The invoice risk assessment criteria are an "early warning filter" that helps tax authorities identify which invoices and businesses need monitoring, inspection, or audit. These criteria are considered a modern tax management tool, enabling tax authorities to detect fraud early and forcing businesses to shift from reactive to proactive invoice control.
The five criteria outlined in Circular 32/2025/TT-BTC show that tax authorities have shifted strongly towards risk management from the source, evaluating people, addresses, money flows, and relationships, instead of just looking at invoices.
What are the invoice risk criteria?
The invoice risk criteria are a set of indicators and assessment criteria used by the General Department of Taxation to identify businesses with unusual or fraudulent practices in invoice management and use.
General concept – What is the “Invoice Risk Criteria Set”?
Invoice risk criteria To be system of signs, indicators and standards by tax authority construction aiming to:
- Assess the level of risk. belong to:
- Businesses that issue invoices
- Electronic invoices are created and used.
- Early detection the behaviors:
- Use of illegal invoices
- Buying and selling invoices
- VAT and corporate income tax fraud
This set of criteria does not immediately conclude that a violation has occurred, but rather categorizes the risk (low – medium – high) to determine the level of monitoring.
Context of tightening regulations on electronic invoices
The development and application of risk assessment criteria stemmed from major changes in tax administration:
100% businesses using electronic invoices
- Electronic invoices are being implemented nationwide.
- The volume of invoice data is enormous and is generated in real time.
The prevalence of sophisticated invoice fraud is increasing.
- "Ghost" businesses, businesses that have absconded.
- Buying and selling invoices for the purpose of:
- Legitimize expenses
- Misappropriating VAT refund money.
- Intermediate business chain roundabout invoices
The tax authorities are shifting to risk-based management.
- Apply Tax management based on Big Data
- Automatic:
- Warning
- Classify
- Identifying risks
Main legal basis
Invoice risk criteria not a spontaneous conceptwhich has clear legal basis, including:
Laws & Decrees
- Law on Tax Administration No. 38/2019/QH14: Regulating tax management based on the risk principle.
- Decree 123/2020/ND-CP
- Regulations on electronic invoices and documents
- Empowering tax authorities: Monitoring – Warning – Applying management measures to risky invoices.
Circular providing guidance
Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC provides detailed guidance on:
-
- Creating, managing, and using electronic invoices.
- Verify and cross-check invoice data.
Internal document of the tax department
Decisions and official documents from the General Department of Taxation:
- Issue a list of high-risk businesses.
- Regulations on invoice risk assessment index
- Instructions for handling invoices showing signs of irregularities.
The significance of invoice risk criteria for businesses.
It's not just "fraudulent businesses" that are affected.
Legitimate businesses can still:
- Receive invoices from risk providers.
- Subject to questioning, investigation, and temporary suspension of deductions.
This directly affects tax benefits.
An invoice deemed risky may lead to:
- VAT not deductible
- Expenses are not considered valid costs when settling accounts.
- Subject to back taxes, fines, and late payment penalties.
Force businesses to change how they control invoices.
Businesses need:
- Proactive supplier review
- Check:
- Legal status
- Invoice risk history
- Complete archive:
- Contract
- Receipt and delivery record
- Payment documents
Businesses with "clean" practices will benefit from good invoice risk management, creating an operational advantage:
- Less subject to inspections and audits.
- Reduce explanation time.
- Stable cash flow and tax deductions.
Structure of the Risk Criteria Index Set according to Decision 78/QD-TCT
The risk assessment index was developed to:
- Taxpayer classification by risk level
- Implement appropriate electronic invoice management measures.
- Increase focused supervision, avoid indiscriminate inspections.
The criteria consist of three groups, each with a different management role.Not all of them are used for scoring.
1. Group I – Criteria for determining taxpayers who must switch from uncoded electronic invoices to coded electronic invoices.
These are the "trigger conditions" that determine the management status, not through scoring.
Purpose:
- Identifying high-risk taxpayers.
- Implement stricter management measures immediately.
- Behavior prevention:
- Buying and selling invoices
- Issuing fictitious invoices
- Tax refund fraud
Main features
- Meeting just one or more criteria can result in being reclassified.
- The transfer decision was issued by the tax authority.
- Applicable to taxpayers using electronic invoices without codes.

Common criteria groups
- Businesses:
- Newly established but problems have arisen. unusually high revenue
- Constantly changing: Legal representative, Head office address
- There are signs:
- Buying and selling invoices
- Not operating at the registered address.
- Has business relationships with:
- High-risk businesses
- Businesses abscond or cease operations.
Heffect: NNT forced to move to electronic invoices have tax authority code To increase control before the invoice is used.
2. Group II – Criteria for identifying taxpayers requiring review and inspection (risk scoring)
These are the core criteria used for quantitative risk management.
Purpose
- Assessing risk levels using a scoring system.
- Select taxpayers to fall into the following category:
- Explanation
- On-site inspection
- Tax inspector (if needed)
Main features:
- Each criterion is:
- Assign weights
- Assign risk scores
- Total score → ranking:
- Low risk
- Medium risk
- High risk
Consequence: Taxpayers with high risk scores will be included in targeted audit/accountability plans.
3. Group III – Reference Criteria Indicators (no scoring)
This is a qualitative group, not used for direct risk classification.
Purpose
- Support for tax officials:
- Identifying abnormal signs
- In-depth profile analysis
- Adding context to Groups I & II
Main features
- No points assigned.
- The management measures are not automatically activated.
- For use with:
- Profile analysis
- Overall assessment
Example of a reference index
- Businesses:
- There are many workers but no salary costs are incurred.
- Disparity between: Revenue – Personnel – Assets
- Unusual fluctuations:
- Monthly revenue
- Business activities compared to the actual invoice
Vplayer: To be "soft signal" to test orientation, not an independent basis for processing.
05 criteria for identifying high-risk situations when registering for e-invoices (according to Circular 32/2025/TT-BTC)
Circular 32/2025/TT-BTC supplements and clarifies the criteria for identifying risks right from the registration stage for using electronic invoices, aiming to:
- Early prevention of behavior purchase and sale invoices
- Restrict the number of "ghost" businesses, businesses established solely to evade taxes.
- Enhancing interconnectedness between tax administration, anti-money laundering, and government data.
These criteria are used to assess the initial level of risk, serving as a basis for:
- Approve or closely monitor electronic invoice registration applications.
- Determine the appropriate form of electronic invoice (with code / enhanced monitoring).
1. Criteria for fraudulent or invoice trading behavior
Identification content
- Owner, legal representative, business owner:
- He was previously found guilty of tax fraud.
- Or related to the buying and selling of invoices (directly or indirectly).
Data sources
- Internal management data of the tax authority
- Records of past administrative violations related to taxes and invoices.
Management significance
This is the "historical" risk criterion, which demonstrates:
- Risk of repeated violations
- Don't judge a business in isolation, but judge the people behind it.
2. Criteria for suspicious transactions according to the Law on Prevention and Combatting Money Laundering
Identification content
Related businesses or individuals:
- Included in the list of suspicious transactions.
- Financial institutions and banks report in accordance with anti-money laundering regulations.
Key new features
- First time in person:
- Bill Management – tax administration
- With the national anti-money laundering system.
Management significance: Creating an additional layer of risk, showing:
- Electronic invoices are not just a tax tool.
- It is also a tool for controlling the flow of money and illegal transactions.
3. Criteria regarding registered office address and business location
Typical risk factors
- The registered address is unclear., difficult to determine by administrative unit
- Headquarters:
- Place at Apartments are not permitted to be used for commercial purposes.
- Or use virtual address
- Have:
- Business location outside the province/city where the head office or branch is located.
- But Undeclared, not clearly managed.
Management significance
These are the criteria that reflect:
- The actual existence of the business
- The tax authority's ability to verify, inspect, and conduct post-audits.
4. Criteria related to organizations that violate regulations and cease operations.
Identification content
- Legal representative or owner: Also the representative/owner of:
- The business has ceased operations but has not terminated its tax identification number.
- The business is not operating at its registered address.
- These organizations:
- There were tax violations.
- There was a violation regarding the invoices.
Management significance
Identify risk linkages within the "business ecosystem," avoiding situations where an existing business violates regulations → a new business is established to continue issuing invoices.
5. Criteria for other risk indicators as determined by the tax authorities.
Additional risk factors:
- Issued by the tax authority
- Official announcements will be made in stages and periods.
Corporate responsibility
- Monitor announcements and instructions from the tax authorities.
- Timely updating of new criteria is necessary to:
- Adjust profile
- Avoid being unintentionally classified as high risk.
Management significance:
This is an open and flexible criterion, which helps to:
- Tax authorities react quickly to new forms of fraud.
- Not being "confined" to fixed criteria
Common practical signs of invoice risk in businesses.
Businesses with invoice-related risks often have Repetitive behavior patterns: legal entity that is easy to establish – short-term operation – unclear address – unusual financial indicators – cross-linking between multiple businesses.
1. Falsification and exploitation of loopholes in business registration.
Common signs
- The business registration procedure is simple, and the documents do not require in-person notarization → this is being exploited for:
- Setting up a "ghost" business
- Quick registration, low cost.
- An individual may own multiple businesses:
- Legal representative
- The controlling owner or shareholder
- These businesses:
- There is no actual business activity.
- For the purpose of issuing and buying/selling invoices only.
Management risk: Tax authorities assess risk based on the "people behind the legal entity," not just on individual businesses.
2. The business is not actually operating at its registered address.
Common signs
- Businesses:
- No physical office
- No warehouses, machinery, or personnel.
- Cannot:
- Verification at the registered address
- Contact the tax authorities when they conduct an inspection.
- Short business lifecycle:
- Operating for 1-2 years
- Then they paused or fled.
Management risks
- Businesses that "sell invoices"
- Businesses are created to legitimize expenses for other parties.
3. Constantly changing tax registration information
Common signs
- Change:
- Multiple registered office addresses
- This leads to a change in the tax authority in charge.
- Acquisition:
-
- The former legal entity is no longer in operation.
- Tax history available, Tax Identification Number (TIN)
- "Reusing" legal entities:
- Invoice
- Unusual revenue generated within a short period of time.
- Management risk: Disrupts the risk history tracking process, making post-auditing difficult.
4. Pause – resume – pause again
Common signs
- Businesses:
- Registering for a temporary suspension multiple times in a row.
- But invoices or transactions still occur.
- Do not perform:
- File your taxes fully.
- Tax payment obligations
- After some time:
- Remove address
- Establishing a new legal entity
Management risks
- "Attack quickly – retreat – escape"
- There is a very high risk regarding invoices and taxes.
5. Financial indicators show risk.
Common financial signs
- VAT payable / domestic revenue:
- Abnormally low (e.g., < 1%)
- Revenue from affiliates:
- Accounts for a large proportion.
- Not suitable for the business model.
- Fixed Assets / Equity Ratio:
- Low, disproportionate to the industry.
- Large revenue fluctuations between consecutive periods:
- Sudden increases/decreases without a logical reason
- The rate of canceled, replaced, or adjusted invoices is high.
- Profit margin on revenue:
- Too low or prolonged low pitch
- But they still issue invoices for large amounts.
Management risks
- The business does not create real economic value.
- The invoice may simply serve the purpose of legitimizing the transaction.
Consequences when invoices and businesses are classified as high-risk.
Being classified as high risk It's not just a "system alert"., which leads to chain reaction Regarding taxes, operations, cash flow, and reputation.
1. Restricting the use of electronic invoices.
Common consequences
- Forced to switch from:
- Electronic invoices without codes
- Convert to electronic invoices with tax authority codes.
- In severe cases:
- The use of invoices has been temporarily suspended.
- Invoices may only be issued with the approval of the tax authorities.
Actual impact on the invoicing process:
- Slower
- Pre-controlled
- This directly impacts sales performance and revenue recognition.
2. Risks related to VAT and corporate income tax.
Tax consequences
- Invoices deemed risky may: Not be eligible for input VAT deduction.
- Related costs:
- There is a risk of these expenses being disallowed as deductible expenses when calculating corporate income tax.
Actual impact on businesses
- Subject to back taxes
- Charged for late payment
- Unexpected tax expenses were incurred.
3. Increase the frequency of inspections and audits.
Consequences of management
- Businesses that have been included:
- Special monitoring list
- Plan for regular or unscheduled inspections and audits.
- Request:
- Regular accountability
- Provide contracts, documents, and transaction records.
Hidden costs are not just fines:
- Time-consuming for: Accounting – Legal – Management
- Disruption of normal business operations

4. Risks of penalties and criminal liability
Administrative penalties
- Penalties for violations: Regarding invoices – incorrect declarations – late tax payments
- Attached: Late payment penalty or remedial measures
Criminal liability (in serious cases)
- If the following behavior occurs: Invoice trading – Tax evasion – Money laundering
- Possible causes:
- Prosecute criminal liability.
- Freeze the account.
- Seize assets
Risk It's not just limited to businesses., but also manager.
5. Impact on cash flow and partnerships
Impact on partners
- Partner:
- Refuse to accept the invoice.
- Request for further explanation
- Extend the payment period
Impact on cash flow
- Bill:
- Not accepted
- Suspended pending verification
- Cash flow:
- Delayed
- Financial plans were disrupted.
Long-term consequences: Damage to the company's reputation.
- Difficult to sign new contracts
- Rated as high risk in the supply chain.
What should businesses do to self-assess and reduce invoice risk?
The core principle: Don't wait for tax authorities to issue a warning before taking action; proactively control the situation from the source – legal aspects, transactions, data, and records. Businesses reduce invoice risks not through clever tricks, but through internal control systems – transparent data – and complete records.
1. Self-review registration documents and legal structure.
What businesses need to do
- Double-check:
- Head office, business location
- Is it in accordance with regulations and is it permitted to operate as a business?
- Review:
-
- Legal representative
- Owner/Shareholder
- Compare these individuals to see if they have:
- Registered under the name of multiple other legal entities
- Related businesses that have previously been affected:
- Cease operations
- Tax and invoice violations
- Risk reduction value: Reduce the risk of being assessed for risk right from the e-invoice registration stage.
2. Quality control of input and output invoices
Mandatory principle
- Only deal with this supplier:
- Has a valid tax identification number.
- Currently operating
- Before accounting:
- Check the legal status of the supplier.
- Check the risk history (if any).
The files must be securely attached.
Each invoice must be accompanied by the following:
- Contract / Purchase Order (PO)
- Handover/Acceptance Report
- Non-cash payment documents (if required)
3. Establish internal control procedures for invoices and expenses.
Key component
- Establish:
- Purchasing process
- Invoice creation and issuance process
- Clear and distinct delegation of authority:
- Purchase
- Receive
- Accounting records
- Pay
Actual value
- Creating fictitious invoices
- Errors caused by one person handling the entire process.
4. Periodically reconcile accounting, inventory, and tax data.
What to do
- Regularly (monthly/quarterly):
- Comparison: Electronic invoice data, Tax reports, Accounting records, ERP/inventory system.
- Early detection:
- Revenue discrepancy
- Inventory discrepancies
- Incomplete/mismatched invoices
Benefits: Addressing errors beforehand avoids being caught off guard when tax authorities conduct an audit.

5. Prepare for accountability.
Required platform
- Document storage:
- Full
- There is a system
- Easy to access
- Apply the principle:
"Each invoice = a complete set of documents"
The standard set of documents includes
- Electronic bill
- Contract / Purchase Order
- Receipt and delivery record
- Payment documents
- Emails and related agreements (if any)
Good explanation = reduces the risk of expense disallowance or retroactive collection of charges.
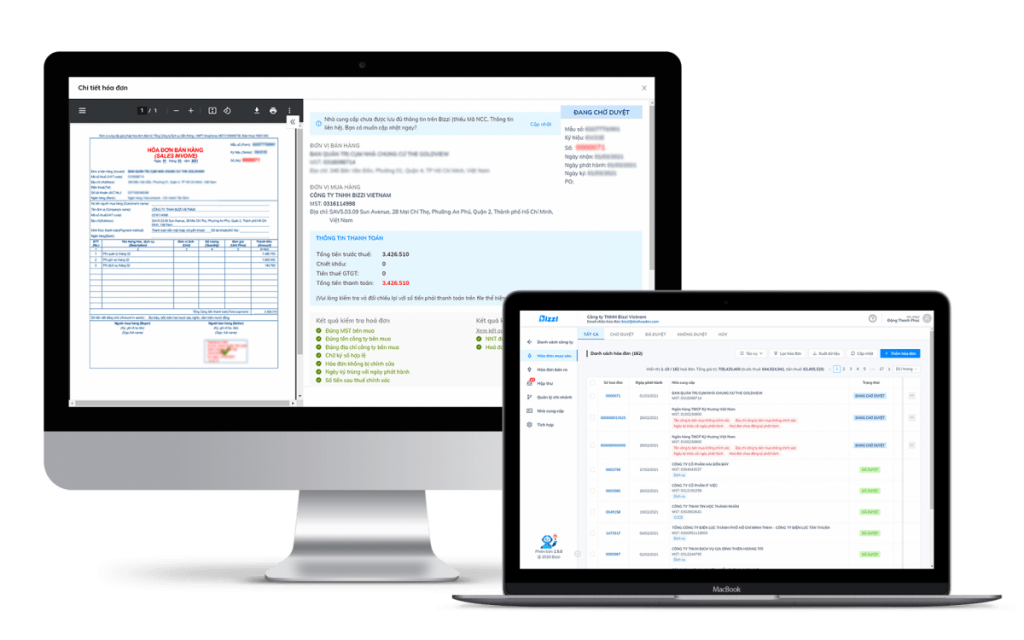
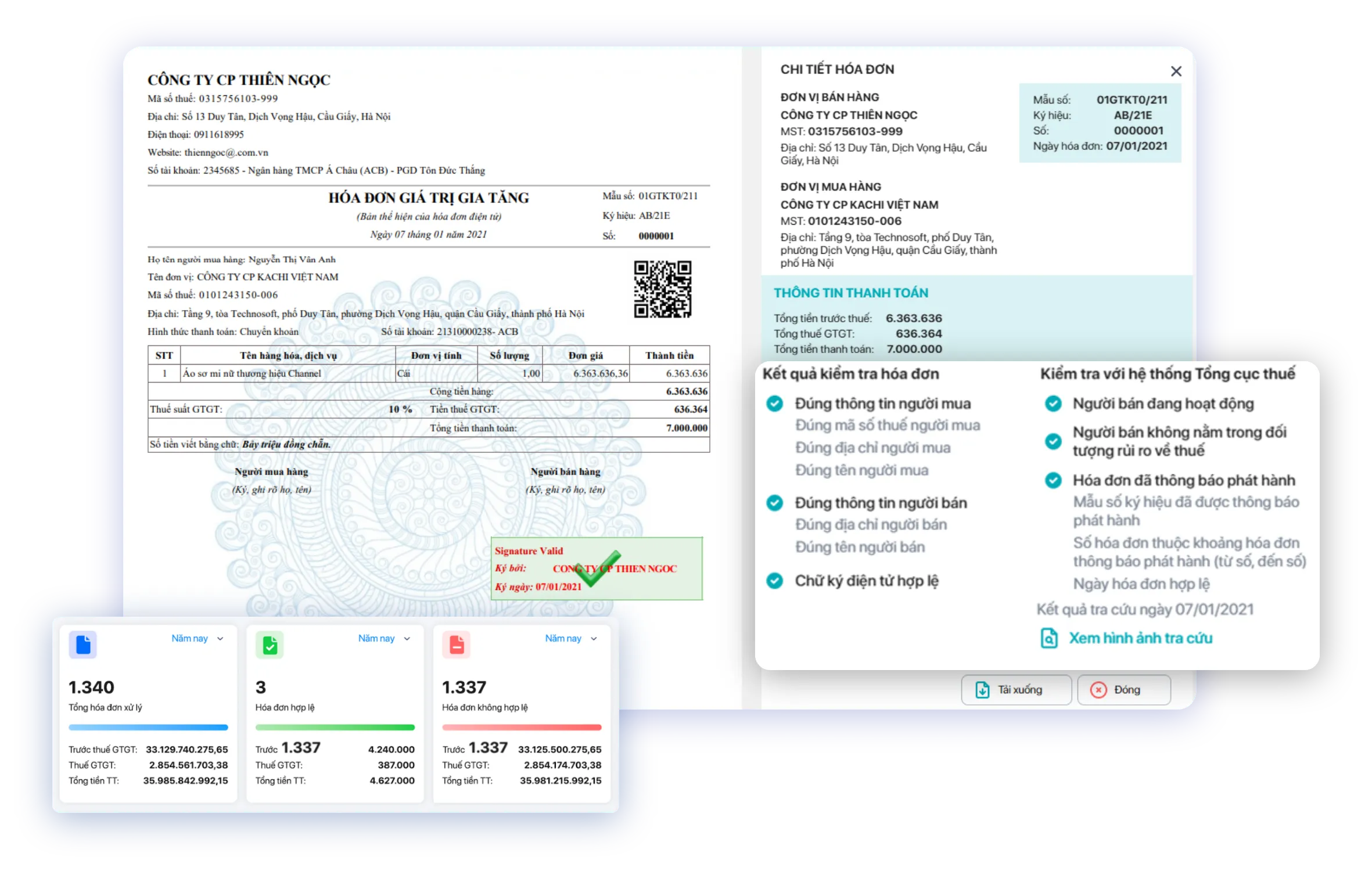
Bizzi Solutions: Helping businesses minimize invoice-related risks.
Bizzi solutions help businesses minimize invoice risks by automating the entire process from receiving, processing, storing, to reconciling input/output invoices. WHO RPA helps detect errors early (duplication, incorrect information, risky vendors), ensures legal compliance, and significantly reduces manual errors, saving time and costs.
Ways Bizzi minimizes invoice risk:
-
- Invoice processing automation (Bizzi IPA)
- Automated collection: Provide a private email address, and a bot will automatically retrieve invoices for processing.
- Fast Extraction & Processing: Utilizing AI & RPA, extract invoice data (electronic & paper) in seconds with high accuracy.
- Reduce errors: Minimize manual data entry, avoid mistakes and duplicate invoices.
- Management and Control of Compliance Risks
- Verification & Alerts: Automatically checks for validity, alerts for tax issues (risky suppliers), and regulatory violations.
- 3-way matching: Automatically compares invoices with purchase orders (POs) and warehouse receipts, minimizing tax risks.
- Secure storage: A centralized, intuitive, easily searchable storage system, ready for auditing.
- Cost Management (Bizzi Expense)
- Expense control: Track expenses in real time and automatically flag expenses that exceed the budget.
- Optimize cash flow: Automated and transparent approval processes enable faster cash flow.
- Electronic Invoice (B-Invoice)
- Issuing legal invoices: Compliant with Decree 123/2020/ND-CP, integrating invoices from POS machines and electronic tickets.
- Invoice processing automation (Bizzi IPA)
- Manage accounts receivable and reduce cash flow pressure when dealing with invoice risks with Bizzi ARM.
-
- Track customer and supplier accounts payable in real time.
- Automated payment reminders help reduce the number of outstanding bills due to disputes.
- Manage accounts receivable and reduce cash flow pressure when dealing with invoice risks with Bizzi ARM.
-
Financial and accounting perspective: Bizzi as an "AI assistant" for risk management.
-
Automating the revenue, expenditure, and invoicing processes helps to ensure clean and consistent data.
-
Increase compliance and reduce the likelihood of being classified as a high-risk category.
-
Key benefits of the invoice risk assessment criteria
Using a set of invoice risk criteria helps businesses detect anomalies early, thereby preventing tax risks (such as back taxes and penalties) and legal and operational risks, while optimizing the management and use of electronic invoices more effectively.
- Legal and financial risk prevention: Helps businesses identify invoices with signs of illegality (fictitious invoices, invoices with errors) to avoid using them, reducing the risk of tax authorities collecting back taxes, penalties, and impacting business operations.
- Enhanced compliance: Encourage businesses to self-assess and comply with tax and invoicing regulations, avoiding being classified as high-risk.
- More efficient management: Electronic invoicing systems enable automatic verification, retrieval, and transparent storage, making it easy to detect errors and anomalies in transactions.
- Cost and time savings: Minimize the effort and costs associated with processing and verifying paper invoices or problematic invoices, and automate many tax administrative procedures.
- Enhancing reputation: Ensuring accuracy and transparency in transactions, building a compliant and professional corporate image.
Conclude
The invoice risk assessment criteria are no longer recommendations, but have become a "mandatory safety standard" in current tax administration. In the context of tax authorities intensifying data analysis, real-time electronic invoice connectivity, and enhanced post-auditing, every input invoice can become a risk if businesses lack appropriate control procedures.
As the volume of invoices increases, manual verification is no longer fast or accurate enough. This is where solutions that support the processing of incoming invoices, such as Bizzi, play a crucial role. Bizzi helps businesses:
- Automatically reconcile invoices with supplier tax data and legal information.
- Early warning of risky invoices based on multiple criteria (issuing company status, risk history, invoice content, etc.).
- Standardize the process of controlling input invoices, reducing reliance on individual experience.
- Saving time for accountants while minimizing systemic tax risks.
Managing invoice risk is not just the responsibility of the accounting department, but an integral part of a company's sustainable financial management strategy. Combining a proper understanding of invoice risk criteria with the application of technological solutions like Bizzi is how businesses can proactively prevent risks, rather than dealing with the consequences after being singled out by the tax authorities.
Register here to receive personalized solutions tailored specifically for your business: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/


