Supply chain model is a theoretical framework that describes how organizations coordinate activities, information, and resources to transform raw materials into finished products and deliver them to end customers. A supply chain model Efficiency not only helps businesses optimize business operating costs but also serves as a platform to control complex expenditures arising throughout the entire value chain, thereby synchronizing work flows and enhancing competitiveness.
In this article, let's join Bizzi to learn more about the nature and types of supply chain model popular and how technology, especially cost management solutions, is reshaping this management approach.
How are supply chains and supply chain models different?
To build an effective strategy, it is first necessary to clearly distinguish two core concepts: Supply Chain and Supply chain model (Supply Chain Model).
What is Supply Chain?
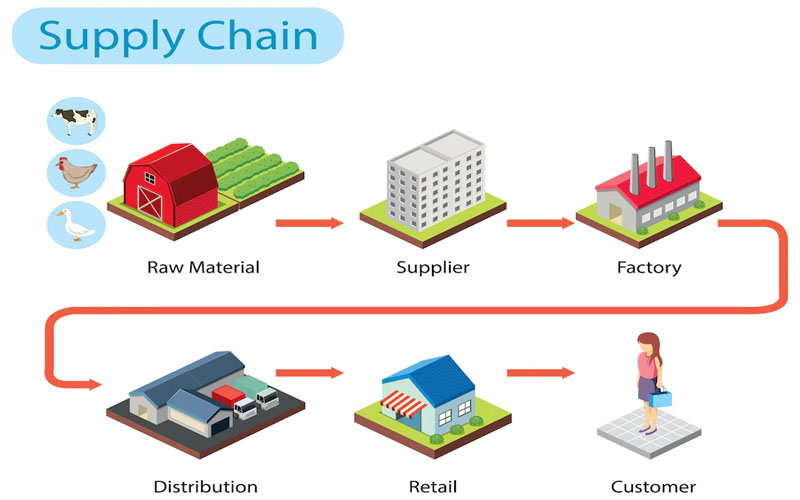
A supply chain is a physical network of organizations, people, activities, information, and resources directly involved in moving a product or service from supplier to customer. It includes everything from sourcing raw materials, manufacturing, warehousing, transportation, until the product is delivered to the end consumer.
What is a Supply Chain Model?
Supply chain model is a strategic management framework that businesses use to design, operate, and optimize their supply chains. It is not the physical supply chain, but rather the “blueprint” that determines how the components in the chain interact with each other to achieve specific business objectives such as reducing costs, increasing speed of response, or maximizing flexibility.
The comparison table below will clarify the differences:
| Aspect | Supply Chain | Supply Chain Model |
| Scope | Network of physical activities (transportation, production, distribution). | Governance framework, strategy and decision-making process. |
| Target | Get products to customers efficiently. | Optimize supply chain cost, performance, speed, and resilience. |
| Object | Suppliers, manufacturers, warehouses, retailers, customers. | Administrators, strategic planning and operations departments. |
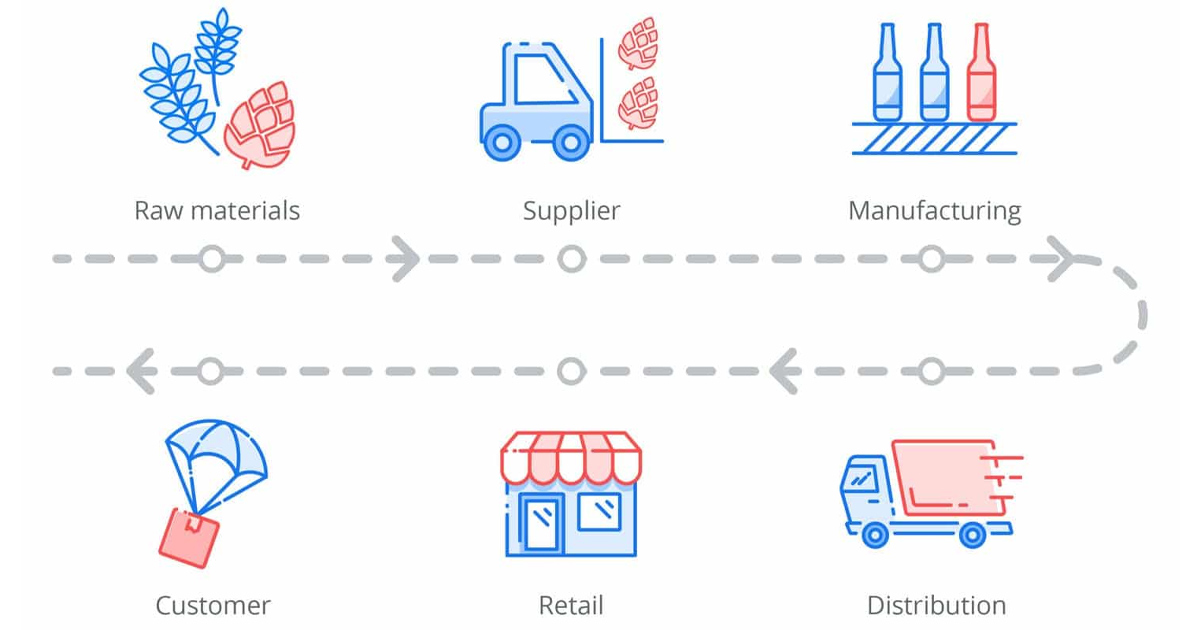
The Importance of Building an Effective Supply Chain Model
Choosing and building a supply chain model Being fit is not just an operational decision, but also a strategic advantage. A well-designed model will directly impact core business performance indicators (KPIs), especially in terms of finance and costs:
- Optimize costs and cash flow: Reduce excess inventory from 30% to 70%, thereby reducing storage and handling costs, and effectively controlling types of hidden costs in the supply chain such as the cost of handling errors or late payments. One supply chain model Efficiency also helps reduce the cash cycle, an important part of which comes from automate payment process To ensure payables are processed on time, maintain good relationships with suppliers.
- Improve customer satisfaction: Improve On-Time In-Full (OTIF) delivery rate up to 15%, ensuring products are always available when customers need them.
- Strengthening competitiveness: Shorten order lead time from 10 days to 7 days, helping businesses respond faster to market fluctuations and surpass competitors.
- Improve inventory performance: Increase inventory turns from 3-4 times/year to 8-10 times/year, showing that capital is used more effectively.
- Enhance cooperation and transparency: One supply chain model It clearly helps improve relationships and synchronize information between partners, from suppliers to distributors.
Key components and stages in a supply chain model
One supply chain model Comprehensive includes many components and is structured in logical stages to ensure smooth flow.
Main ingredients
- Partner: Includes raw material suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers and end customers.
- Support Services: Includes providers of logistics services (logistics and transportation, warehousing, packaging) and financial services (payments, credit, insurance).
- Core activities: Includes purchasing, inventory management, manufacturing, warehouse operations and customer service.
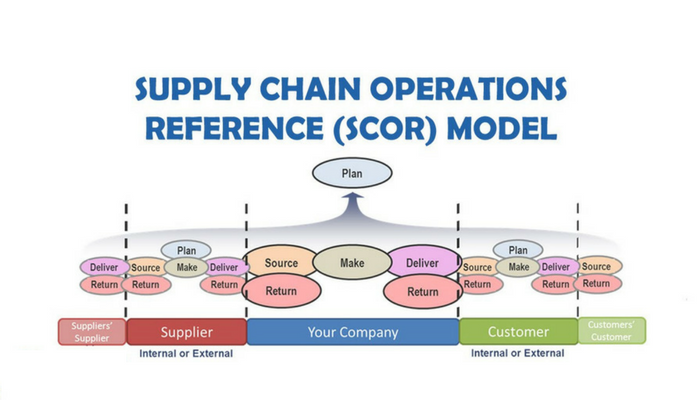
Basic stages according to the SCOR reference model
The SCOR (Supply Chain Operations Reference) model is an international standard reference framework that divides supply chain model into key management processes. The updated version has added a “Return” phase to reflect the circular nature of modern economics.
- Plan: The overall strategic planning phase, which includes demand forecasting, inventory management, pricing, and production planning.
- Source: Focus on finding, selecting, negotiating and managing relationships with suppliers. This stage incurs many costs that need to be tightly controlled.
- Make: The stage of converting raw materials into finished products, including production scheduling, quality control and plant efficiency.
- Delivery: Manage the process from order receipt to product delivery to customers, including order management, warehousing, transportation and logistics.
- Return: Managing the flow of returned products, including handling defective goods, recycling, repair or disposal. This stage is increasingly important in building a sustainable supply chain.
10 Popular Supply Chain Models and When to Apply Them
The choice supply chain model depending on the industry characteristics, market demand and strategic goals of the business. Below are the 10 most popular models:
| Model | When is it appropriate? | Advantage | Limit |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Continuous Flow | Fast moving consumer goods (FMCG) industry, products with stable demand, large quantity production. | High efficiency, low cost per unit. | Lack of flexibility, difficult to change products. |
| 2. Quick Response | Fast fashion, cosmetics, trend products. | Reduce time to market, respond quickly to trends. | Demand forecasting is difficult, operating costs are higher. |
| 3. Agile | Electronic technology, highly competitive market, demand is difficult to predict. | Ultra-fast response to fluctuations, highly customizable. | High costs due to maintaining spare capacity. |
| 4. Flexible | Seasonal products (winter clothes, moon cakes), demand fluctuates strongly. | Easily scale up/down production seasonally. | Complex management and planning costs. |
| 5. Cost-Optimized | Basic commodities, highly competitive industry on price. | Lowest possible operating costs, requiring tools business expense management closely monitor any charges that arise. | Less flexible, high risk of disruption if something goes wrong. |
| 6. Customized Response | Manufacturing of automobiles, furniture, personal computers. | High customer value, increased loyalty. | High production costs, long waiting time. |
| 7. Lean | Stable market, focus on eliminating waste. | Reduce costs, increase efficiency, stable quality. | Vulnerable to unexpected changes. |
| 8. SCOR (Supply Chain Operations Reference) | Businesses want to standardize processes and measure performance. | Provide standardized data sets that are easy to compare and improve. | Focus on process, sometimes lacking strategy. |
| 9. PDCA (Plan – Do – Check – Act) | Businesses want to continuously improve small processes. | Simple, easy to apply, creates a culture of improvement. | Not a comprehensive model, just a tool. |
| 10. Six Sigma (6 Sigma) | The manufacturing industry requires extremely high precision and quality. | Reduce errors to near zero (3.4 errors/million opportunities). | Requires large investments in training and data analysis. |
Applying technology to build an effective supply chain model
Technology is an indispensable lever to deploy and optimize supply chain model in the digital age. The application of technology helps businesses increase speed, reduce costs, increase transparency and flexibility.
Characteristics of an effective supply chain model
One supply chain model is considered effective when it meets the following criteria:
- Synchronization: Must be fully aligned with overall business strategy and goals.
- Customer-oriented: Customer needs and experiences are at the center.
- Flexible: Ability to adapt quickly to market fluctuations.
- Transparent: Data is shared seamlessly between partners in the chain.
The role of Industry 4.0
The Industrial Revolution 4.0 is the main driving force behind the process. digital transformation in the supply chain, reshaping the supply chain model through disruptive technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and financial process automation. These technologies enable the construction of “smart supply chains” that can self-forecast, self-optimize, and self-adjust in real time.
ERP and SCM: The inseparable management duo
ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) is the backbone system that integrates all business processes, while the Supply Chain Management (SCM) module in ERP focuses specifically on monitoring and coordinating the end-to-end flow of goods and information. The goal of this duo is to synchronize data and automate logistics, inventory, purchasing and order fulfillment processes.
Bizzi solves financial bottlenecks in supply chain models
While not a comprehensive SCM system, Bizzi.vn is a financial automation platform that serves as an important piece of the puzzle, helping to solve cash flow and cost bottlenecks – the lifeblood of every business. supply chain model.
Bizzi focuses on solving 3 core financial problems:
- Invoice Processing: Automating input invoice processing with AI reduces manual processing time by up to 80%, eliminates errors, and ensures timely payment to suppliers. 3-way automatic reconciliation (Invoice – PO – GRN) helps to tightly control purchasing costs.
- Expense Control: The Bizzi Expense platform allows for real-time budget setting and monitoring, tightly controlling costs incurred during supply chain operations (logistics, transportation, and warehousing costs).
- Debt Management: Automating debt collection and receivable tracking improves cash flow, ensuring financial stability for the entire system.
Through the ability Integration with ERP systems leading (Oracle NetSuite, SAP, Microsoft Dynamics), Bizzi synchronizes financial data with SCM processes, providing a comprehensive and accurate picture of operating costs, serving as a powerful complementary solution to optimize supply chain model available
Conclude
Each supply chain model Each model has its own advantages and disadvantages, and no one model is perfect for every business. The key to success lies in choosing the right model for your business, combining smart technology applications to automate processes, optimize costs and exceed customer expectations.
Bizzi.vn, as a dedicated financial automation platform, is a powerful tool to help businesses tightly control costs and improve cash flow – the foundational elements for the sustainability of any supply chain model any.
Read more: