A business facing invoice risk doesn't necessarily mean the invoice will be rejected. Carelessness in verifying partners and archiving documents can lead to negative consequences, even for genuine transactions.
This article by Bizzi will provide a list of 1500 businesses at risk from invoice-related issues, and offer solutions on what businesses need to do to avoid these risks.
What are the risks associated with invoices in businesses? Why is it necessary to check the invoice list before receiving an invoice?
Billing risks are different from purchase and sale invoicesHowever, it is still enough to cause tax problems for businesses receiving invoices. Therefore, businesses facing invoice-related risks need to understand the nature of the issue to find appropriate solutions and avoid violating current laws.
1. Definition of "invoice risk businesses" (from the tax authority's perspective)
Businesses at risk of invoice-related issues are those that have been placed on a warning list by the tax authorities due to signs of non-compliance with invoice and tax obligations, or the potential risk of using illegal invoices.
Risk assessment does not automatically conclude that a violation has occurred, but it does signal:
- Invoices issued by this business need to be closely monitored.
- Partner businesses may have their tax rights affected upon receiving the invoice.
2. Differentiate between easily confused concepts
Businesses at risk regarding invoices.
- Placed on the tax authority's watchlist/warning list.
- This could be due to: unusual address changes, long-standing tax debts, inactivity at the registered address, unusual tax declarations, etc.
- It's not necessarily about buying and selling invoices, but the issued invoices carry a risk of being rejected.
Businesses that buy and sell invoices
- This involves issuing or purchasing fictitious invoices that do not reflect actual transactions of goods/services.
- This is a violation of tax laws.
- The invoice is definitely invalid; the business using it will be subject to back taxes and penalties.
The business only made procedural errors (it was not classified as high-risk).
- Administrative errors: late submission of reports, incorrect information entry, incorrect declaration, etc.
- There were no signs of fraud or tax evasion.
- If the adjustments have been made in accordance with regulations → The invoice is still accepted..
3. Why is it essential for accountants and businesses to pay attention to this?
Risk of losing tax benefits
- Input invoices from high-risk businesses may include:
- VAT not deductible
Increased likelihood of being inspected or audited.
- Invoice records from high-risk businesses often suffer from:
- Request for explanation
- Reviewing documents, contracts, payments, and shipping.
The risk of collateral damage even if the transaction is genuine.
- Businesses buy genuine goods and make genuine payments.
- But even if the partner is rated as high risk, the business still:
- It takes time to explain.
- Under pressure to collect outstanding taxes and adjust accounting records.
- Impact on cash flow and reputation

The tax authorities are publishing lists of businesses at risk regarding invoices.
Currently, tax authorities and other relevant agencies have published several lists to assist accountants in searching and controlling invoices, including:
List of businesses involved in invoice trading, posing a high risk to taxation.
This includes businesses identified as engaging in illegal invoice trading or posing a high risk according to tax assessments. Businesses in this group are at risk of issuing illegal invoices.
- 113 businesses Selling invoices illegally as per the official document. 3385/TCT-TTKT August 1, 2024 – General Department of Taxation.
- List 168 "ghost" companies Serving the buying and selling of invoices (updating continuously).
- List Businesses that absconded in 2024
List of 637 businesses at risk regarding VAT invoices.
The summary includes:
- 524 businesses invoice risk According to Official Letter 1798/TCT-TTKT (05/2023);
- 113 businesses selling invoices illegally According to Official Letter 3385/TCT-TTKT (08/2024).
This is a list commonly used by tax authorities to review and control the risks associated with invoice usage.
The list is updated periodically (it is not fixed).
In addition to the aforementioned list of 637 businesses, tax authorities, police, and other relevant agencies may continuously issue new documents to supplement the list of businesses with invoice-related risks based on actual data (for example, multiple small groups of 30-300 businesses in each document, categorized by locality).
- 31 businesses according to the Official Letter 633/CV-CSKT(D3) October 17, 2024 – Nam Dinh Police Department.
- 305 businesses according to the Official Letter 24903/VPCQCSĐT-Đ3 October 31, 2024 – Ho Chi Minh City Police Department.
- 185 businesses The Nghi Son Police (Thanh Hoa province) announced the buying and selling of invoices on September 30, 2024.
- 66 businesses according to the Official Letter 5108/CTTBI-TTKTI September 16, 2024 – Thai Binh Provincial Tax Department.
- List as per Official Document 8237/CTTPHCM-TTKT2 August 20, 2024 – Ho Chi Minh City Tax Department.
- 1,498 businesses Invoice risks in Phu Tho province in 2023.
- 742 businesses Tax and invoice risks as per the Official Letter. 3379/CCT-KT2 – Tax Department of Thu Dau Mot City.
- Official document 2731/VPCQCSĐT September 30, 2025 regarding 237 businesses no production or business activities, of which 225 businesses are registered with their headquarters in Ho Chi Minh City.
How can I tell if my business partner is a high-risk company in terms of invoices?
To determine whether a business has an invoice risk, accountants should not rely solely on intuition, but should combine formal research with an assessment of actual risk indicators.
1. Check on the official channels of the tax authorities.
This is the step obligatory before receiving input invoices.
Channels to check:
- General Department of Taxation Portal:
Check the business's operational status (active, temporarily suspended, abandoned address, subject to enforcement action, etc.). - List of businesses at risk regarding invoices, published by the tax authorities.:
This includes lists of businesses involved in buying and selling invoices, and businesses with high risk regarding VAT invoices (for example, group 524/637 businesses). - Notices and warning letters from the local Tax Department. (if any).
Important Note:
- Risk list Updated periodically, not fixed.
- A business There may not be a violation at the time of the transaction.but were still classified as high-risk due to other unusual signs.
So, Look up the information at the time the invoice is received. is extremely necessary.
2. Identifying businesses with invoice-related risks through a "25-sign criteria"
In addition to the published list, the tax authorities also use... Risk assessment criteria (often referred to as the 25 indicators) to classify businesses. Businesses/partners may be classified as high-risk if certain factors appear. one or more of the following signs:
Legal and operational signs
- Frequent changes in legal representative, address, and business activities within a short period of time.
- The business is not operating at its registered address or has absconded.
- The registered capital is large but disproportionate to the actual scale of operations.
Invoice indicators
- Export electronic invoices with high value and frequency, but not suitable for the company's capabilities.
- The invoice content is general, repetitive, and lacks detailed descriptions of goods/services.
- Issuing invoices to multiple businesses in various provinces/cities with no clear connection.
Financial & Tax Indicators
- High revenue but no corresponding expenses.
- They declare high output VAT but lack suitable assets, personnel, and warehousing facilities.
- Regularly paying taxes late, being subject to enforcement actions, or receiving reminders about tax obligations.
Receiving invoices from businesses with invoice-related risks: are they tax-deductible and can they be considered expenses?
The answer isn't always "no," but depends on when the invoice is generated and the level of risk for the issuing business.
General principles
The tax authorities do not disallow expenses simply because the partner is on a risk list, but rather consider the nature of the transaction.
Invoices are only eligible for VAT deduction and considered reasonable expenses when:
- The transaction was genuine;
- Goods/services have been actually provided;
- There is complete supporting documentation (contract, delivery receipt, non-cash payment, etc.);
- The purchasing business did not collude, was unaware of, or abet the buying and selling of invoices.
Invoices issued before the date the business absconded/was identified as a risk.
Processing principle:
- VAT may still be deductible and included as an expense if:
- Transactions that occurred before the tax authorities determined that the business had absconded or was placed on a risk list;
- The purchasing business can prove that the transaction is genuine.
Practical application:
- Accountants will often be asked to explain the records;
- The tax authorities conduct a more thorough inspection but do not automatically classify invoices by type.
This is why keeping complete records right from the start is extremely important.
Invoices issued after the date the business is deemed to have absconded/become a risk.
The risk is very high. Typically:
- VAT is not deductible;
- These expenses are not deductible when calculating corporate income tax.
- It may be deemed that there were no actual transactions or that the invoices were used illegally.
In this case, the purchasing business finds it very difficult to protect its tax rights, even with supporting documents.
The deductions were claimed, but then notification was received that the issuing company was at risk.
This is the situation very popular Businesses face invoice-related risks. How to handle them:
- Business Not subject to immediate automatic retroactive collection.;
- The tax authorities will:
- Send notifications;
- Business requirements Provide explanations and additional documentation to prove the actual transaction..
The result depends on:
- Completeness of the documentation;
- The time the invoice is issued;
- The question is whether the purchasing company acted in good faith.
If Transaction cannot be provenThe invoice may be affected by:
- Excluded from expenses;
- Collect back the VAT that was previously deducted.
- Calculate the late payment penalty.
Legal consequences of dealing with businesses that have invoice-related risks.
Dealing with businesses that engage in invoice-related risky transactions can lead to serious legal consequences involving taxes, administrative penalties, and, more seriously, criminal charges. Businesses may face criminal prosecution (for tax evasion, illegal invoice trading) if they intentionally or severely violate regulations, significantly impacting their finances, cash flow, and reputation.
1. Tax consequences
- Expenses are excluded when calculating corporate income tax.
- VAT is not deductible or may be subject to retroactive collection.
- Arise:
- Late payment penalty
- Tax collection over multiple periods
2. Administrative penalties
Depending on the degree:
- Penalties for false declarations.
- Penalties for using illegal invoices.
- Penalties for violations related to document storage.
Even if unintentionalHowever, businesses can still be penalized for a lack of control.
3. Criminal risk (serious cases)
If the authorities determine:
- Business Knowing the invoice trading partner
- Or there are signs colluding, assisting
Criminal liability may be considered in connection with this. crime of buying, selling, and using invoices illegally.
So what can businesses do to avoid risks associated with invoices?
What can businesses do to avoid risks related to invoices?
Invoice risk doesn't stem from a single incorrect invoice, but from a lack of control procedures. Discovering a partner is at risk for invoice-related issues doesn't automatically mean your business is "at fault," but improper handling can lead to tax risks spreading to your own company. The solution should be implemented in stages as follows:
Before any new transaction occurs
The most important principle: Proactive prevention. Businesses should implement the following:
- Stop or postpone new transactions with partners on the invoice risk list.
- Check the legal status of the partner company:
- Status of operation on the General Department of Taxation's portal
- Is there a notice stating "not operating at the registered address," "ceased operations," or "absconded"?
- Review the contract:
- Payment terms, invoices, tax obligations
- Clause for termination/cancellation of the contract if the partner violates tax obligations.
- Switch to a partner with a more transparent track record to avoid cascading risks.
With invoices already received from risky businesses
The tax authorities don't automatically accept invoices just because the transaction "says it's real" — everything depends on the documentation and the ability to prove it. Businesses need to act now:
- Review all received invoices and categorize them:
- Invoices issued before the time the business was identified as having risk.
- Invoices issued after the risk was recorded.
- Prepare all necessary documents to prove the actual transaction, including:
- Contract
- Acceptance/Delivery Report
- Non-cash payment voucher
- Email, quotation, and related documents.
- Assessing tax risk:
- The invoice may be disqualified from VAT deduction.
- The expenses may not be included when settling corporate income tax.
- Proactively work with tax advisors/legal departments to find solutions early (adjustments, expense exclusions, provision for doubtful debts, etc.).
Upon receiving a notification or invitation to work from the tax authority.
A cooperative attitude, clear records, and rigorous internal control procedures significantly reduce the risk of attribution. Businesses should:
- Read the notice carefully: Is it a request for explanation, a notification of a high-risk invoice, or a decision to conduct an inspection or audit?
- Prepare a complete and focused explanatory document:
- Proof that the transaction is genuine.
- Prove that the purchasing business was unaware of and did not abet the transaction.
- Do not provide unsubstantiated explanations or submit disjointed documents.
- Record all interactions with the tax authorities (minutes, emails, official letters).
- Have a contingency financial plan ready:
- Tax collection
- Late payment penalty
- Administrative penalties (if any)
Business risk control process for invoices
In the context of tax authorities increasingly tightening the management of electronic invoices, invoice risk control cannot rely solely on "accounting experience," but requires clear procedures and supporting technology.
Basic internal control procedures (mandatory)
Step 1: Check the tax identification number and business status before signing the contract.
- Look up the partner's tax code here:
- General Department of Taxation Portal
- Electronic Invoice Portal
- Determine the condition:
- Operating normally
- Temporarily suspended / out of service
- Remove business address
- There is a risk warning regarding the invoice.
Principle: No contract – no order – no payment if the partner shows clear signs of risk.
Step 2: Check the invoice immediately upon receipt.
- Check:
- Does the invoice exist in the tax system?
- Seller information, Tax ID, invoice date
- Time of issuance relative to the company's legal status.
- Early detection:
- Invoices issued after the business has absconded/received a warning.
- The invoice shows signs of irregularities in value and content.
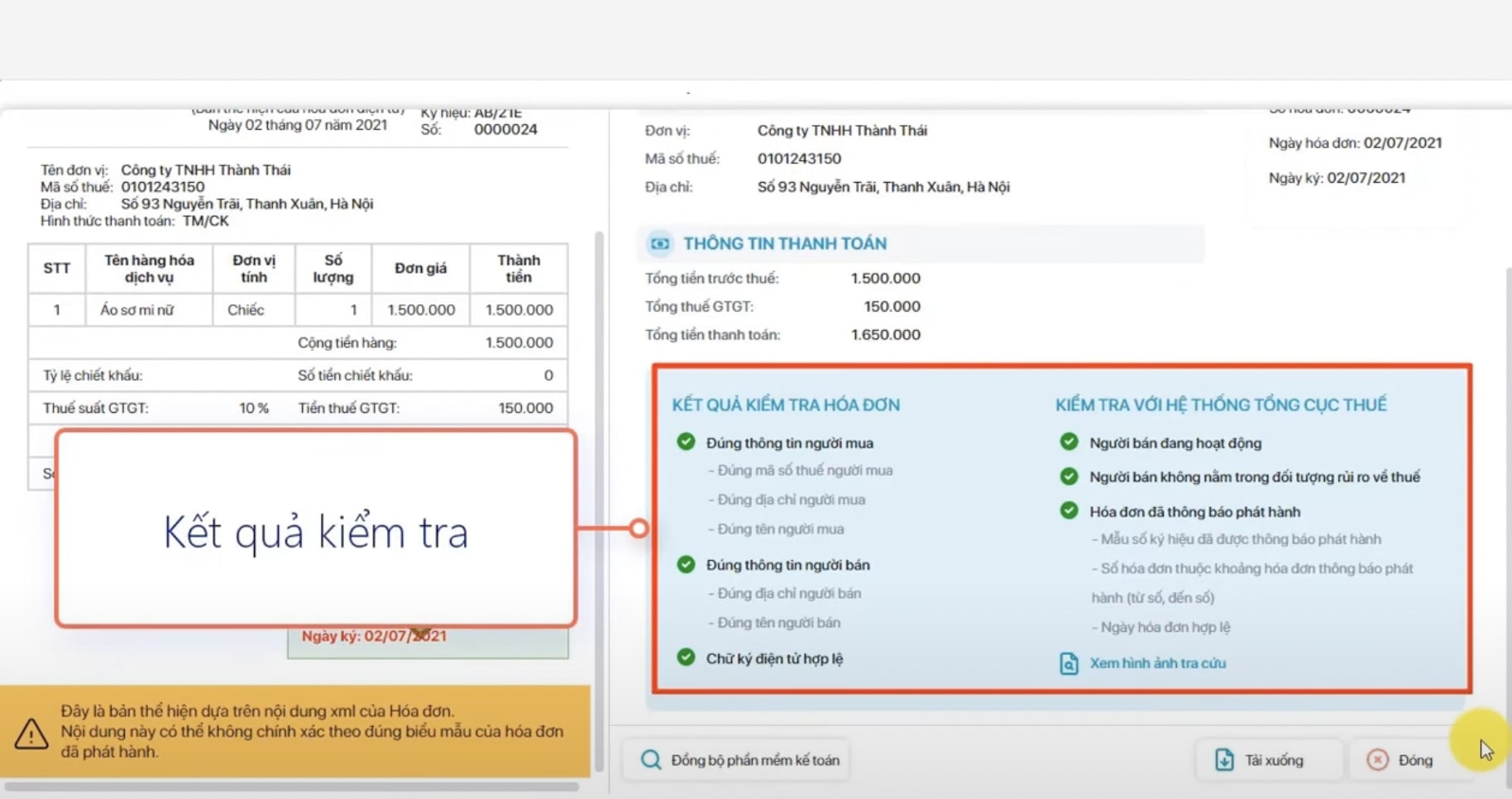
Step 3: Compare the four core elements.
- Contract
- Delivery/Warehouse Receipt/Acceptance Slip
- Bill
- Payment documents
Without proof of the actual transaction, invoices are easily rejected during tax audits.
Step 4: Flag the supplier as "risky".
- Internal observations from suppliers indicate the following:
- Unusual information changes
- Large transaction value but weak record.
- Previously on the list of risky invoices
- Apply:
- Stricter control procedures
- Request additional documents before making payments or filing taxes.
Applying automated solutions
When dealing with a large volume of invoices, manual control is prone to errors, time-consuming, and human-dependent. This is where technology comes into play, automating invoice control:
- Automatically read electronic invoice data.
- No manual input required.
- Reduce data errors.
- Automatically check tax identification number (MST) and business status.
- Compare with tax data.
- Discovering businesses that have ceased operations, absconded, or are at risk.
- Supplier risk early warning
- When included in the risk list published by the tax authorities.
- When there is a "pattern" similar to that of businesses that buy and sell invoices.
(unusual invoice values, high frequency, weak records, etc.)
- Three-way reconciliation (PO – GR – Invoice)
- Transaction mismatch detected.
- Prevent invoices where "goods arrive first - items arrive later - or there are no items"
Platforms like Bizzi It acts as an “automatic control layer,” supporting accounting and finance right from the invoice receipt stage.
Benefits of combining processes and technologies
- Significantly reduce manual search time: Accountants don't need to manually check every tax identification number and every invoice.
- Reduce the risk of receiving invoices from risky businesses right from the start: Early detection – before filing – before payment.
- Prepare your documents in advance for explanations to the tax authorities: All data, inspection history, and documents are stored systematically.
- Protecting the tax rights of businesses: Avoid having expenses disallowed, losing VAT deductions, or being subject to back taxes or late payment penalties.
Frequently Asked Questions about Businesses at Risk of Invoice Issues
Common invoice-related risks in businesses include information errors, invalid invoices, insufficient documentation for non-cash payments, or businesses showing signs of high risk… Below is a compilation of questions related to this topic.
1. What are the risks associated with invoices in businesses?
This is a business that has been warned by the tax authorities as having a high risk related to the issuance or use of invoices, which could affect the tax deduction rights of its trading partners.
2. How do I know if a supplier is on the risk list?
Businesses can look up their tax identification numbers on the General Department of Taxation's portal or use automated software for early checking and warnings.
3. Are invoices from high-risk businesses eligible for VAT deduction?
It's uncertain. The tax authorities may disallow deductions and expenses if the actual transaction cannot be proven and properly documented.
4. What should I do if I've already filed the invoice but then receive a risk notification?
It is necessary to review the records, prepare supporting documents to prove the transaction was genuine, and comply with the tax authorities' request for explanations.
5. Should you continue doing business with a company that has been listed as risky?
It is recommended to temporarily halt new trades, reassess the risk level, and only resume when strict control measures are in place.
Conclude
Controlling invoice-related risks for businesses isn't something that arises during an audit; it's a process that needs to be implemented from the outset. The question is, what should businesses do to avoid risks from invoices?
Overall, businesses should do a good job right from the invoice receiving stage, as this will significantly reduce costs, risks, and pressure later on. To avoid dealing with businesses that pose invoice risks, businesses need to establish strict control procedures (checking information, comparing contracts/transactions), choose reputable partners, use electronic invoicing software with automatic verification features, continuously update legal regulations, and proactively explain matters to tax authorities when requested, avoiding the use of illegal invoices.
In addition, the application of technologies such as electronic invoice software Electronic invoices (e-invoices) with automatic error checking features to ensure compliance with regulations will help to tighten input control. Furthermore, solutions like Bizzi support the complete and organized storage of electronic invoices; and regularly monitor new documents and policies from the General Department of Taxation and the Ministry of Finance.
To try the software and receive personalized business solution consulting, register here: https://bizzi.vn/dat-lich-demo/