.
Compliance with the above instructions helps businesses promptly and accurately handle errors related to electronic invoices, ensure compliance with legal regulations and avoid unnecessary risks.
2.5 Regulations on the time of invoice issuance for banking services
According to Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC, enterprises and economic organizations can authorize a third party to issue electronic invoices during the sale of goods and provision of services. This authorization helps optimize the invoice management process and ensure compliance with current legal regulations.
Contents of authorization invoice:
The authorized electronic invoice must include complete information about both the authorizing party and the authorized party, specifically:
- Name, address and tax identification number of the principal.
- Name, address and tax identification number of the authorized party.
This ensures transparency and clarity in business transactions.
Authorization procedure:
The authorization to issue electronic invoices must be made in writing in the form of a contract or agreement between the two parties, including the following main contents:
- Information about the parties: Name, address, tax identification number and digital certificate of the authorizing party and the authorized party.
- Information about authorized electronic invoices: Invoice type, invoice symbol and invoice sample number symbol.
- Purpose of authorization: The reason and scope of work that the authorized party will perform.
- Term of authorization: The start and end time of the assignment.
- Payment method of authorized invoice: Payment methods and conditions between the parties involved.
Drawing up a detailed authorization document helps to clearly define the responsibilities and rights of each party, while minimizing risks during the cooperation process.
Notice to tax authorities:
Authorizing the issuance of electronic invoices is considered a change in the registration information for using electronic invoices. Therefore, both the authorizing party and the authorized party must notify the direct tax authority in accordance with the provisions of Article 15 of Decree 123/2020/ND-CP. This ensures that the tax authority promptly grasps and manages changes related to the use of electronic invoices by enterprises.
Strict compliance with regulations on electronic invoice authorization not only helps businesses operate more effectively but also ensures transparency and legality in business transactions.

2.6 Electronic invoice from cash register
Electronic invoices with tax authority codes generated from cash registers must comply with Article 11 of Decree 123/2020/ND-CP and Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC.
Applicable objects:
Enterprises, households and individuals doing business pay taxes according to the declaration method and provide goods and services directly to consumers.
Required content on invoice:
- Name, address, tax identification number of seller.
- Buyer information (if required).
- Name of goods, services, unit price, quantity, payment price.
2.7 Expired documents
| STT | Legal documents expire from July 1, 2022 | Regulation content |
| first | Decree 51/2010/ND-CP | Regulations on invoices for sale of goods and provision of services. |
| 2 | Decree 04/2014/ND-CP amending and supplementing a number of articles of Decree 51/2010/ND-CP | Regulations on invoices for sale of goods and provision of services. |
| 3 | Decree 119/2018/ND-CP | Regulations on electronic invoices when selling goods and providing services continue to be effective until June 30, 2022. |
| 4 | Decision 30/2001/QD-BTC dated April 13, 2001 of the Ministry of Finance | On promulgating the regime of printing, issuing, managing and using tax stamps. |
| 5 | Circular 191/2010/TT-BTC dated December 1, 2010 | Instructions for management and use of transport invoices. |
| 6 | Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC dated March 14, 2011 of the Ministry of Finance | Instructions on creating, issuing and using electronic invoices for selling goods and providing services. |
| 7 | Circular 39/2014/TT-BTC dated March 31, 2014 of the Ministry of Finance | Amended and supplemented by Circular No. 119/2014/TT-BTC dated August 25, 2014, Circular No. 26/2015/TT-BTC dated February 27, 2015 of the Ministry of Finance. |
| 8 | Decision 1209/QD-BTC dated June 23, 2015 of the Minister of Finance | On the pilot use of electronic invoices with tax authority authentication codes. |
| 9 | Decision 526/QD-BTC dated April 16, 2018 of the Minister of Finance | On expanding the scope of pilot use of electronic invoices with tax authority authentication codes. |
| 10 | Decision 2660/QD-BTC dated December 14, 2016 of the Minister of Finance | On the extension of implementation of Decision No. 1209/QD-BTC dated June 23, 2015. |
| 11 | Circular 303/2016/TT-BTC dated November 15, 2016 of the Ministry of Finance providing guidance | On printing, issuing, managing and using all types of documents for collecting fees and charges belonging to the state budget. |
| 12 | Circular 37/2017/TT-BTC | Amending and supplementing Circular 39/2014/TT-BTC (amended and supplemented by Circular 119/2014/TT-BTC dated August 25, 2014, Circular 26/2015/TT-BTC dated February 27, 2015 of the Ministry of Finance). |
| 13 | Circular 68/2019/TT-BTC | Guidance on the implementation of a number of articles of Decree 119/2018/ND-CP dated September 12, 2018 of the Government regulating electronic invoices. |
| 14 | Circular 88/2020/TT-BTC amends and supplements Article 26, Circular 68/2019/TT-BTC | Guidance on the implementation of a number of articles of Decree 119/2018/ND-CP regulating electronic invoices. |
2.8 Transfer of invoice data to the Tax authorities
Sellers using electronic invoices without codes must transfer data to the tax authorities. Data transfer is done via the General Department of Taxation's Electronic Information Portal, which can be transferred directly or through an organization providing electronic invoice services.
2.9 Criteria for organizations providing electronic invoice services
Organizations providing electronic invoice services must meet the following criteria:
- As a business operating in the field of information technology, there is public service information.
- Have at least 5 university-level personnel majoring in information technology.
- Have technical infrastructure and software that meet the requirements for creating, processing, storing electronic invoice data, connecting and transmitting data with users and tax authorities.
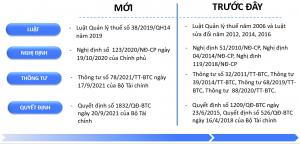
3. Compare Circular 78 on electronic invoices with previous Decree 123/2020/ND-CP
Time limit for applying electronic invoices:
- Previously, according to Decree 119/2018/ND-CP, the mandatory deadline for switching to electronic invoices was November 1, 2020. However, Decree 123/2020/ND-CP has adjusted this deadline to July 1, 2022.
Electronic invoice number:
- According to both Decree 119/2018/ND-CP and Decree 123/2020/ND-CP, the invoice number consists of a maximum of 8 digits, from 1 to 99,999,999.
- Enterprises start numbering from 1 on January 1 or the date of invoice usage and end on December 31 of each year. If this principle is not followed, the electronic invoicing system must ensure that invoice numbers increase over time and each number is used only once.
Time of digital signature and electronic invoice creation:
- According to Decree 119/2018/ND-CP, the time of issuing an electronic invoice is determined by the time the seller signs the invoice.
- Decree 123/2020/ND-CP and Circular 78 on electronic invoices continue to provide detailed regulations on the time of issuing electronic invoices, ensuring consistency with actual business operations.
Handling the transition from old to new regulations:
- Enterprises that are using paper invoices or electronic invoices according to the old circular can continue to use them until they switch to electronic invoices according to Circular 78 on electronic invoices and receive a notice of acceptance of registration to use invoices according to Decree 123/2020/ND-CP. After that, the enterprise must destroy the remaining paper invoices.
Register and manage invoice templates:
- According to Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC, enterprises must notify the issuance of invoices with the form and registered invoice number range. Meanwhile, Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC only requires enterprises to register to use electronic invoices with tax authorities through an electronically signed registration form, without requiring the registration of invoice forms.
- Handling Invoices with Errors:
- According to Circular 32/2011/TT-BTC, the handling of erroneous invoices depends on whether the invoice has been declared for tax or not and the level of error. Meanwhile, Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC allows users to choose to replace or adjust invoices regardless of whether tax has been declared or not.
These changes aim to facilitate businesses in implementing and managing e-invoices, while ensuring transparency and efficiency in tax management.
4. Bizzi – Solution to help businesses comply with Circular 78 on electronic invoices
In the context of increasingly strict regulations on electronic invoices, businesses need a flexible and effective solution to comply with Circular 78. Bizzi is the optimal choice to help automate processes, manage invoices easily and ensure compliance with legal regulations.
Automate the billing process: Bizzi helps businesses fully automate the process of processing input and output invoices, minimizing errors compared to manual processing. As a result, businesses can save time, optimize resources and strictly comply with the regulations of Circular 78.
Meet the technical requirements:
Bizzi ensures to fully meet the requirements on format, storage, and transmission of electronic invoices as prescribed in Circular 78, including:
- XML format standard as specified.
- Digital signature ensures legality.
- Connect directly with tax authorities to send, receive and look up invoices quickly.
Centralized invoice management:
The Bizzi system provides a centralized invoice management platform, making it easy for businesses to:
- Look up and search for invoices quickly.
- Prepare invoice reports as required by Circular 78.
- Ensure transparency and accuracy in the invoice control process.
Integration with accounting systems:.
Bizzi has the ability to flexibly integrate with popular accounting software such as SAP, MISA, FAST... to help:
- Automatic invoice data synchronization.
- Reduce manual data entry work.
- Ensure data accuracy and consistency as required.
Update information: Bizzi always promptly updates the latest changes of Circular 78 on electronic invoices and related legal documents, helping businesses easily comply with regulations without worrying about policy changes.
Implementation costs: Bizzi's solution has reasonable implementation costs, suitable for all business sizes. This helps businesses save costs compared to building their own system or using other expensive solutions on the market.

Conversion time: With a professional support team, Bizzi helps businesses convert to an electronic invoice system according to Circular 78 quickly and easily, minimizing disruption to business operations.
Technical complexity: Bizzi has a friendly, intuitive, easy-to-use interface, suitable for all users, including those without in-depth knowledge of technology. Thanks to that, businesses can quickly deploy and use it without having to invest too much in staff training.
Data Security: Bizzi applies advanced security measures to ensure absolute safety for business invoice information:
- Encrypt data to high standards.
- Secure storage system, ensuring data integrity.
- Meet security requirements as prescribed in Circular 78.
With an advanced automation system, Bizzi not only supports businesses in issuing and managing electronic invoices in accordance with regulations, but also helps optimize accounting processes, saving time and costs. Register today to experience a safe, effective and legally compliant electronic invoice solution!
In addition, Bizzi also provides B-Invoice electronic invoice solution. This solution from Bizzi Vietnam is designed to simplify and improve the efficiency of invoice management for businesses. Built on a modern technology platform, B-Invoice fully complies with current legal regulations, including Decree 123/2020/ND-CP and Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC.
Bizzi Vietnam's B-Invoice stands out with features such as fast electronic invoice issuance, allowing digital signature and mass invoice issuance right on the software; creating more than 100 diverse invoice templates, customized according to the business brand; providing detailed reports on invoice usage, supporting effective management; and flexible integration with ERP systems, accounting and sales software, helping to synchronize data easily.
Sign up for a free trial at: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/

5. Frequently Asked Questions
5.1 Does Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC require the application of electronic invoices?
Yes. According to Circular 78 and Decree 123/2020/ND-CP, from July 1, 2022, all businesses, business households, and business individuals must use electronic invoices, except for some special cases considered by the tax authority.
5.2 How is an electronic invoice from a cash register different from a regular electronic invoice?
Cash register invoices are generated immediately upon sale and have a direct data transfer connection to the tax authority. Meanwhile, regular e-invoices can be generated after the transaction and sent in batches.
5.3 Do electronic invoices from cash registers need a digital signature?
Not required. According to Circular 78, electronic invoices from cash registers do not require the seller's digital signature, as long as they meet the criteria for data connection with tax authorities.
5.4 Are newly established businesses required to register for electronic invoices immediately?
Yes. When registering for tax, businesses must register to use electronic invoices with the tax authority before issuing valid invoices.


