During tax settlement or document review, many businesses find themselves in this situation. The invoice was rejected.VAT cannot be deducted, and expenses cannot be included as deductible costs when calculating corporate income tax. The issue is not just about taxes, but directly affects... Accounting methods and adjustments financial report and the risk of retroactive collection and penalties..
This article provides detailed instructions. How to account for rejected invoicesAnalyzing each specific case and establishing the correct handling principles ensures that accountants do not make mistakes from the outset.
Quick Summary – for Accountants & CFOs
Accounting for rejected invoices This involves adjusting accounting and tax records for invoices that are not accepted by the tax authorities for VAT deduction or inclusion as deductible expenses when settling corporate income tax. Incorrect handling can lead to penalties for the business. Tax collection, expense deductions, and penalties according to Decree 125. and financial reporting discrepancies.
The key point: The problem isn't just with the accounting entry, it's with... Invoice control process before accounting.
What is a risk invoice and why is it directly related to accounting?
Risk invoice This is not a term defined in law. It is a phrase. Tax authorities and risk management systems (TMS) Used to refer to invoices that show signs of irregularities and require verification.
Some common signs include:
- The invoice does not exist or cannot be retrieved from the electronic invoicing system.
- The business that issued the invoice has abandoned its business address, ceased operations, or absconded.
- The invoice data does not match between eInvoice, TMS, and the tax return.
- The transactions on the invoices were fictitious, part of a circular buying and selling scheme.
- Incorrect invoice information required: Tax identification number (MST), tax rate, invoice date, and product description.
"The invoice has been rejected." This is the final result when the tax authorities... That invoice is not accepted for VAT deduction or for inclusion as a deductible expense when calculating corporate income tax..
Key point: When an invoice is rejected, Accountants are required to process the accounting for rejected invoices.Otherwise, the business may face:
- Tax collection.
- Adjusting financial statements.
- Administrative penalties according to Decree 125/2020/ND-CP.
Cases where invoices are deemed invalid and affect accounting.
Invoices are typically classified as risky or rejected when they fall into the following categories:
- Invoices from businesses that have absconded, ceased operations, or abandoned their registered address.
- The invoice does not exist or contains incorrect data compared to the electronic invoicing system.
- The transaction was fictitious or part of a chain of invoice trading.
- The invoice has an incorrect tax identification number (MST), incorrect tax rate, incorrect invoice date, or incorrect required information.
- Invoices from businesses on the TMS system's high-risk list.
- The invoice shows signs of alteration, erasure, duplicate numbers, or duplicate symbols.
These situations require accountants to clearly identify:
- Should the expenses be recorded in the accounting system?
- Is VAT deductible?
- When should the adjustments be made to avoid missing the deadline?
Why do many businesses still have expenses disallowed even though they have accounted for them correctly?
In reality, the vast majority of invoices were rejected. not resulting from accounting errors, which comes from:
- Do not check the supplier's status before receiving the invoice.
- No comparison of Purchase Order – Gross Price – Invoice
- Lack of documentation right from the moment the transaction occurred.
This is why many businesses are switching. Control invoices right from the start.Instead of addressing the issue after being notified of the risk.
→ See the input invoice control process that many businesses are currently implementing.
General principles for handling and accounting for rejected/risky invoices.
When handling risky invoices, accountants need to adhere to the following documents:
- The conditions for deductible expenses are stipulated in Article 4 of Circular 96/2015/TT-BTC.
- Conditions for VAT deduction according to the VAT Law 2024 (effective July 1, 2025).
- Decree 123/2020/ND-CP on electronic invoices.
- Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC on the implementation of electronic invoices.
- Decree 125/2020/ND-CP on administrative penalties for tax and invoice violations.
These documents clearly specify when an invoice is considered legally valid. If it does not meet the requirements, the invoice will be rejected during a tax audit or settlement.

Accountants are not permitted to delete or reverse recorded expense entries if a transaction actually occurred. Accounting expenses reflect the actual transaction, while tax expenses are only the portion accepted by the tax authorities.
When records are incomplete or awaiting verification, accountants should not make direct entries. Some accounts are used for pending transactions:
- Account 338 – Other payables
- Account 138 – Other receivables
- Internal account for tracking risk invoices
Once a conclusion is reached, adjust VAT and expenses according to their true nature. Suspending these adjustments helps businesses avoid the risk of incorrect period adjustments or recording uncertain expenses.
Each risk invoice must be processed at a specific time: before preparing the financial statements and before the annual tax settlement.
How can we minimize the number of rejected invoices that need to be accounted for?
Is there a way to Do we not need to process these accounting entries frequently? Some businesses significantly reduce the number of rejected invoices by:
- Check the tax identification number (MST) and supplier status immediately upon receiving the invoice.
- Reconciling the three documents: Purchase Order – Retail Price – Invoice
- Label the risks and start billing from the beginning.
This is the workflow that many businesses are using during implementation. Bizzi Invoice & AP Automation.
→ See how Bizzi assists with pre-accounting invoice control.
How to account for each type of rejected invoice
When an invoice is rejected by the tax authorities (VAT type, expense type, or both), the accountant Do not handle machinery.The most important principle is: Clearly distinguish between accounting expenses and tax expenses..
Accounting expenses reflect actual transactions; tax expenses are the portion accepted by the tax authorities during tax settlement.
Below is a detailed accounting guide for each common type of invoice.
The purchase invoice was rejected.
Cases where only VAT is excluded.
This is a common situation where the transaction is real but the invoice is fake. Not eligible for tax deduction (For example: High-risk supplier, incorrect criteria, cash payment exceeding 20 million VND...).
At that time, Input VAT that is disallowed must be directly included in the cost or cost of goods sold., depending on the nature of the purchase:
Debit 642 / 154 / 156 (VAT portion excluded)
There are 133 (non-deductible input VAT)
Accounting expenses are still fully recorded; only the VAT portion is no longer in account 133.
In cases where the value of the goods is also disqualified.
It happens when The tax authorities did not accept the entire invoice.This is often due to transactions that cannot be substantiated or the supplier absconding.
In that case, the accountant needs Reversing recorded costs or inventory, and track this expense separately for tax purposes:
Debt 138 / 331
There are 156 / 642 / 154
This expenditure These expenses are not deductible when settling corporate income tax. and will be disqualified under criterion B4.
The sales invoice was rejected.
In cases where the invoice does not reflect a real transaction.
If the tax authorities conclude No transactions occurred.The business is required to readjust all related taxes and expenses.
Debit 811 – Other Expenses
There is item 3331 – Value Added Tax payable.
There are 3334 - Corporate income tax arrears to be collected.
This is a high-risk situation as it could lead to administrative penalties or legal prosecution.
In cases where the transaction is real but the invoice is incorrect...
If a physical transaction exists (involving goods, services, and documents), the accountant will... Maintain accounting revenueThis only adjusts the tax portion as required by the tax authorities. Revenue is not reversed if the economic nature remains unchanged.
The office expense bill (electricity, water) was rejected.
When only VAT is excluded
The portion of input VAT that is not deductible will be included in the expenses:
Debt 642
There are 133
When expenses are excluded
In cases where the tax authorities do not accept the expense (lack of contract, incorrect recipient, etc.), the accountant will... still keep the expenses on the accounting books.but it will be excluded when settling taxes. Item B4 – Non-deductible expenses.
This helps the financial statements accurately reflect the actual costs incurred.
Interest expense invoices – financial expenses are disallowed.
Interest expense It is still accounted for normally in account 635. Because it reflects actual financial obligations.
If the loan:
- Exceeding the regulated limit.
- Insufficient documentation.
- Not for business/production purposes.
then that interest expense It is only disqualified during corporate income tax settlement.At item B4, no VAT adjustment is required because interest expense is not subject to VAT.
Invoices for raw materials and tools/equipment were rejected.
Only VAT is excluded.
The disallowed VAT is allocated to costs or the cost of goods sold:
Debt 154 / 623 / 627 / 642
There are 133
Expenses were also excluded.
When the entire invoice is rejected, the accountant needs to reverse the recorded amount of raw materials/tools and equipment:
Debt 138 / 331
There are 152 / 153 / 154
This amount is then excluded from deductible expenses when settling taxes.
Invoices for the purchase of fixed assets were rejected.
Only VAT is excluded.
The portion of VAT that is not deductible will be:
- Reduce account 133
- Increase the original cost of fixed assets (Account 211) or related expenses.
This increases depreciation costs in subsequent periods.
All assets were disqualified.
If the fixed asset is not accepted by the tax authorities:
- Reversal of the original cost of account 211
- Adjusting depreciation already recorded.
- The loss is recorded as follows:
Debit 811 – Other Expenses
Marketing and advertising expense invoices were rejected.
When only VAT is excluded
Debit 641 / 6427
There are 133
When expenses are excluded
Marketing and advertising costs It remains unchanged in the accounting records. to reflect actual operations, but will be disqualified during tax settlement. B4 indicator.
The required documentation is needed to decide whether to retain or reject an expense when the invoice is considered risky.
When the tax authorities assess an invoice as risky, The invoice is not the only deciding factor.In fact, the tax authorities always review it. the entire transaction chainFrom the initial agreement to the final payment, to determine whether the transaction was genuine or not.
A suspicious invoice The cost may still be acceptable. if the business can prove the nature of the transaction through a complete and consistent set of documents.
Below is the "backbone" of the dossier which accountants are required to have.
1. Contract and contract addendum
The contract is the primary legal basis for proving:
- Pre-agreed transaction
- It has a clear target, value, time, and responsibility.
Contract addendums (if any) help clarify:
- Price change
- Change in mass
- Adjust the implementation schedule.
Many invoices were rejected because There is no contract, or the contract was signed after the invoice date., which led to the transaction being deemed "legitimized".
2. Purchase Order (PO)
A purchase order is proof that specific purchase intent, especially important for:
- Purchase goods
- Batch service
- Repeat transactions with the supplier
The tax authorities usually check the following:
- Purchase Order Date ↔ Invoice Date
- Purchase Order content ↔ Invoice content
- Quantity – Unit Price ↔ Delivery Receipt
Mismatched purchase orders (POs) are a very easy-to-spot risk indicator.
3. Handover and Acceptance Report
This is the document Proof that the transaction has been completed..
- For goods: delivery and receipt record, quantity verification.
- Services offered: work acceptance report, completion confirmation.
Without this document, the tax authorities often ask:
"Has the goods/services actually been delivered?"
4. Inventory Receipt and Delivery Notes
Inventory receipts and delivery notes help to prove:
- The flow of goods
- Time of expense
The tax authorities usually check the following:
- Date of receipt ↔ date of invoice
- Quantity received ↔ Quantity on invoice
- Delivery location ↔ contract information
Missing warehouse receipts major drawback when explaining the risk invoice.
5. Payment documents (UNC, bank statement)
Bank payment is mandatory conditions with many types of costs that are substantial.
The payment documents must show:
- The correct payer and receiver
- The payment details match the invoice.
- A reasonable time for payment.
Cash payments, round-trip transfers, or payments with unclear terms are high-risk indicators.
6. Emails, communication logs, internal documents
This is a group of documents. supplementary but extremely valuable in difficult cases.
Email, chat, and system logs help to prove:
- The actual exchange process
- Negotiate, adjust, and confirm the work.
- A genuine transactional relationship between the two parties.
During numerous inspections, Email is a very effective way to "win over" the situation. when the primary documents are not strong enough.
7. Invoice verification report from the tax authority
When invoices are subject to verification, records of meetings, notices, or conclusions from the tax authorities are mandatory documents to be retained.
This is the basis for:
- Decision to keep or exclude expenses
- Adjust accounting entries at the right time.
- Explanation will be provided in subsequent issues.
8. Explanatory letter and response from the business.
The explanatory letter is A document summarizing all of the company's arguments.:
- Explain the nature of the transaction.
- Reference to documents
- Commitment to legal liability
A clear, logical, and well-supported document can helping businesses keep costs down. even if the bill was initially suspicious.
Risks associated with incorrect accounting or failure to properly classify risky invoices.
Risk invoices are not just a matter of accounting techniques. If a business... improper processing and accountingThe risks involved don't stop at the exclusion of expenses; they can lead to further complications. Tax, legal, and financial consequences Very serious.
Input VAT deduction is disqualified.
When an invoice is deemed invalid by the tax authorities, the entire Input VAT that has already been deducted will be disallowed.Businesses are forced to:
- Refund the deducted tax amount.
- Adjust the tax returns for the relevant periods.
This increases actual costs and directly impacts cash flow, especially for businesses with a large volume of invoices.
Expenses disallowed during corporate income tax settlement.
The costs from a risk invoice if it is not accepted will:
- Excluded from deductible expenses.
- Increase taxable profit
As a result, Corporate income tax payable has increased., even if those costs have actually been incurred in the course of business operations.
Penalized under Decree 125/2020/ND-CP
In addition to tax arrears, businesses may also face:
- Punish 20% Underdeclared Tax Amount
- Calculate late payment penalty calculated from the time the tax liability arises.
During inspections, this is a penalty that often costs businesses "more than they realize."
The risk of being accused of aiding and abetting the buying and selling of invoices.
If a business frequently uses risky invoices or lacks strict control procedures, the tax authorities may assess the business as follows:
- Irresponsibility in document control.
- There are signs of complicity in the buying and selling of invoices.
This is a particularly serious risk because it could lead to extended verification and comprehensive inspection.
Financial reporting discrepancies
Incorrect accounting of risky invoices leads to:
- Cost-profit discrepancies
- Incorrect key financial indicators
This directly affects:
- Bank loan eligibility
- Business credit rating
- Reputation when working with partners and investors.
The accountant's direct responsibilities
In many cases, The accountant is directly responsible for providing explanations. When:
- Incomplete documentation
- Misaccounting
- Do not track risk invoices separately.
When disputes arise with tax authorities, accountants are often the first to be asked to provide explanations and face the greatest pressure.
In shortThe biggest risk doesn't lie in the risk bill itself, but in... Incorrect accounting and handling of risky invoicesBusinesses need to maintain tight control from the outset, standardizing accounting and tax processes to protect their expenses, financial reports, and their accounting team.
The process of verifying invoices before accounting for rejected invoices (reducing the risk of being disallowed).
In practice, tax audits and inspections involve a large proportion of risks. No discrepancies arise at the accounting stage., which appeared from Initial invoice receipt and verification phaseAn invoice that is properly controlled from the outset will significantly reduce the likelihood of being flagged as risky, requiring explanations, or being disallowed later on.
Below is a standard invoice control process that many businesses are applying, combined with automated tools like Bizzi to minimize manual errors.
1. Receive and read the invoice.
As soon as the input invoice is received, the following steps need to be taken. Read – classify – associate with context of use for that invoice.
At this stage, Bizzi provides support:
- Automatically download electronic invoices from multiple sources.
- Read invoice data (OCR + eInvoice).
- Classified by:
- Supplier
- Departments using
- Project, purpose of expenditure
Sorting from the outset helps accountants. see the clear cost pictureThis avoids the situation where you only find out what the bill was for after it arrives.
2. Verify the validity of the invoice.
This is the most important step to Eliminate risks before accounting for rejected invoices..
The following need to be checked simultaneously:
- Supplier tax identification number.
- The operating status of the eTax system (active, inactive, abandoned address, etc.).
- The required elements of an invoice are as follows:
- Decree 123/2020/ND-CP
- Circular 78/2021/TT-BTC
Bizzi offers automatic assistance:
- Look up the supplier's tax identification number (MST).
- The supplier is listed as being in the high-risk category.
- Mark invoices that show suspicious signs (incorrect details, unusual data).
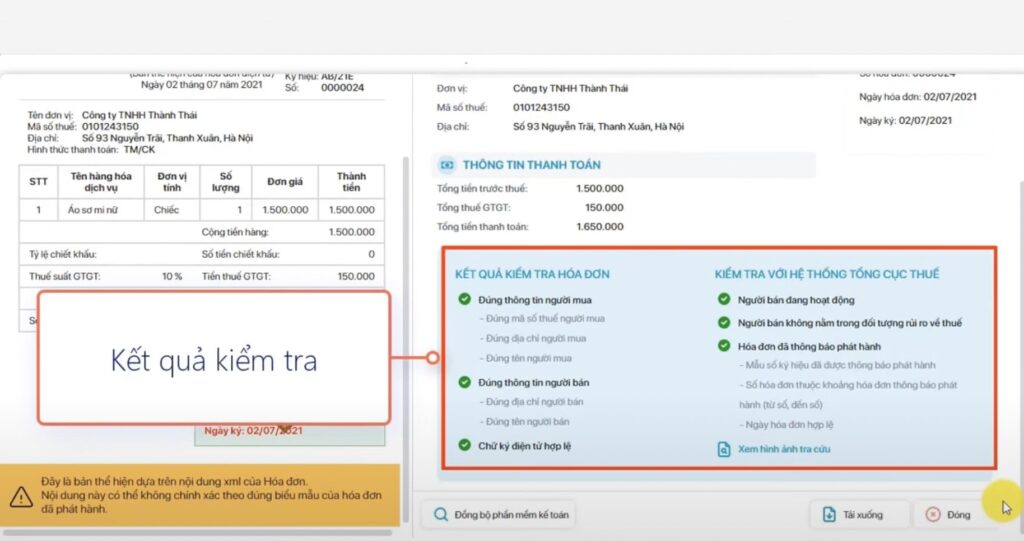
As a result, accountants don't have to manually check each invoice, which is especially useful for businesses with a large volume of invoices.
3. Three-way reconciliation (PO – GR – Invoice)
Three-dimensional comparison is key criteria which tax authorities often use to assess whether a transaction is genuine or not.
Performed by Bizzi:
- Automatic matching between:
- PO (Purchase Order)
- GR (Handover/Acceptance Record)
- Invoice
- Highlight the discrepancies:
- Quantity
- Unit price
- Types of goods/services
If the Purchase Order (PO), Gross Receipt (GR), and Invoice don't match, the invoice is highly likely to be flagged as a risk during an audit.
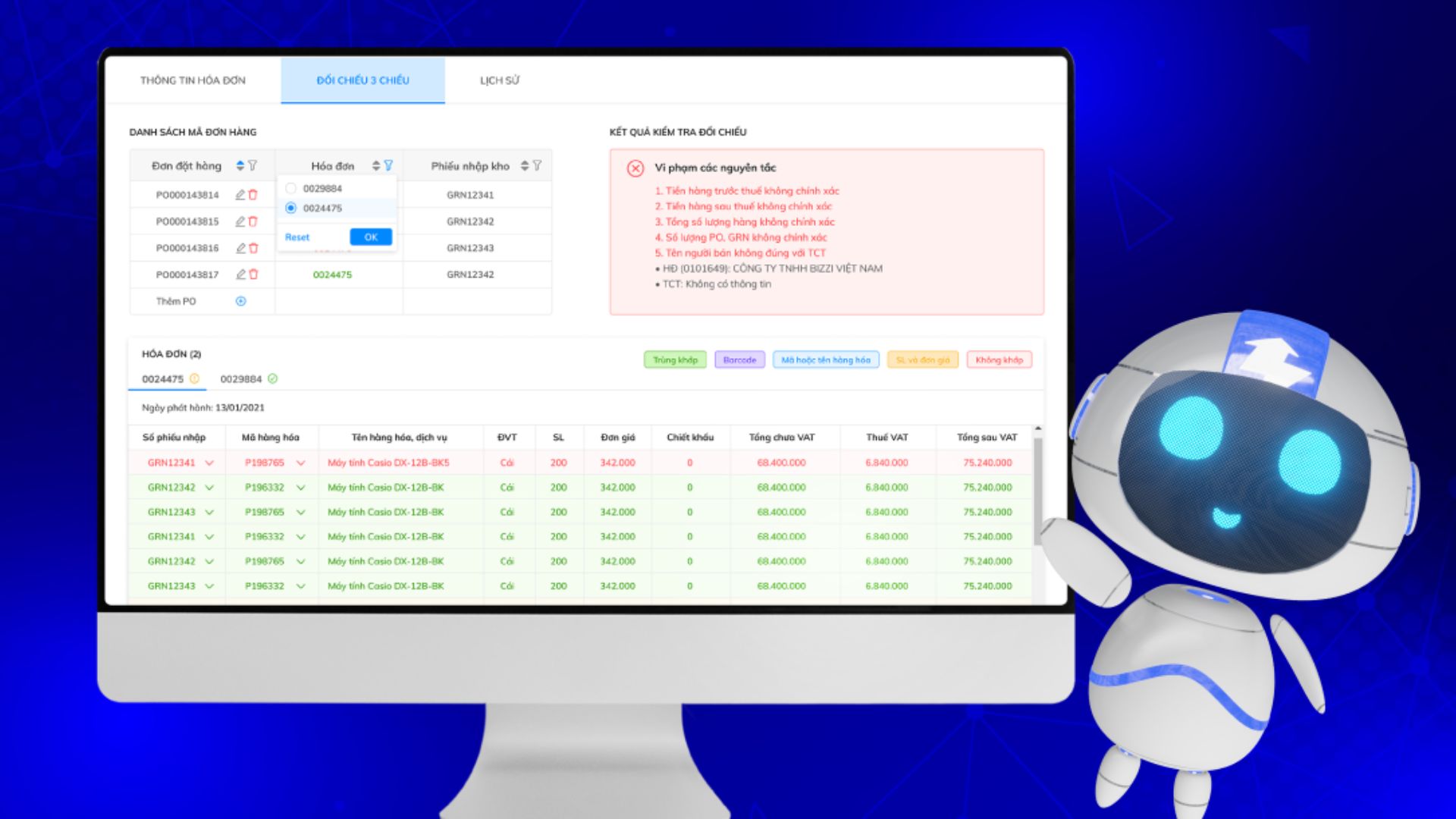
4. Label invoices with risk information.
After verification and comparison, each invoice needs to be assign explicit state Before accounting:
- Clean invoice: Complete documentation, all requirements met → normal accounting.
- Invoice missing documents: Additional requirements for contract, acceptance testing, and payment must be met before accounting entries are made.
- Risk invoice: Track it separately or exclude it immediately; do not include it directly in the expenses.
Bizzi allows you to label and track invoices by status, helping accountants. Do not confuse safe invoices with risky invoices..
5. Accounting and budget allocation
Only when an invoice meets all the requirements will the accountant proceed to record the rejected invoice.
Bizzi connects to the Expense module, which helps to:
- Track expenses by department and project.
- Compare actual costs with the approved budget.
- Warning about budget overruns or unusual expenses.
This helps businesses not only control tax risks, but also control operating costs.
Typical case
A business receives Notification Form 01 requests explanation of input invoices.By controlling invoices from the start on Bizzi, businesses have access to:
- PO
- GR
- Invoice
- Payment documents
All records were extracted within 1 day, submit explanations promptly and no expense excluded when the tax authorities conduct an audit.
Frequently Asked Questions
Some frequently asked questions regarding the process of accounting for excluded invoices.
Should risk invoices be accounted for as expenses?
Do not record the transaction immediately. When the invoice is classified as high-risk and No official conclusion has been reached yet.The accountant should hang up separate monitoringOnly record expenses when all necessary documentation is available and the transaction is confirmed as valid.
How is VAT accounted for when it is disallowed?
Input VAT is disallowed. Not deductible and must included in the cost or cost of goods sold. depending on the nature of the expense (management costs, cost of goods sold, inventory).
What should be done with invoices from many years ago that have been rejected?
Accountant retroactive adjustment According to the tax authority's conclusion, supplementary declarations must be filed, and back taxes and late payment penalties (if any) must be paid. No adjustments can be made to expenses of the current period.
Should you keep or discard high-risk invoices?
The safety principle is: Until a conclusion is reached, it will be suspended., Once a conclusion is reached, eliminate or adjust. In accordance with the true nature and regulations of tax and accounting. Avoid hasty accounting entries that lead to incorrect periods.
How should advertising expenses that are excluded from tax be accounted for?
Advertising expenses are still recorded. complete in the accounting recordsThe portion of the expenses not accepted by the tax authorities will Disqualified at criterion B4 when settling corporate income tax., without removing accounting expenses.
Conclude
Accounting for rejected invoices This requires accountants to have a correct understanding. nature of the transaction and understand the regulations regarding Tax - AccountingThe crucial point is not whether the invoice is rejected by the tax authorities, but rather... Clearly distinguish between accounting expenses and tax expenses..
The principle of safe handling is: If you're unsure, hang it up.Once an official conclusion has been reached by the tax authorities, then... Adjust the correct account and period.Incorrect accounting or hasty processing of risky invoices can lead to expense disallowances, tax arrears, and directly impact financial statements.
One A clear invoice control process is in place before accounting., combined with automated tools such as Bizzi, helping businesses minimize risks when accounting for rejected invoices, maintaining legitimate expenses and proactively and sustainably protecting financial statements.


