In a volatile business environment, budget planning is not only a technical step but also a strategic tool that helps businesses shape their financial future. With a comprehensive budget plan, businesses can predict costs and revenues, allocate resources effectively and control financial risks. So how to budget How to be both realistic and support quick decision making?
This article will guide you through the standard 4-stage process in detail, analyze 4 in-depth budgeting methods, and especially the cost management automation solution from Bizzi - the future of corporate financial management.
What is a budget plan and why do businesses need it?
Plan budget is a detailed financial forecast that helps businesses build a roadmap for effective resource use to achieve business goals. Not only limited to revenue and expenditure figures, the budget plan also reflects the organization's capacity and adaptability to the market and financial risks.
Budgeting: The Core Financial Management Tool
A budget plan is a comprehensive financial forecast that helps a business clearly define expected revenue, operating costs and resource allocation for each strategic objective during the planning period (usually quarterly or annually).
Not only a financial control tool, the budget plan also reflects the proactive management thinking of the board of directors, from fundraising, Expense management, arrive profit optimization.
In addition to financial factors, the budget plan also acts as a compass in orienting the use of non-financial resources such as human resources, time and technology, to ensure efficiency and sustainability in business operations.

5 outstanding benefits when businesses plan their budgets
Budget planning is not only a basic financial management requirement, but also a strategic tool to help businesses increase their operational capacity, proactively respond to fluctuations and improve business efficiency.
- Converting strategy into financial goals: Helps turn long-term plans into specific targets for revenue, costs and investments, making them easy to track and measure.
- Performance measures and control tool: Is the basis for comparing plans and reality, thereby evaluating performance, detecting deviations and making timely adjustments.
- Increase predictability and proactive management: Allows businesses to anticipate financial risks, prepare response plans, and proactively restructure cash flow or allocate resources.
- Control spending and use budget wisely: Limit budget overspending and loss thanks to monitoring and early warning mechanisms when there are discrepancies
- Optimize profits and cash flow: Helps businesses track value-creating expenses, adjust products or services according to profit margins, and improve cash efficiency.
A well-planned budget not only helps businesses have a comprehensive view of their business operations, but also acts as a "financial strategy map" to guide sustainable growth and development.
Common types of budget plans in businesses
In progress how to budget To be effective, businesses need to understand the common types of budgets to choose the right tool for their goals and operating context. Depending on purpose of use and Applicable period, the budget is divided into several types as follows:
Classification by purpose
Based on the purpose of use and scope of planning, business budgets are divided into different types. Each type of budget serves a separate aspect of management, helping businesses to comprehensively control financial and non-financial activities.
- Operating budget: A type of budget that forecasts revenue, expenses, and profits for a planned period, usually shown on the income statement. This is an essential tool for monitoring operational efficiency and determining the break-even point.
- Cash flow budget: Focus on the actual cash flow in and out of the business. Presented through cash flow statement It is expected that cash flow budget will help businesses proactively balance liquidity and avoid the risk of cash shortage.
- Financial budget: Includes forecasts of assets, capital sources, revenues and expenditures and key financial indicators. Financial budgets help businesses assess their ability to mobilize and use financial resources to achieve long-term goals.
- Master Budget: Is a summary of the budgets of each department and the entire enterprise. It provides a comprehensive view of the financial situation, helping the leadership synchronize strategies and monitor implementation efficiency.
- Static Budget: Based on assumptions that do not change throughout the budget period. This type of budget is suitable for businesses with stable processes and little fluctuation in markets or output.

Classification by time
Classifying budgets by time helps businesses clearly define management goals in each stage, thereby choosing appropriate forecasting and resource allocation methods. There are two common types of budgets by time:
- Short-term budget plan: Usually built on a 3-month, 6-month or 1-year cycle. This is a suitable tool for businesses operating in fast-changing industries such as retail and technology.
- Long-term budget planning: Can last from 3 to 10 years, oriented towards strategic goals such as market expansion, infrastructure investment or product improvement. Long-term budgeting requires accurate forecasting and in-depth analysis of industry trends.
6 mandatory principles when planning a business budget
To ensure effectiveness and feasibility in practice, how to budget There are a few core principles that businesses need to follow to help them maintain financial control while remaining flexible to adapt to market fluctuations.
- Closely linked to business goals: Every element of the budget plan should reflect the business's development strategy. This helps ensure that the budget is a tool to serve a purpose, not simply a cost-revenue table.
- Ensure clear and transparent basis: Budget items must be based on specific data such as financial reports, operating indicators, investment plans, etc. Transparency makes it easy to check, adjust and protect the budget when submitting for approval.
- Time suitable for business characteristics: For businesses operating in the technology, e-commerce, etc. industries, the budget should be divided quarterly to ensure flexibility. Conversely, manufacturing or construction businesses can apply annual or medium-term plans.
- Create separate budgets for each department: Allocating detailed budgets to each department (marketing, production, operations, etc.) helps increase feasibility and effective management. Then, the business synthesizes it into a company-wide budget for easy comparison and analysis.
- Transparency in approval, data security: The process of budget preparation - approval - adjustment must be clear, in accordance with the correct authority. However, budget information must be kept confidential and only shared with relevant people such as the CFO or the Executive Board.
- Avoid common budgeting mistakes:
- Don't extend the budgeting process beyond 3–4 months.
- Limit constant change that causes disorientation.
- Avoid making a budget that is too detailed, causing waste of resources.
- Don't skip quarterly or mid-year reviews.
- Balance between financial and operational-strategic goals.
Adhering to the above principles helps businesses plan realistic budgets that can be measured, adjusted effectively, and support timely financial decisions.
7 Common Mistakes to Avoid When Budgeting
Mistakes in accounting budgeting that you need to be aware of include:
- Don't extend the budgeting process beyond 3 – 4 months.
- Limit constant change that causes disorientation.
- Avoid making a budget that is too detailed, causing waste of resources.
- Don't skip quarterly or mid-year reviews.
- Lack of involvement of relevant departments in the budgeting process.
- Rely solely on past data without forecasting changing factors.
- Not making contingency plans for unexpected situations.
Adhering to the above principles helps businesses plan realistic budgets that can be measured, adjusted effectively, and support timely financial decisions.
Step-by-step guide to detailed budget planning
Budget planning is a strategic process that helps businesses control finances, allocate resources effectively, and guide short- and long-term development. Below is a basic four-stage process in budget planning that every business should apply.
Step 1: Preparation and goal setting phase (Financial and strategic input)
This stage is the foundation for determining the quality of the budget:
- Collect necessary input data: Businesses need to synthesize information such as strategic objectives, business plans, PESTEL analysis, market factors, previous financial results, sales plans, prices and distribution channels to make accurate forecasts.
- Prepare budgeting guide: A dedicated team should be established to develop processes, forms, timetables and assumptions that serve as a basis for consistency across departments. You can refer to and download 18 Excel file templates for corporate financial management support work more conveniently
- Identify financial and non-financial goals:Each department based on strategic direction will set specific goals to build appropriate budgets.
Step 2: Budgeting Phase
Here, the business begins to concretize the numbers:
- Revenue forecast: Estimated based on past sales figures, expected growth, market trends, pricing policies and distribution strategies.
- Calculate capital sources and expected costs: Identify production costs, operations, marketing, customer service, and potential investments. Consider variable costs and potential risks.
- Balance of income and expenditure: Evaluate profitability by comparing income and expenses, then adjust to ensure feasibility and optimize resources.
Step 3: Review and approval phase
This phase ensures accuracy and coherence across the organization:
- Consolidate budgets from departments:The budgeting team will compile all the figures into a master budget.
- Review and synchronize budget: Organize inter-departmental meetings to compare, adjust and unify indicators.
- Finalization and official approval: The completed budget is submitted to the Board of Directors/Management for approval and implementation.
Step 4: Implementation, monitoring and adjustment phase
The budget is not just a static plan but needs to be monitored regularly:
- Develop a contingency plan: Develop alternative scenarios to be prepared to respond to unplanned risks or fluctuations.
- Monitor and evaluate actual performance: Set up a periodic monitoring system, analyze the difference between budget and reality, and promptly adjust to optimize financial efficiency.
Detailed Budgeting Methods: Choosing the Right One for Your Business
To build how to budget To be effective, businesses need to choose a method that suits their business model, scale of operations, and financial goals. Below are four popular methods that many businesses apply:
Incremental Budgeting
This method is based on the previous year's budget data, then adds a growth percentage based on inflation, price increase forecasts, or revenue targets.
- Advantage: Simple, easy to deploy, suitable for businesses with stable cost structure.
- Disadvantages: It is easy to sustain ineffective spending that lacks flexibility in a rapidly changing business environment.
Activity-Based Budgeting
Businesses analyze key activities, determine costs related to each specific item, including fixed costs, variable costs, volume and unit prices.
- Advantage: Link costs to specific activities, optimize resource allocation and control budgets.
- Suitable for: Businesses need to closely monitor the performance of each department or process.
Value-Creation Budgeting
Focus on ROI (Return on Investment) analysis of each expense, only selecting expenses that bring value higher than the predetermined minimum threshold.
- Advantage: Aiming at investment efficiency, optimizing profits and expenses.
- Suitable for: Businesses oriented towards sustainable growth, prioritizing value over cost quantity.
Zero-Based Budgeting
Not relying on old budgets, all expenses must be built from scratch, with clear reasons and priorities. ZBB method forces budget makers to Explain and Justify the necessity of each expense.
- Advantage: Eliminate redundant costs, promote frugal thinking and innovation.
- Disadvantages: Time consuming, requires specialized staff and complete data.
- Suitable for: The company is restructuring and wants to control the budget tightly from the root.
Limitations of traditional budgeting processes in a volatile environment
While traditional budgeting methods still have value, they often face significant limitations when businesses operate in a rapidly changing and complex business environment.
- Manual errors: Manual data entry and calculation in Excel is prone to errors, reducing budget accuracy.
- Lack of real-time control: Traditional methods often only allow for periodic performance evaluation, do not provide an instant view of spending situation, making it difficult to make timely adjustments.
- Difficulty in reconciling invoices with the budget: The process of comparing actual expenses with the approved budget becomes complicated and time-consuming, especially when the number of invoices is large.
- Lack of flexibility: Adjusting budgets in response to market fluctuations or strategic changes is often slow and inefficient.
- Information security: Sensitive budget data can be easily exposed or modified without proper management systems.
Optimize budget management with technology (Bizzi)
In the context of strong digital transformation, the application of technology to how to budget not only help businesses increase the speed of processing financial information but also ensure accuracy, transparency and efficiency in spending management. Solutions such as Bizzi Expense and Bizzi Travel is becoming the preferred choice for many businesses in their journey to digitize budget management.
The role of technology solutions in cost control
Modern accounting software like expense automation platforms like Bizzi Act as a “financial assistant” to support businesses:
- Create and track smart budgets: Support financial budgeting details and real-time monitoring.
- Automate the revenue and expenditure process: Reduce manual errors and speed up accounting processing.
- Comprehensive cost control: Integrated alerts, approvals and spending analysis help businesses control budgets effectively.
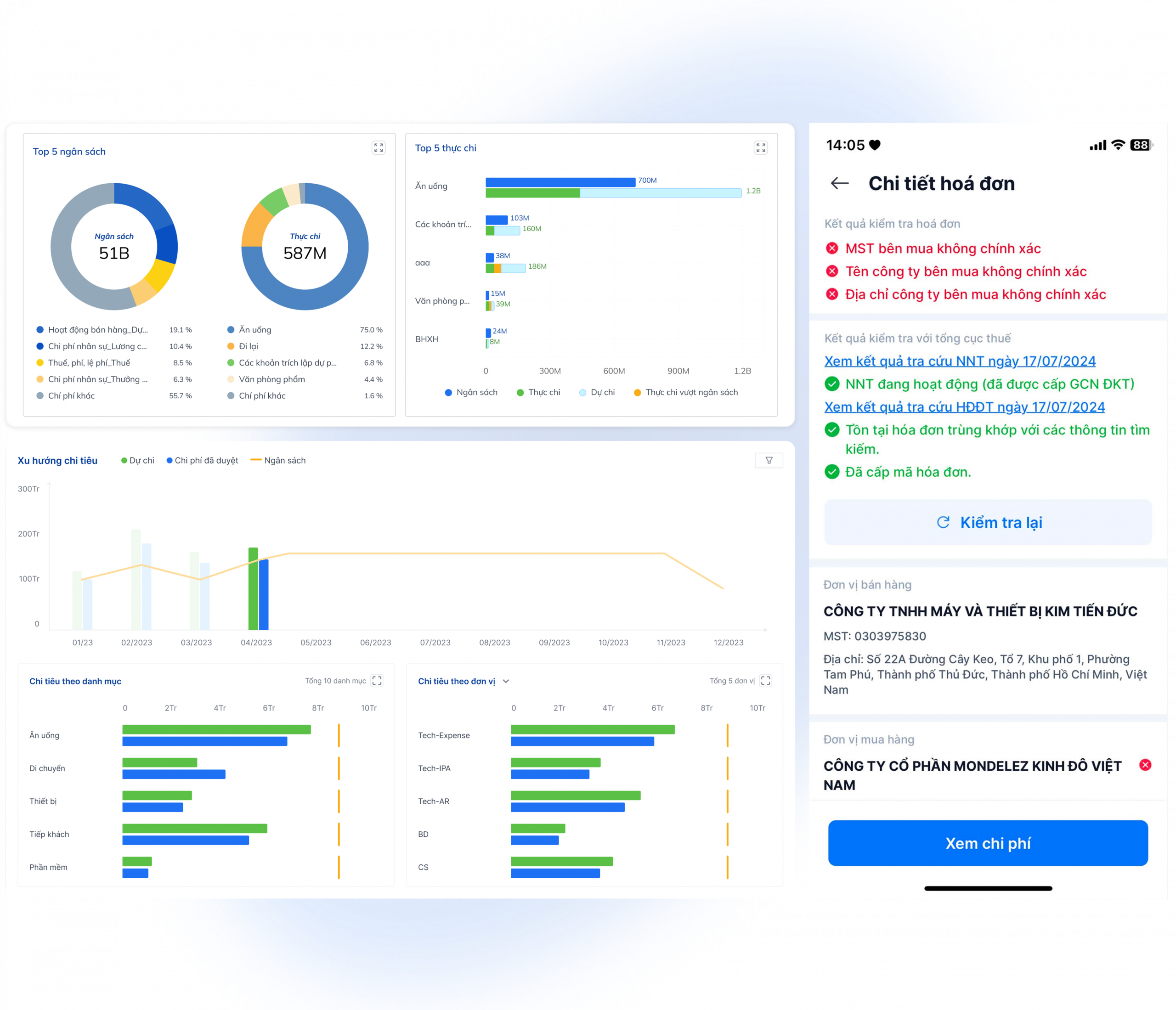
Outstanding budget management support features
Solutions such as Bizzi Expense and Bizzi Travel Provides a powerful toolkit to help businesses master how to budget, include:
- Set up flexible budgets: Allocate budgets by team, department or project.
- Automatic budget overrun monitoring and alerting: Timely warning when there are signs of exceeding the allowable spending limit.
- Flexible approval system: Build approval processes by department, level, or expense type.
- Real-time cost tracking: Visual reporting by category, department or project.
- Establish and enforce spending policies: Ensure compliance with internal corporate regulations.
- Comprehensive expense management: Track all expenses during business trips, integrate automatic ticket booking according to budget.
- Attach spending to specific tasks: Helps track budget usage for each project.
Benefits of applying technology to budget management
The application of modern technology brings many practical values to businesses in the process of building and implementing budget plans:
- Increase initiative and transparency: Helps managers easily monitor and adjust budgets to suit business realities.
- Save cost and time: Automate manual tasks, reducing operating costs and risk of error.
- Improve financial management efficiency: Allows businesses to optimize resources, evaluate investment efficiency and manage cash flow more closely.
To improve the efficiency of invoice management as well as automate the financial and accounting processes of the business. Register to experience Bizzi's comprehensive solution suite today!
- Link to register for a trial of Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/
Conclude
Understand and apply correctly how to budget is the foundation. But are you ready to completely transform your processes, eliminate the risk of manual errors, and automate invoice reconciliation against budget? Explore Bizzi Solution to control your finances smarter.


