The payment accountant is not only the person who makes the payment, but also the person who controls the cash flow, helps the business operate smoothly, avoids financial risks and maintains prestige with partners. This is an important link between functional departments and the finance and accounting department.
In this article, let's Bizzi Learn more about what payment accounting is as well as the payment accounting process in a business.
Concept and role of payment accounting
Payment accounting is the accounting department responsible for managing and recording the business's revenue and expenditure transactions, including income and expense documents in cash or by transfer.
What is the definition of payment accounting?
A payment accountant is a person who prepares receipts and payments, directly monitors and manages money, as well as accounts for transactions or economic activities arising related to revenue and expenditure activities in the enterprise.
This position specializes in the accounting department, responsible for monitoring, recording and processing the company's payments. The payment accounting function is to perform tasks related to using cash flow to pay entities related to the company's business operations.
- see more article: What is sales accounting? The role of sales accountant in business
The role and tasks of payment accounting in business
Payment accountants play an important role in collecting and summarizing the receipts and expenditures of the enterprise. They are positions that play an important role in the production and business operations of the enterprise.
The task of payment accounting is to ensure that payments are made on time and accurately, not only helping businesses maintain their reputation, but also helping to control cash flow effectively, avoiding cash shortages or late payments.
Position in accounting system
In the organizational structure of the accounting department, the work of the payment accountant usually reports directly to the chief accountant or head of the accounting department.
The task of the payment accountant is to coordinate closely with other departments such as general accounting, accounts receivable accounting, and bank accounting to ensure that financial information is fully updated and accurate.

Detailed job description of a payment accountant
Payment accountants undertake many important tasks related to the cash flow and debts of a business.
Manage your revenues
- Carry out money collection operations from internal and external entities of the enterprise (shareholders, recovery of excess advances, other internal collections, compensation, deposits, collateral, and collection of customer debts).
- Keep track of bank deposits.
- Track customer card payment activity.
- Monitor receivables and urge debt collection.
- Control cashier activities in the business.
- Directly receive and check the validity of related documents from the cashier department.
- Closely manage documents related to business revenues.
- Accounting for transactions related to business revenues.
Manage expenses
- Weekly and monthly plan to pay debts to suppliers.
- Proactively contact suppliers if payment plans are not secure.
- Perform accounting operations for cash payments or bank deposits to suppliers, compensation payments, and fine payments.
- Carry out internal business expenditures such as salary, bonus, allowance, and advance payment payments.
- Track advance transactions.
- Closely manage documents related to business expenses.
- Accounting for business transactions related to expenses.
Cash Management
- Coordinate with the treasurer to perform revenue and expenditure transactions in accordance with regulations.
- Reconcile and check end of day cash balance with cashier to ensure accuracy and completeness.
- Prepare periodic cash balance reports for the board of directors (can be daily reports depending on the business).
Control cashier operations
- Receive relevant documents from the cashier department.
- Check and verify the validity of documents.
See more articles: What does cost of sales include?
Other jobs
- Participate in financial planning and cash flow forecasting.
- Propose effective debt management solutions for businesses.

What are the basic accounting operations of payment accounting?
The following entries illustrate the basic tasks of the payment accountant, note that in practice there may be special cases that require different handling.
The accounting function of payments is related to cash collection.
- Withdraw bank deposit to cash fund: Debit account 111 / Credit account 112.
- Collecting employee refunds: Debit account 111 / Credit account 141.
- Collecting advance payments from customers: Debit account 111 / Credit account 131.
- Sales of VAT taxable goods collected in cash: Debit account 111 / Credit account 511, Credit account 3331.
- Collecting receivables from customers: Debit account 111 / Credit account 131.
The accounting profession deals with cash disbursements.
- Withdraw cash and deposit it into the bank: Debit account 112 / Credit account 111.
- Cash advance payment to employees: Debit account 141 / Credit account 111.
- Deposit, prepayment for purchase in cash: Debit account 331 / Credit account 111.
- Payment for purchasing materials, tools and supplies, and goods in stock: Debit account 152, 153, 1561, 1331 / Credit account 111.
- Pay due debts to suppliers: Debit account 331 / Credit account 111.
- Payment for purchased services: Debit account 627, 641, 642, 1331 / Credit account 111.
- Paying salaries to employees in cash: Debit account 334 / Credit account 111.
The accounting of payments is related to collecting money through the bank.
- Collect employee refunds and deposit them into bank accounts: Debit account 112 / Credit account 141.
- Collect advance payment from customers by bank transfer: Debit account 112 / Credit account 131.
- Sales subject to VAT collected immediately by bank transfer: Debit account 112 / Credit account 511, Credit account 3331.
- Collecting customer receivables by bank transfer: Debit account 112 / Credit account 131.
The practice of payment accounting involves disbursing money through banks.
- Withdraw bank deposit to cash fund: Debit account 111 / Credit account 112.
- Advance to employees by bank transfer or check: Debit account 141 / Credit account 112.
- Deposit, prepayment for purchase by bank transfer: Debit account 331 / Credit account 112.
- Purchase of materials, equipment, and goods imported into the warehouse and pay immediately via bank transfer: Debit account 152, 153, 1561, 1331 / Credit account 112.
- Pay due debts to suppliers by bank transfer: Debit account 331 / Credit account 112.
- Pay for outside services via bank transfer: Debit account 627, 641, 642, 1331 / Credit account 112.
- Salary payment transfer to employees: Debit account 334 / Credit account 112.
- Pay tax by bank transfer: Debit account 333 / Credit account 112.
- Transfer money between bank accounts: Debit account 112 (receiving account) / Credit account 112 (transferring account).
- Loan principal repayment: Debit account 341 / Credit account 112.
- Interest payment: Debit account 635 / Credit account 112.
What is the payment accounting process?
Below is the process of handling payment accounting transactions, presented in sequential steps for easy understanding and application in business practice:
For cash receipt and payment processing:
- Cash payment transactions: Based on the payment documents sent in -> Receive, check the completeness, reasonableness, and validity of the documents and payment content -> Review payment records -> Prepare and submit payment vouchers for signature (Chief Accountant, Director) -> Transfer documents to the cashier for payment -> Record cash disbursement transactions in the books -> At the end of the day, reconcile accounting book data with the cashier and inventory the fund.
- Cash collection operations: Based on cash collection transactions (withdrawal of bank deposits, revenue from sales, etc.) -> Receive and check documents arising related to cash collection -> Prepare and submit receipts for signature (Chief Accountant, Director) -> Transfer documents to the cashier for cash collection -> Record cash collection transactions in the books -> At the end of the day, reconcile accounting cash book data with cashier and inventory the fund.
For the process of processing bank deposit receipts and payments:
- Bank deposit payment transaction: Based on payment request via bank -> Create payment order (money transfer) or Check (cash withdrawal) -> Submit for signature (Chief Accountant, Director) -> Transfer documents to bank to make transaction -> Record bank deposit payment transactions in books -> Periodically reconcile bank cash book with bank subsidiary ledger.
- Bank deposit collection operations: Based on the bank's credit note -> Record bank collection transactions in the books -> Periodically reconcile the bank's cash book with the bank's subsidiary ledger.

Learn more about Digital solutions and optimization of accounts receivable accounting here
What documents and records will be required in the payment accounting process?
In addition to understanding the nature of the payment accounting task, this position also requires personnel to master and proficiently use documents and books related to financial operations.
Accounting documents:
- Value added tax invoice.
- Sales invoice.
- Payment documents: Receipt, payment voucher, check, cash deposit slip, payment order, debit note, credit note.
- Quotation, order, purchase contract, sales contract.
- Debt reconciliation record.
- Warehouse receipt, warehouse delivery note.
- Detailed list of debts.
- Advance payment request, advance payment paper.
- Payroll, timesheet.
- Other documents related to revenue and expenditure transactions.
Accounting system:
- Cash ledger, bank deposit ledger.
- Cash book, bank deposit book.
- Cash receipts journal, cash payments journal.
- Detailed book of accounts receivable (131, 331, 141, 333, 334…).
- General journal.
- Payment tracking book with buyers and sellers.
- Other books according to the management needs of the business.
Related reports:
- Report on deposit and balance status.
- Fund inventory report.
- Details of receivables and payables.
- Summary of receivables and payables.
- Analyze receivables and payables by due date.
- Debt status report.
- Debt aging report.
- Cash flow statement.
- Balance sheet.
- Payment accountants also need to master how to prepare and present financial reports such as Balance Sheet, Income Statement, Cash Flow Statement to have an overview of the financial situation.
What skills and qualities are required of a payment accountant?
To do well in the position of payment accountant, the worker needs to ensure certain requirements. Below are some of the necessary skills and qualities:
Advanced skill
- Professional knowledge of accounting: Mastering principles, standards, accounting regimes, and related tax regulations.
- Reporting and accounting skills.
- Financial analysis and statistics skills.
- Reporting skills.
- Corporate financial management skills.
- Ability to analyze data accurately and quickly.
- Know how to check data and link with other accounting subsystems.
Soft skills
- Proficient in using accounting software and Microsoft Office tools (Excel, Word). If not proficient, it will take a lot of time and reduce efficiency.
- Good communication skills to work with internal departments and external partners (customers, suppliers, banks).
- Good presentation skills (regularly have to present reports to superiors).
- Time management skills, prioritizing work.
- Ability to work under pressure, especially at month/quarter end.
Personal qualities
- Good personality, honest, straightforward.
- Good health, active, diligent.
- Careful, meticulous, tidy, and responsible for work.
- Enthusiastic, confident.
- Have team spirit, good cooperation and teamwork skills.
- Agile.
- Spirit of learning, updating new knowledge.

Important notes when doing payment accounting
To perform the work accurately, quickly and effectively, payment accountants need to note:
Manage and update business
- Regularly check and update payment accounting transactions such as cash receipts and payments, and bank deposits.
- Ensure full and accurate reflection of transactions in accounting books.
Check and complete documents
- Ensure that accounting documents (receipts, payment vouchers) have the signatures of at least 3 parties: The person making or cashier, The person delivering/receiving money, and The person approving (Chief Accountant/representative).
- For cash collection: Approval signature may not be required immediately upon receipt, but must be completed and recorded within the day.
- For spending money: If within the limit and authorized, payment vouchers can be prepared and recorded in advance, but information and signatures must be completed at the end of the day.
Organize and store documents
- Store invoices, books, and documents carefully, scientifically, and in the order of cash book and detailed bank transaction book.
- Avoid losing documents or not finding them when needed for verification.
Monitoring, reporting and coordination
- Regularly monitor cash receipts and payments, bank deposits.
- Prepare reports for leaders to grasp the revenue and expenditure situation and have appropriate financial plans.
- Regularly communicate with accounts receivable or the accounts receivable department.
Check and compare data
- Know how to check data and link with other accounting subsystems.
- Ensure correct data matching, avoid incorrect or missing accounting.
Increase productivity with the help of accounting software
Using smart software or tools brings many practical benefits to payment accounting, especially in optimizing performance, minimizing errors, and increasing transparency. Below are the specific supports that the software brings:
Automate invoice processing:
- Automatically collect invoices from email, vendor systems, or other software.
- Identify and extract invoice data (amount, tax code, invoice date, etc.) using OCR or AI.
- Reduces manual data entry time by up to 70-80%.
Smart data comparison and checking:
- Automatically compare invoices - contracts - payment requests.
- Warning about duplicate invoices, incorrect information, and invoices that do not match the purchase order (PO).
- Reduce the risk of fraud, errors or duplicate payments.
Cash flow management and payment planning:
- Create a payment schedule and reminders to avoid penalties or loss of reputation.
Allows for decentralized payment approval, making the process transparent and compliant with internal policies.
Accounting – banking – ERP data integration:
- Direct connection to ERP systems, banks, accounting software (SAP, MISA, Bravo, ...).
- Automatically update payment status, reducing manual operations and errors.
- Support exporting debt and cost reports in real time.
Save time, increase productivity:
- One accountant can process 2-3 times more invoices than if done manually.
- Free up time for accountants to focus on analytical and management tasks.
Legal Compliance – Secure Electronic Storage:
- Store invoices and electronic documents in accordance with tax authority regulations.
- Easy to look up and check when needed for auditing and tax settlement.
What are the specific support features of the software for payment accounting?
- Cash management: Allows to create all documents related to cash receipts/payments (withdrawal of bank deposits, refunds, advances, prepayments to suppliers, deposits in banks, temporary payments...).
- Bank deposit revenue and expenditure management: Allows to create all bank payment documents (Payment orders, checks, etc.), and account for bank collection transactions (customer advances, advance recovery, loans, interest collection, etc.).
- Automatic accounting: Automatically account for revenue and expenditure transactions. If foreign currency is received, automatically account for exchange rate differences.
- Debt management: Track debt details by customer/supplier, classify debt age, warn of overdue debt, calculate late payment interest, and create diverse debt reports.
- Cash flow management: Track multi-currency cash/deposit balances, plan income and expenditure, and forecast cash flow.
- Transaction processing: Helps track cash balances and bank deposits in detail.
- Reconciliation of accounts receivable: Automatically reconcile debts periodically, send reconciliation table via email.
- Report: Provides a variety of reports on debt, cash flow, allows customization and export to popular formats.
- Integration: Connect with other accounting subsystems (general, sales, purchasing) and other business management software.
- Security: Detailed access permissions, transaction tracking, automatic data backup.
Bizzi: A powerful assistant to help payment accountants improve performance
In the busy business world, people working in the position of payment accountants often have to “shoulder” hundreds of documents, invoices, reconcile debts and process expenses every day. Large workload, high risk of errors, long processing time – these are the challenges that always “pull back” work efficiency.
But now, everything is different with Bizzi - a powerful assistant for accountants!
Automate Processes – Reduce Manual Burden
- Automatically collect and read electronic invoice data from email or accounting software.
- Extract information (supplier, amount, tax code…) with accurate AI, no need to type by hand.
- Quickly synchronize data into ERP systems (SAP, MISA, Bravo...) with just a few clicks.
Smart Invoice Information Check – Minimize Errors
- Bizzi integrates invoice – contract – PO reconciliation tool, helping to detect discrepancies from the beginning.
- Warning of risky invoices, invalid invoices, suppliers stopping operations, etc.
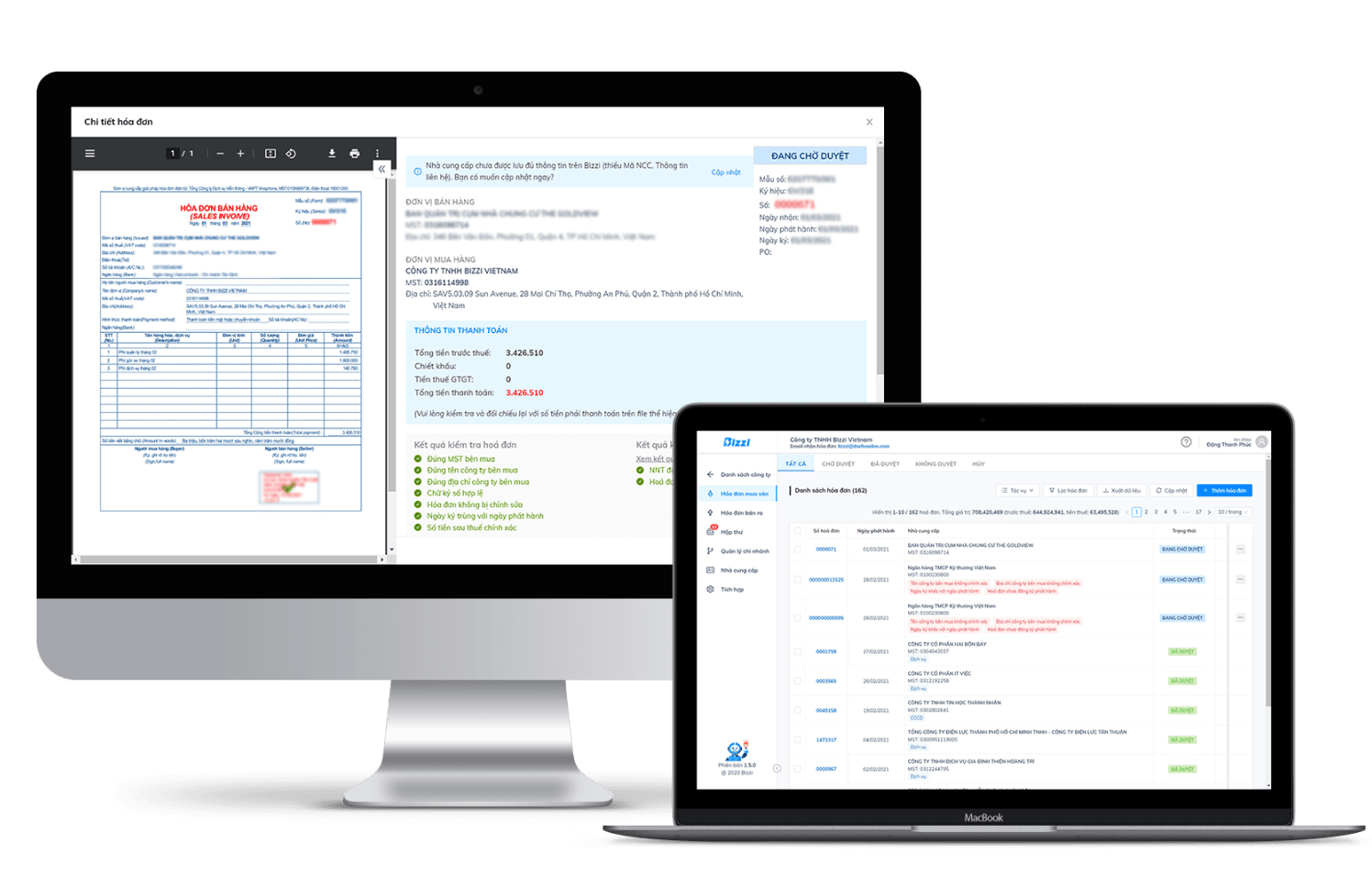
Shorten Processing Time – Speed Up Payments
- Instead of taking 3-5 minutes/invoice, it only takes 15-30 seconds for accounting to process.
- Reduced 80% data entry time, doubled productivity during peak season (month-end, quarter-end).
Transparency – Real-time monitoring – Easy management
- Managers and chief accountants can review and monitor payment and disbursement processes in real time.
- Reports on debt, expenses, and balances are updated automatically and instantly.
Smart connectivity – Flexible deployment
- Seamlessly integrates with popular accounting software and internal approval workflows.
- Easily expandable to branches and departments, helping payment accountants work effectively anywhere.
Conclude
In short, the position of payment accountant plays an important role in ensuring the accuracy and timeliness of financial transactions, contributing to maintaining a healthy cash flow and effective debt control for the business.
With Bizzi, the payment accountant is no longer just a “voucher runner” – but a proactive, smart and efficient cash flow manager. Let Bizzi help you reduce pressure, increase speed, improve expertise – and more importantly, maintain the financial reputation of the business.
- Link to register for a trial of Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/
- Schedule a demo: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/


