In the context of businesses increasingly focusing on comprehensive management and optimizing operational processes, SAP ERP software has emerged as one of the most popular enterprise resource planning solutions in the world. However, many Vietnamese businesses are still wondering: What is SAP software? How to use SAP software? How to overcome common limitations when implementing SAP?
This article will help you understand SAP ERP, guide you on how to use SAP software and its main subsystems, and suggest solutions to combine with the Bizzi financial automation platform to maximize the effectiveness of SAP in your business.
What is SAP ERP software?
SAP (Systems, Applications, and Products in Data Processing) is a technology corporation from Germany, founded in 1972, currently one of the leading suppliers ERP solutions world leader, serving over 400,000 customers worldwide.
SAP ERP SAP Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is an enterprise resource planning system that helps comprehensively manage business activities such as finance, purchasing, sales, production, logistics, human resources, etc. on a unified data platform.
SAP ERP stands out with its ability to integrate data between departments, control processes throughout, helping businesses:
- Accurate financial management and accounting
- Efficient supply chain and production tracking
- Synchronized warehouse, purchasing and sales management
- Real-time data analytics to support decision making
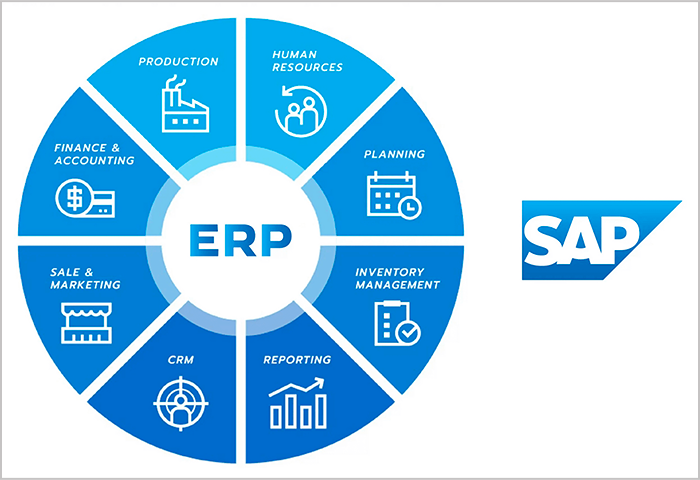
Core subsystems of SAP ERP
The SAP ERP system includes many modules specialized:
- FI – Financial Accounting: Financial Accounting
- MM – Material Management: Purchasing and inventory management
- SD – Sales & Distribution: Sales and distribution management
- PP – Production Planning: Production planning and management
- HCM – Human Capital Management: Human resource management
- SCM – Supply Chain Management: Supply chain management
- CRM – Customer Relationship Management: Customer relationship management
- BI – Business Intelligence: Business analysis
Benefits of SAP implementation
- Integrate data across departments, reduce errors, and improve operational efficiency
- Accurate financial management, real-time analysis, optimized purchasing – sales – warehouse processes
- Applicable to manufacturing, retail, multinational businesses... requiring in-depth management
SAP ERP Software User Guide – Process and Operation
When first accessing the system SAP ERP, many users often feel overwhelmed by the complexity and large number of subsystems and functions. To help businesses and users grasp easily, below are SAP software user manual in detail, from data setup to operating key operations.
1. Set up Master Data – The foundation for all transactions
Master Data plays the role of “backbone” in SAP operations. This is the initial setup step, ensuring that purchasing, sales, manufacturing or financial processes have enough background data to operate smoothly.
Required catalog data types:
- Business Partner (BP):
- Used to manage customer and supplier information.
- Information such as: tax code, address, payment information, credit terms are declared here.
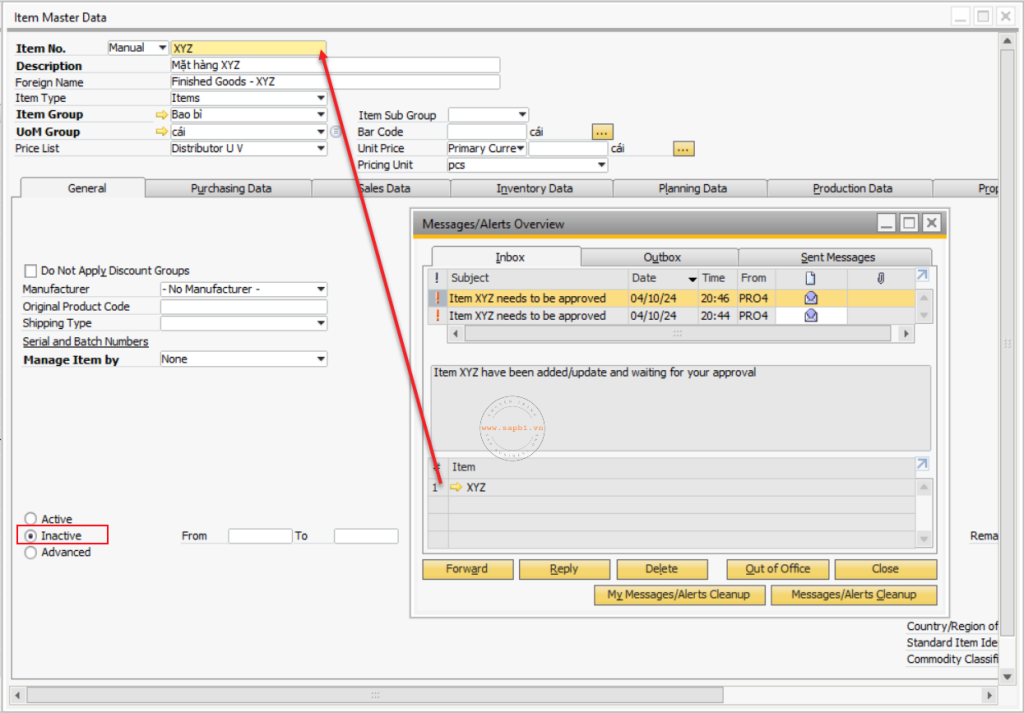
- Item Master Data:
- Manage catalog of goods, products, raw materials, services.
- Including: product code, description, product group, unit, selling price, warehouse standard.
- Warehouse Master:
- Set up storage, storage locations, warehouse structure.
- Support inventory tracking by location, avoiding loss of goods.
Note: Master Data needs to be updated accurately and consistently across the system to avoid errors when processing transactions.
2. Purchasing Subsystem (MM)
Subsystem Material Management (MM) support management of the entire purchasing process, from purchase request to supplier payment. Below are 8-step standard purchasing process in SAP ERP:
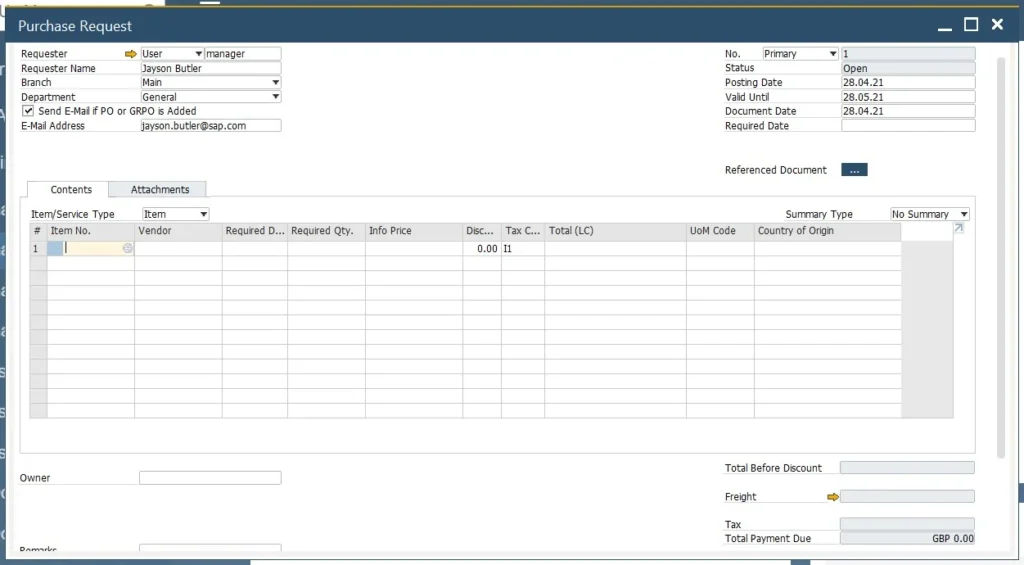
- Purchase Request:
-
- The department that needs the goods creates a purchase request on the system, clearly identifying the type, quantity, and time needed for the goods.
- This is the step that triggers the internal review process.
- Purchase Quotation:
-
- Send request for quotation to supplier.
- Record quotations on SAP for comparison, negotiate prices and terms.
- Purchase Order:
-
- Create formal purchase order on SAP after approval.
- This is a legally binding document for the supplier.
- Goods Receipt PO (Receipt & Warehouse):
-
- When the goods arrive, the warehouse department confirms the quantity, quality and creates a warehouse receipt according to the order.
- This is the basis for payment and inventory tracking.
- Landed Costs:
-
- Record shipping costs, taxes, customs fees… related to the shipment and allocate them to the value of the goods.
- Helps determine cost of goods accurately.
- Goods Return:
-
- If the goods are defective or incorrect, create a return order on the system.
- If the goods are defective or incorrect, create a return order on the system.
- A/P Invoice (Recording payable invoices):
-
- Accountants record supplier invoices, linking them to purchase orders and warehouse receipts.
- As a payment basis, avoid incorrect or duplicate payments.
- A/P Credit Memo (Decreased Adjustment):
-
- Used when there is a record of a discount, rebate or returned goods.
3. Sales Subsystem (SD) – 7 standard steps SAP B1
Sales & Distribution (SD) is a subsystem that manages the entire sales process, from quotation to delivery, invoicing and revenue recognition.
7 standard steps of sales process in SAP ERP:
- Blanket Agreement (Framework Agreement):
- Establish long-term agreements with customers, such as recurring supply contracts.
- Sales Quotation:
- Make quotation according to customer request, confirm transaction conditions.
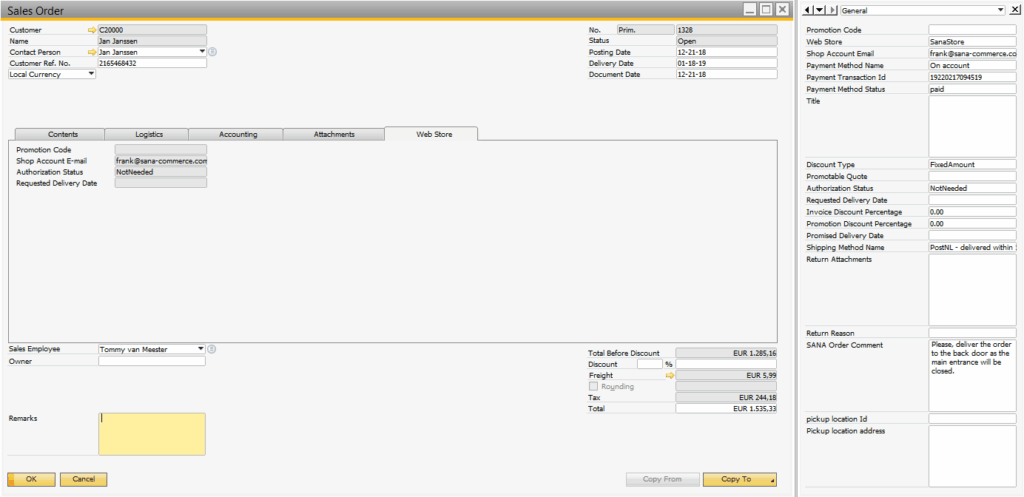
- Sales Order:
- Once the customer agrees, convert the quote into an order.
- Strictly manage payment and delivery terms.
- Delivery:
- Make warehouse delivery note and deliver goods to customers.
- Connect inventory and update order status.
- Return:
- Record returns when there is a problem, handle debt adjustments.
- A/R Invoice (Accounts Receivable):
- Issue financial invoices, record revenue and customer debts.
- A/R Credit Memo (Recording of revenue reduction):
- Adjust invoices for discounts, rebates, or returns.
4. Warehouse Management (WM/MM)
Warehouse management subsystem in SAP (usually implemented through modules) Warehouse Management (WM) or Material Management (MM)) supports businesses in comprehensively managing import - export - inventory, transfer and inventory of goods in the warehouse. All warehouse transactions are recorded. real-time on the system, helping to ensure accuracy, transparency and support effective decision making.
Main functions:
- Goods Receipt – Goods receipt
When goods are received from suppliers, finished products from factories or returned goods, the warehouse operation is performed. The system will update the inventory immediately after the receipt is successfully “posted”.
- Goods Issue – Warehouse Release
Including material export for production, export for sale, export for transfer or export for destruction. Each form of warehouse export is managed by separate business codes, making it easy to control the reasons and related costs.
- Stock Transfer – Internal warehouse transfer
Used to transfer goods between warehouses (e.g. from the main warehouse to a branch warehouse) or between storage locations within the same warehouse. SAP records warehouse transfers to ensure inventory data is correct for each location.
- Inventory Counting – Periodic inventory
The system allows creating inventory plans, printing vouchers, entering actual data and automatically comparing with system data. Any discrepancies will be recorded and adjusted according to approved procedures.
- Inventory Revaluation – Adjusting inventory value
For cases of changing cost price, re-evaluating inventory according to accounting standards. SAP supports recording inter-system adjustment entries (accounting, warehouse, assets, etc.).
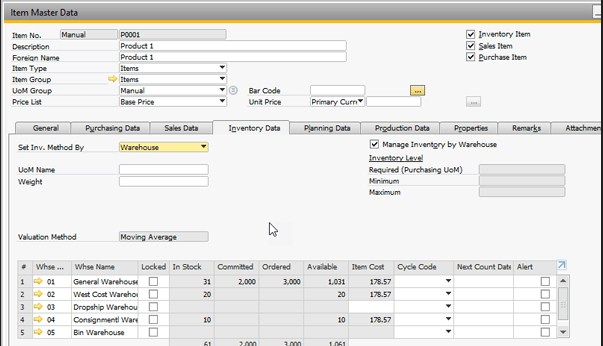
Note: All operations in the Warehouse subsystem are directly linked to other subsystems such as Accounting (FI), Purchasing (MM), Sales (SD), and Production (PP). Thanks to that, all changes in quantity and value of goods are reflected. right away, reduce errors and support more effective internal control.
5. Production Subsystem (PP)
Subsystem Production Planning (PP) in SAP helps businesses manage the entire production process – from planning material requirements to recording finished products in inventory. The system helps to strictly control costs, progress and production efficiency. Below are the basic business steps in the production process using SAP:
- BOM – Bill of Materials
A detailed list of raw materials, semi-finished products and components needed to create a complete product. BOM helps clearly define the product structure, serving the planning and control of materials.
- Production Order – Production Order
This is a formal order created to request the production of a product in a specified quantity and time. This order is directly linked to the BOM and the production process time standard.
- Material Issue – Raw material issue
When production starts, the warehouse department will issue materials according to the production order norms. The SAP system will automatically deduct the inventory and record the corresponding costs.
- Production Execution – Production Execution
During the production process, users can record completed steps, achieved output, machine or labor usage time. This helps to monitor production progress and efficiency in real time.
- Goods Receipt – Receive finished products
When the product is completed, the finished product will be entered into the warehouse through the Goods Receipt step. SAP automatically updates the inventory, goods value and reflects it to related subsystems such as accounting and sales.
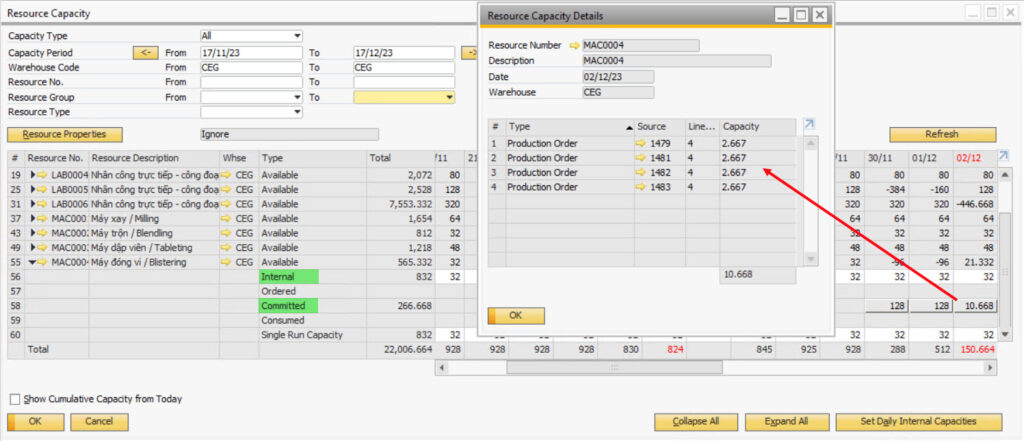 Through the PP subsystem, businesses can improve planning capabilities, optimize materials, control waste and ensure delivery progress – key factors in modern production management.
Through the PP subsystem, businesses can improve planning capabilities, optimize materials, control waste and ensure delivery progress – key factors in modern production management.
6. Accounting - Finance Subsystem (FI)
The FI (Financial Accounting) subsystem in SAP ERP plays a central role in financial management, ensuring that businesses have comprehensive control over cash flows, liabilities, assets and prepare real-time financial reports. This is the foundation that helps the management quickly grasp the financial situation and make timely and accurate decisions.
The main operations in the FI subsystem include:
- General Ledger: Record all summary entries arising during the period, linked with other subsystems such as sales, purchases, warehouse, helping accounting data to always be updated synchronously and accurately.
- Accounts Receivable (A/R): Manage receivables from customers. The system allows tracking of invoices, payment terms, debt reminders and detailed reports for each customer.
- Accounts Payable (A/P): Manage payables to suppliers. Businesses can easily control payment deadlines, arising costs and plan reasonable cash flow.
- Asset Accounting: Supports the management of the entire life cycle of fixed assets – from asset recording, value allocation, depreciation calculation to liquidation. This feature helps businesses control assets effectively and comply with accounting regulations.
- Bank Transactions: Record and reconcile bank receipts and payments. Automatically update account balances, helping accountants accurately control actual cash flow.
- Currency Revaluation: Feature of revaluation of foreign exchange rates for liabilities or assets according to accounting standards, ensuring financial statements reflect current values.
Thanks to the FI subsystem, the financial activities of enterprises are standardized, transparent and easy to control, thereby improving operational efficiency and legal compliance.
7. Basic operation instructions on SAP GUI / SAP B1
Depending on the size of the business and the deployed system, users will operate on SAP GUI (for SAP ECC or S/4HANA) or SAP Business One (SAP B1) – a simpler version for small and medium-sized businesses. Here are the basic steps to get you familiar with the system:
- Log in to the system: Use the provided account information to log in to the SAP GUI or SAP B1 interface. The interface will display the main subsystems and navigation bar.
- Select subsystem or quick access by T-code: With SAP GUI, users can enter transaction codes (T-codes) to quickly access the desired function. On SAP B1, functions are divided into clear menus such as accounting, sales, purchasing, warehouse, etc.
- Enter data according to standard forms: Each transaction (e.g. creating invoices, entering orders, recording payments…) has a predefined data entry form. Users just need to fill in the correct information and check carefully before saving.
- Save tickets and check status: After completing, click “Post” (or “Add” on SAP B1) to save the document to the system. You can check the status or change history of the document through the related screens.
- Export reports and extract data: SAP supports many types of reports that can be customized according to needs. Users can use the tool ALV Report, or extract data directly to Excel for analysis, comparison or internal reporting.
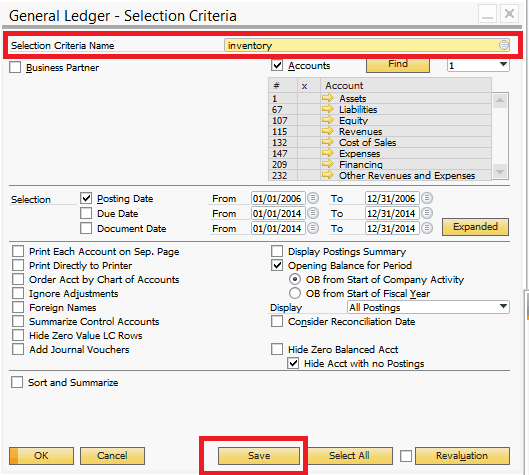
With its unique interface, SAP requires users to be familiar with the operating procedures and system logic. However, once mastered, SAP will become an extremely powerful tool to support data management and control for businesses.
8. Common difficulties when using SAP ERP
Although SAP ERP is one of the most powerful business management systems available today, there are still many practical challenges that businesses need to anticipate when using the software. Below are some common difficulties when operating this system:
- Complex multi-step process, time-consuming manual data entry:
The SAP ERP system requires users to perform many steps in a strict sequence, from creating orders, importing goods to paying. However, many steps still have to be done manually – especially in accounting data entry or document processing – leading to errors, wasting time and slowing down the operation progress.
- Lack of automation in invoice management and document reconciliation:
One of the common bottlenecks is that SAP ERP does not have built-in functions to automate electronic invoices or reconcile PO – GR – INV (Purchase Order – Warehouse Receipt – Invoice). Manually reconciling documents is not only time-consuming but also poses a risk of errors and accounting fraud.
- Users need to understand T-code, UX/UI experience is limited:
SAP operates on a set of commands called T-code – forcing users to memorize and enter the correct code for each function. This makes it difficult for non-IT professionals or those new to the system. SAP's user interface (UX/UI) is also considered unfriendly and unintuitive, hindering the process of familiarization and daily operations.
Therefore, when implementing SAP ERP, businesses need to have a suitable training roadmap, combined with supporting solutions to reduce manual operations, increase efficiency and user experience.
Bizzi – SAP Integrated Financial Automation Solution
Bizzi cannot replace ERP however Bizzi Acts as an intelligent automation layer, helping businesses optimize invoice processing and manage costs more effectively, especially when deployed SAP.
What is Bizzi and how does it integrate with SAP?
Bizzi is a SaaS platform that automatically processes input invoices, helping businesses:
- Read – classify – extract data from electronic invoices.
- Compare PO – GR – INV (order – receipt – invoice).
- Push data into SAP over a secure API connection.
Bizzi is designed to Seamless integration with SAP, which adds automation to traditional accounting processes, which often rely heavily on manual operations.
Benefits of combining SAP + Bizzi:
- Save up to 80% of manual data entry time
The entire input invoice processing process is automated, reducing manual work for accountants.
- Reduce errors – increase compliance
Data is automatically standardized and compared according to electronic invoice standards in Vietnam, limiting the risk of errors or procedural errors.
- Clear approval process, transparent cash flow
Bizzi supports a 3-layer approval process, clear user authorization – helping finance departments easily control cash flow and spending limits.
- Enhance user experience – no need to remember T‑code
Bizzi's user-friendly interface helps accountants work faster, without having to access multiple screens in SAP. Bizzi becomes the main touchpoint, connecting smoothly with the back-end SAP system.
Case Study – Imexpharm & Bizzi: Input invoice automation integrated with SAP ERP
Imexpharm is one of the leading pharmaceutical manufacturers in Vietnam with over 47 years of development, owning many factories that meet EU-GMP standards and is the first company in Vietnam to implement SAP S/4HANA Cloud according to international accounting standards IFRS.
Early 2024, Imexpharm deploys Bizzi to automate the entire input invoice processing process and integrate the solution with SAP ERP. The goal is Increase operational efficiency, optimize financial document management, and improve data accuracy.

Challenges before using automation solutions
- The accounting system must manually enter thousands of invoices each month, which is error-prone and time-consuming.
- The process of comparing purchase orders (POs), warehouse receipts (GRs) and invoices (INVs) is lengthy and requires a lot of manual work.
- Data is not synchronized between the billing system, internal accounting and the SAP ERP system.
How is the Bizzi solution deployed?
Bizzi offers a comprehensive automation platform for the input invoice process:
- Automatically receive and process electronic invoices via robot connected to dedicated email.
- Smart 3-way comparison (Invoice – PO – GR) with accuracy > 99%, supporting multiple scenarios such as 1PO–nINV–nGR or nPO–nINV–nGR.
- Automatic data extraction Switch to SAP ERP via API, completely eliminating the step of manually entering each voucher.
- Centralized invoice storage and the ability to quickly look up and report according to management requirements.
Results achieved
- 100% invoices are processed automatically, from extraction, classification to reconciliation, in just minutes.
- Processing time reduced from 2–3 days per month to minutes – saves more than 80% time compared to manual process.
- Minimize errors Thanks to accurate and precise data reconciliation, synchronization between Bizzi and SAP ERP.
- Improve the performance of finance and accounting teams: from manual operations to higher value data review and analysis.
- Transparent financial processes & clear controls: clear approval authority, audit trail of all invoice processing activities.
In case of Imexpharm is a clear demonstration of the effectiveness of Combines a powerful ERP platform like SAP B1 and the Bizzi financial automation solution. With the scale of processing thousands of invoices each month, the accounting team previously had to spend many days manually entering and checking data - both time-consuming and prone to errors.
Thanks to Bizzi, Imexpharm has Reduce processing time to just a few minutes, ensuring accuracy and real-time data synchronization with the SAP B1 system. The project not only improves operational efficiency but also contributes to building a transparent financial system that is ready to expand in the future.
This is an important step in the comprehensive digital transformation journey of the leading pharmaceutical company in Vietnam.
Sign up for a free Bizzi trial today to get started!
Conclude
Above are all the instructions for using SAP software. Deploying SAP ERP software helps businesses standardize processes, increase control and transparency in finance and accounting. However, with the technical characteristics and complex processes, users can easily encounter barriers during actual operation.
The combination of SAP and automation platforms such as Bizzi is the solution to those difficulties – helping to optimize the data entry process, document reconciliation and improve user experience. Instead of spending time on manual operations, the finance team can now focus on data analysis, planning and making strategic decisions for the business.
In the digital age, ERP is not only a management tool - but also a platform connecting smart solutions to help businesses accelerate sustainable digital transformation.
When first accessing the system SAP ERP, many users often feel overwhelmed by the complexity and large number of subsystems and functions. To help businesses and users grasp easily, below are SAP software user manual in detail, from data setup to operating key operations.


