In the context of digital transformation, the application of technology to achieve connectivity, synchronization and transparency in operations is a vital factor. Amidst that trend, the term ERP is becoming increasingly popular. So exactly What is ERP? and how can it revolutionize the way businesses operate, especially in optimizing and managing costs?
This article will provide a comprehensive overview of What is ERP?, from definition, history, the ERP software features core, comparison with other software, to important notes when implementing to optimize resources, control spending effectively and create sustainable competitive advantages.
Origin and development history of ERP system
ERP systems did not come into existence overnight, but are the result of a decades-long evolution, stemming from the need to manage manufacturing. Here are the key milestones:
- 1960s – MRP (Material Requirements Planning): This is the predecessor system, focusing entirely on planning raw material requirements for production.
- 1980s – MRP II (Manufacturing Resource Planning): MRP was extended to MRP II, integrating other factory management functions such as human resources, finance and engineering, not just limited to materials.
- 1990s – The Birth of ERP: Terminology ERP Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) officially appeared, marking a quantum leap. The system now integrates all departments and processes of a business—from manufacturing, finance, HR to supply chain and sales—into a single platform, often deployed on-premise.
- 21st Century – Cloud ERP: The explosion of cloud computing technology has given birth to Cloud ERP. This solution helps businesses, especially small and medium enterprises (SMEs), access ERP with lower investment costs, flexible access via the internet and easy scalability.
Core Features of an ERP System
To understand better What is ERP?, it is necessary to master the main features that make it powerful. An enterprise resource planning system is not just a software, but a technology-based management philosophy.
- Full integration: ERP integrates all departments and processes (finance, HR, manufacturing, supply chain, sales…) into a single system, breaking down individual information “silos”.
- Centralized database: All business data is stored in one place. This ensures consistent, accurate and real-time information, which is the foundation for transparent reporting and cost control.
- Module-based design: Businesses can choose to deploy functional modules that suit current needs and expand in the future, providing high flexibility.
- Standardize the process: ERP applies business processes according to international standards, helping businesses optimize operations, minimize errors and improve performance, especially complex financial processes such as disbursement approval or payment.
- Security and authorization: The system allows detailed access authorization for each user according to role and position, ensuring data security and tight internal control.
Core ERP Software Features
A complete ERP system is made up of many different functional modules, each module is responsible for a separate business but all are closely linked together. Below are the most popular modules, with special emphasis on the role of cost management:
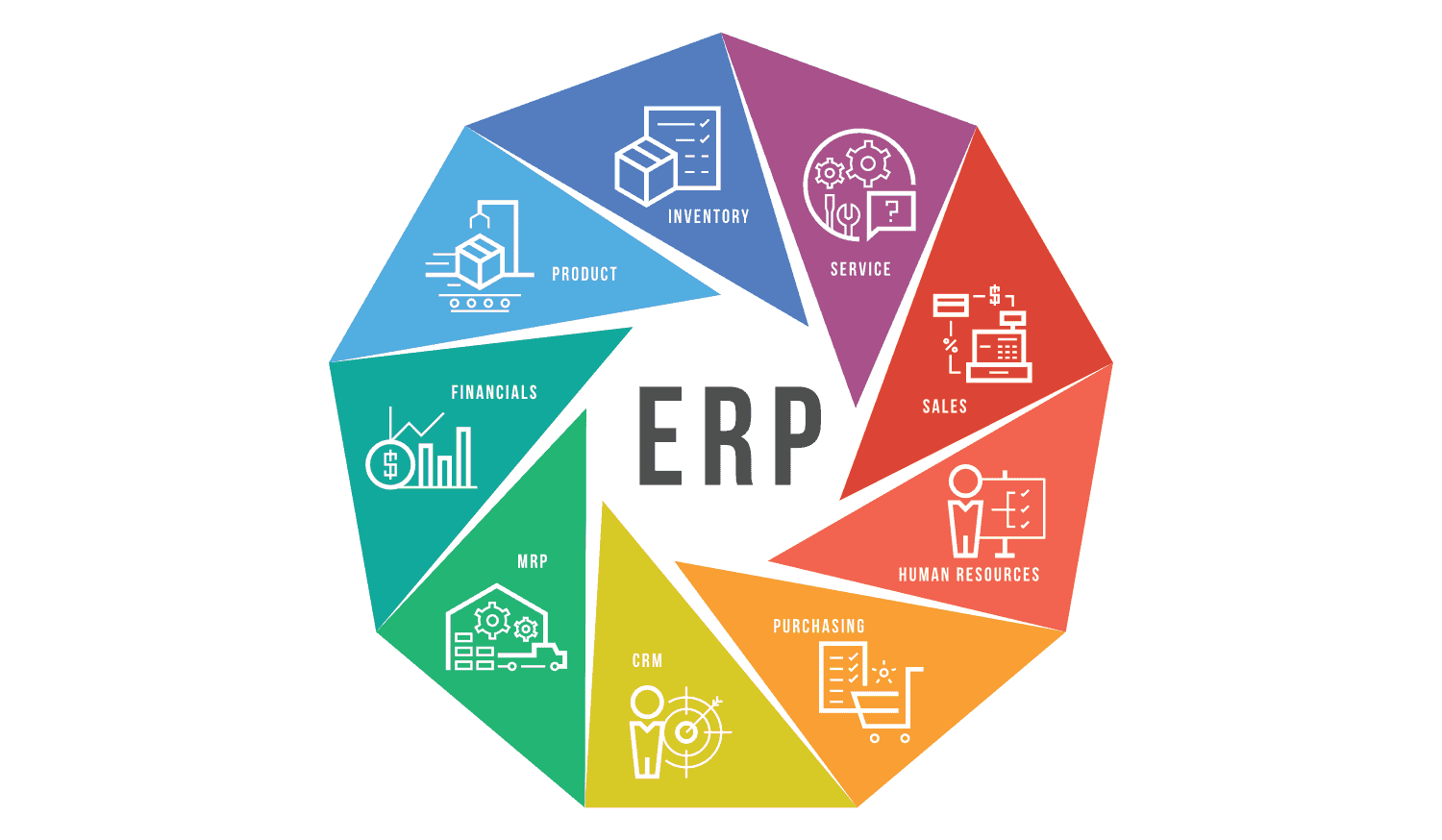
The ERP software features Common core functions of an ERP system
| Functional Module | Detailed Description |
|---|---|
| Finance – Accounting | This is the backbone of the ERP system, helping to manage the general ledger, receivables, fixed assets, cash flow and generate financial reports. In particular, this module helps businesses standardize and optimize processes. Accounts Payable Management, one of the core operations to control spending. |
| Sales & Distribution Management | Automate your sales process from quoting, order management, delivery, invoicing to debt tracking. This module is directly synchronized with warehouse and accounting. |
| Purchasing Management | Streamline the procurement process from creating requisitions, selecting suppliers, placing orders, receiving goods and checking invoices. This module directly supports management purchase cost, helping businesses control inputs and optimize budgets. |
| Inventory Management | Track inventory quantities, locations, and movements in real time. Optimize inventory levels to avoid wasted capital and unnecessary warehousing costs. |
| Production Planning & Control | Production planning, bill of materials (BOM) management, production progress monitoring, quality management and product costing. |
| Human Resource Management (HRM) | Manage employee information, timekeeping, payroll, benefits, recruitment and business expense management. |
| Customer Relationship Management (CRM – often integrated) | Store and manage customer information, transaction history, support marketing and customer care activities. |
| Management reporting (Business Intelligence – BI) | Provide multi-dimensional analytical reports and dashboards on costs, revenue, and profits, helping management make strategic decisions based on accurate data. |
Compare ERP and other software (CRM, HRM, Accounting software)
Many businesses often wonder whether to choose ERP or other specialized software. The comparison table below will clarify the difference:
| Criteria | ERP system | CRM Software | HRM Software | Accounting Software |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Comprehensive (integrating all departments) | Customer Focus (Sales, Marketing, Service) | Focus on employees (Recruitment, Compensation, Benefits) | Focus on finance (Income, Expense, Bookkeeping) |
| Main objective | Consolidate operations, optimize resources, standardize processes and control overall costs. | Increase revenue, improve customer relationships. | Effective human resource management and development. | Ensure financial accuracy and compliance. |
| Target audience | Every department in the business. | Sales, Marketing, Customer Service Department. | Human Resources Department and department heads. | Accounting and Finance Department. |
| Nature | A single integrated system. | A dedicated software that can be integrated with ERP. | A dedicated software that can be integrated with ERP. | A dedicated software that can be integrated with ERP. |
Brief conclusion: ERP is an “all-in-one” system that covers the entire business. Meanwhile, CRM, HRM, and accounting software are specialized solutions for specific areas. An ERP system usually includes these functional modules.
Outstanding benefits of ERP software
Successful implementation of an ERP system brings strategic benefits, helping businesses not only operate more efficiently but also grow sustainably.
- Centralized and transparent data management: Eliminate fragmented, misaligned data. All information, especially financial and cost data, is updated in real-time on a single platform.
- Increase work performance: Automate repetitive tasks (like data entry, invoice reconciliation), standardize approval processes, and help employees save time and focus on higher-value work.
- Strategic decision support: Provide multi-dimensional and instant management reports, helping management quickly grasp cash flow and cost structure to make accurate business decisions.
- Tight internal controls and security: Detailed authorization system and Audit Trail feature help prevent fraud, ensure compliance and transparency in all spending transactions.
- Optimize costs and increase revenue: This is the most important benefit. ERP helps reduce waste in manufacturing, optimize inventory, and provide a solid foundation for business cost management closely, thereby improving profit margins.
- Improve collaboration: Break down information barriers between departments (e.g. between Purchasing and Accounting), making payment and expense processing workflows smoother.
ERP Cloud vs. ERP On-premise: Which choice for businesses?
When deciding to implement ERP, one of the first important choices is between the Cloud and On-premise models.
| Criteria | ERP Cloud (SaaS) | ERP On-premise |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure | Server management and maintenance provider. Business access via internet. | Enterprises invest and manage servers and network infrastructure themselves. |
| Expense | Low initial cost (pay per subscription). Easy to manage software costs. | Initial costs are very high (purchase of permanent license, hardware). |
| Deployment | Faster, easier. | Complicated, time consuming. |
| Maintenance & Upgrades | The provider automatically updates. | Businesses have to do it themselves, which costs money and resources. |
| Accessibility | Flexible, access anytime, anywhere with internet. | Restricted to the company's internal network. |
| Customize | Less customization capabilities. | Flexible customization according to specific requirements. |
Current trends: Cloud ERP is becoming the preferred choice, especially for small and medium enterprises thanks to its flexibility and affordability.
Which businesses should apply ERP software?
In theory, any business can benefit from ERP. However, the investment becomes urgent when your business shows the following signs:
- Medium and large scale or with many branches: As the process becomes complex, the number of transactions is large and data needs to be synchronized between locations.
- Using too many separate software: Employees have to repeatedly enter data on multiple systems (accounting, sales, warehouse, etc.), which is time-consuming, error-prone, and difficult to summarize cost reports.
- Difficulty in accessing business information: It takes too much time for management to get an overall report on inventory, cash flow or spending efficiency of each department.
- Manual, cumbersome management process: Paper-based, email-based processes for approving expenses, processing invoices, and paying suppliers cause delays, lack of transparency, and risk of loss.
- Growing fast and want to scale: Businesses need a solid foundation to standardize processes and prepare for future expansion without disrupting operations.
Cost and ROI of ERP Implementation
Implementing an ERP is a significant and strategic investment. The cost includes not only the software purchase but also many other factors.
Main expenses:
- License Fee: For On-premise ERP.
- Subscription Fee: For ERP Cloud.
- Consulting and implementation costs: Costs for partners to conduct surveys, customize, install, and train. This is often the largest expense.
- Infrastructure costs: Server, network (for On-premise).
- Internal personnel costs: Time and effort of the project team.
- Annual maintenance and support costs.
According to industry reports, total implementation costs can range from tens of thousands of dollars to millions of dollars, depending on the size of the business and the scope of the project. For example, a report by Panorama Consulting Group found that the average cost of an ERP project can account for between $41.3T and $71.3T of a company's annual revenue.
Return on Investment (ROI): Despite the high cost, the ROI of ERP comes directly from reduced operating costs, increased productivity, and especially the ability to make smarter spending decisions. ROI is usually clearly seen after 2-3 years of stable system operation.
Popular ERP providers in Vietnam and the world
The ERP market is very diverse with many suppliers from international to domestic.
- International Supplier (Tier 1):
- SAP: Global market leader, renowned for powerful solutions for large enterprises such as SAP S/4HANA.
- Oracle: SAP's main competitor, offering solutions like Oracle NetSuite (Cloud) and Oracle Fusion.
- Microsoft: Providing Microsoft Dynamics 365 solution suite, deeply integrated with Microsoft ecosystem.
- International Suppliers (Tier 2 & 3):
- Odoo: Open source ERP platforms are highly flexible and popular among SMEs due to their affordability and high customizability.
- Infor, Epicor: Specialized solutions for manufacturing and distribution.
- Vietnam Supplier:
- Bravo, MISA, 3S ERP: These companies provide ERP solutions that are “tailored” to suit the operational characteristics, accounting regulations and laws of Vietnam.
Risks and important notes when implementing ERP
ERP implementation is a complex project with a high failure rate. To be successful, businesses need to prepare carefully and anticipate risks.
- Choosing the wrong solution or implementation partner: Not clearly defining needs or choosing an inexperienced partner are leading causes of failure.
- Lack of commitment from management: ERP projects need strong support and direction from top management.
- Unclear Project Scope (Scope Creep): Continuously changing or adding requirements during implementation will increase costs and extend time.
- Not standardizing processes before implementation: “Garbage in, garbage out.” Automating an already inefficient expense approval process will only increase uncontrolled expenses.
- End user resistance: Employees who are not adequately trained or do not understand the benefits of the new system will tend to resist change.
- Unrealistic budget and timeline: Underestimating the cost and time required will result in the project stalling midway.
Optimize ERP system in Vietnam with complementary solutions
Implementing ERP helps businesses standardize core processes. However, ERP systems, especially international solutions, are sometimes rigid and difficult to customize to meet specific business needs such as input invoice processing or complex payment approval processes in Vietnam.
This is where add-on solutions like Bizzi come in. Bizzi is an invoice processing and payment control automation platform designed to Seamless integration with ERP systems popular (SAP, Oracle, Microsoft, Odoo, Bravo…) via API.

How does Bizzi complement ERP?
- Automate input invoice processing: Bizzi automatically collects, extracts data, and reconciles invoices with purchase orders (POs) and warehouse receipts. Validated data is automatically pushed into ERP, eliminating manual data entry and enabling How to issue electronic invoice and manage more effectively.
- Digitize the payment process: The platform helps to establish flexible expense approval flow, control budgets and synchronize two-way payment status with ERP, ensuring transparency and tight control over business cost management.
- Flexible integration, no need to modify the original ERP: API integration helps businesses expand the capabilities of existing ERP systems quickly and cost-effectively without affecting the core operating structure.
The combination of a solid ERP system and a flexible add-on solution like Bizzi helps businesses achieve standardization and the ability to quickly adapt to specific business requirements, optimizing the entire process. effective digital transformation.
Conclude
ERP is a strategic system, the technological backbone for businesses in the digital age. Understanding What is ERP?Its core features and benefits will help businesses choose and apply the right solution to optimize operations and enhance competitiveness.
However, ERP implementation is a complex journey that requires careful preparation. For businesses in Vietnam, combining ERP with specialized support software such as Bizzi is a smart way to thoroughly solve the problem of cost management, flexibly meet emerging needs and maximize the value of their technology investment.


