In recent years, along with the tax authorities' efforts to strengthen the management of electronic invoices and the application of risk analysis systems, behavioral patterns have become more prevalent. purchase and sale invoices This is becoming one of the most serious legal and tax risks for businesses. In many cases, businesses not intentionally cheatingHowever, due to lax invoice control, they inadvertently became involved in a chain of invoice trading, leading to tax arrears, heavy penalties, and even criminal liability.
So What is invoice trading?Why is this behavior dealt with so severely, and what can businesses do to prevent it?
What is invoice trading?
Before discussing risks or penalties, businesses need to understand the following: How is the buying and selling of invoices understood from the perspective of the tax authorities?Because this understanding determines the entire process of inspection, examination, and subsequent handling.
What is the concept of buying and selling invoices?
Buying and selling invoices is an act Buying, selling, leasing, and transferring the right to use invoices. but not related to actual transactions involving the purchase or sale of goods or the provision of services..
In other words, the invoice was created. just to legitimize the documents, which does not reflect actual economic transactions.
Key points the tax authorities consider:
- Bill does not reflect the nature of economic transactions..
- Not fully available Product flow – service flow – cash flow.
It is necessary to distinguish clearly:
- Issue a legitimate invoice.: There is a real transaction, a contract, delivery, acceptance, and payment.
- Buying and selling invoices: only the invoice, but There are no corresponding economic transactions..
Types of invoices that are commonly bought and sold.
In reality, the buying and selling of invoices does not take place in a single form. Tax authorities usually classify them according to... the nature of the use and purpose of the fraud.
Common types include:
- Buying and selling VAT invoices (red invoice) to increase costs or deduct VAT.
- Invoice rental According to the % ratio, the value is used to legitimize the expenses.
- Fake invoices, counterfeit invoices Issued by a "phantom" company.
- Electronic bill does not exist in the tax system.Only PDF/XML files are available, but they cannot be searched.
During the inspection, it is sufficient to... a weak link In the invoice chain, all transactions are subject to risk assessment.

What is the legal nature of buying and selling invoices?
From a legal perspective, buying and selling invoices is not simply an administrative violation, but could also have other implications. escalating into a criminal risk.
This behavior falls into the following category:
- Invoice fraud
- Tax evasion
- Concealing the flow of money
- There are signs of money laundering (in serious cases).
And it is strictly prohibited according to:
- Tax Administration Law 2019
- Decree 123/2020/ND-CP
- Decree 125/2020/ND-CP
- Article 203 of the 2015 Penal Code
Important Note: It's not just the person who issues the invoice who gets penalized. invoice users They also bear corresponding legal responsibility.
Why does the buying and selling of invoices occur?
The buying and selling of invoices didn't happen by chance. There are underlying reasons behind it. Financial, tax, and management motivations very specific.
1. Evading Corporate Income Tax (CIT)
This is the most common cause in the cases that have been discovered.
Businesses purchase invoices for the following reasons:
- Increase deductible expenses
- Reduce taxable profit
- "Filling in" expenses for undocumented expenditures.
Many businesses consider this a short-term solution, but when it comes to final accounting, the risks become apparent. All costs were excluded. It is very large.
2. Value Added Tax (VAT) Fraud
Some businesses purchase input invoices for the following purposes:
- Increase in deductible VAT
- Incorrect tax refund
In the current management system, VAT is the most heavily scrutinized indicator. Because data can be quickly cross-referenced across multiple systems.
3. Legitimizing expenses and assets "off the books"
Invoices are used for:
- Legalizing expenses outside of a planned budget.
- Concealing vested interests
- Creating a “legal shell” for illicit money flows.
This is a group of risks that often lead to expanded investigation.
4. Improve your financial profile.
Some businesses use invoices for:
- Creating fictitious revenue
- Increase the reporting scale.
- Serving loan and bidding purposes.
The risk is that if discovered, the business Serious damage to reputation with banks and partners..
5. Weak internal controls
Many businesses are facing risks. not due to intentional fraud, which is due to:
- There is no invoice approval process.
- No reconciliation of Purchase Order – Gross Price – Invoice
- Manual processing, lack of warning tools.
These are the businesses that are most likely to "accidentally fall into a trap".
Legal framework regarding the buying and selling of invoices and illegal invoices.
To assess whether an act constitutes a violation, tax authorities always rely on the following: specific legal framework, not based on emotions.
Key legal documents
The buying and selling of invoices is regulated by:
- Tax Administration Law 2019
- Decree 123/2020/ND-CP
- Decree 125/2020/ND-CP
- Article 203 of the 2015 Penal Code
These documents clearly stipulate Responsibilities of both the invoice issuer and the invoice user..
What constitutes a legal or illegal invoice?
In reality, the line between legal and illegal is blurred. It is not related to the invoice format., which lies in the nature of the transaction.
Legitimate invoice:
- Right design, right time.
- The correct issuer.
- There was a real transaction.
- It is available on the tax authority's electronic invoicing system.
Illegal invoices including:
- Fake invoice.
- Invoices from businesses that have ceased operations and abandoned their addresses.
- Invoices are issued when a business temporarily suspends operations.
- The invoice was not registered for issuance and does not exist in the system.
Buying and selling invoices in the eyes of the tax authorities.
The tax authorities consider this to be the following behavior:
- Buying and selling invoices not linked to transactions.
- Use the invoice to:
- Legitimate expenses.
- Tax deductions/refunds.
- Borrow money from the bank.
- Money laundering.
Typical violations related to the buying and selling of invoices.
In practice, during tax audits and inspections, the tax authorities... Don't just look at a single invoice., which evaluate The use of invoices throughout the entire transaction chain.Below are some of the most typical violations that are often detected and dealt with.
Using fictitious invoices or invoices for purchases made outside the company.
This is the most common behavior and also a "red flag" in the tax risk management system.
Common symptoms:
- There were no economic contracts or contracts signed that were merely ceremonial.
- There are no delivery receipts or service acceptance reports.
- No actual payments or round-trip payments, or payments made on behalf of others, occurred.
In essence, a business only buy invoices, without purchasing corresponding goods or services. When the cash flow – goods flow – invoice flow don't match, the invoice is almost certainly deemed illegal.
Legalizing expenses and claiming tax refunds.
Many businesses use external invoices to "cover expenses" for expenditures that lack valid supporting documents.
Common behaviors:
- Recording fictitious expenses to reduce corporate income tax payable.
- Creating fictitious goods and services to increase input VAT for tax deduction or refund purposes.
- Extending the invoice chain through multiple intermediary companies to conceal the source of the invoices.
This is a group of behaviors. were severely punished.This not only leads to revenue losses but also distorts tax data.
Using invoices to obtain loans and manipulate financial statements.
Some businesses don't buy invoices to evade taxes, but rather to "beautify" their financial records.
The purpose is usually:
- Creating fictitious revenue to increase bank credit limits.
- Scale up your business when participating in bidding and fundraising.
- Concealing the actual state of poor business performance.
The risk lies in the fact that when tax authorities or banks conduct cross-checking, the business may... Loss of both credibility and access to capital..
A chain of "ghost" businesses specializing in selling invoices.
This is a form of organized violation, often closely monitored by tax authorities and economic police.
Characteristic:
- Establishing a business solely for the purpose of issuing VAT invoices.
- There is no actual business activity.
- Sell invoices based on a % value (1–5%).
- After a short time, they abscond, dissolve, or cease operations.
Businesses purchase invoices from these "phantom businesses". It is very difficult to defend the costs., even if there is a "legitimate" contract or document.
High-risk business types and models associated with invoice trading.
Not all businesses have the same probability of risk. In tax administration practice, there are certain types of businesses. The group of business models is always under "monitoring"..
A shell company, not actually operating.
This is the highest risk group in any assessment system.
Common symptoms:
- There are no actual staff or only 1–2 people.
- There are no warehouses, machinery, or assets to support production and business operations.
- The registered address does not exist or is not operational at the registered address.
The invoices issued by this group of businesses are almost default to being suspected.
Newly established business issuing high-value invoices.
The tax authorities specifically monitor these businesses:
- Established 3–12 months ago.
- Low registered capital.
- But they issue invoices for large, consistent sales.
If financial capacity, personnel, and assets disproportionate to salesThe business will then be placed under verification.
Virtual service company
Service businesses, which are generally described as such, are a group that is very susceptible to scrutiny.
For example:
- "Other services"
- "Integrated service fee"
- "Consulting, support, and brokerage" does not have a specific output product.
If it cannot be proven value createdService invoices are easily mistaken for sales invoices.
The business is on the tax authority's high-risk list.
Once a business has committed a violation, the data will be stored in the system.
The review sources include:
- Tax Management System (TMS).
- eTax data, eInvoice data.
- History of inspections, audits, and penalties.
Businesses in this group will be Let's examine it more closely in the following episodes., even after the previous violation has been rectified.
Identifying fake invoices, fictitious invoices, and risky invoices.
Early identification is the most effective way to avoid risk. In fact, the bill of risk. They often reveal signs in multiple layers., and it's not just on the surface of the invoice.
Indicators on invoices and systems
This is the first and easiest test to perform.
Warning signs:
- Unable to retrieve invoices on the electronic invoice portal.
- Incorrect tax identification number, incorrect seller name, or incorrect seller address.
- The invoice date does not match the actual transaction date.
If even one of these elements doesn't match, the invoice is already under suspicion.
Signs regarding accompanying documents
The invoice is just the "final result," but the tax authorities are always looking at the rest. backend documentation.
Risk factors:
- There was no economic contract or agreement signed after the invoice.
- There are no purchase orders, acceptance reports, or warehouse receipts.
- Large cash payments were made without any bank transfer documentation.
Lack of supporting documents is a common reason businesses face difficulties. loss of cost protection.
Indicators of the business issuing the invoice.
Even if the invoice looks "good," the issuing company is still the deciding factor.
Special attention is needed when:
- Newly established business, small capital, but constantly issuing invoices.
- The business is temporarily suspended, has ceased operations, or has abandoned its address.
- There is no website, and no clear operational information.
Quick check before accounting
To reduce risk, accountants and finance departments should develop a habit of performing quick checks using checklists:
- Look up your invoice on the electronic invoice portal.
- Look up the tax identification number and business operating status.
- Compare the contents of the invoice with:
- Contract
- Purchase Order (PO)
- Handover/Acceptance Record (GR)
- Payment documents
If a mismatched linkTherefore, invoices should be placed under risk monitoring instead of being accounted for immediately.
Tax risks and consequences of using unauthorized sales invoices.
Using unauthorized sales invoices is not just an accounting error or a short-term tax trick. In fact, it is an act classified by the tax authorities as a crime. high risk groupThis can lead to a range of serious tax, financial, and legal consequences for businesses.
Risks related to VAT and corporate income tax.
This is the direct and almost certain consequence when an invoice is deemed illegal.
Specifically:
- Input VAT is not deductible.
All VAT declared and deducted from illegal sales invoices will be disallowed. Businesses are required to:- Supplementary declaration/adjustment.
- Repay the incorrectly deducted tax amount.
- Expenses that are excluded from deductible expenses when calculating corporate income tax.
Expenses arising from external purchase invoices will not be considered valid expenses. This results in:- Increase taxable profits.
- Increase the amount of corporate income tax payable, even if the expenses have actually been incurred.
- Tax collection and calculation of late payment penalties.
In addition to the back taxes, businesses also have to pay late payment penalties calculated based on the number of days of violation, significantly increasing the total financial loss.
Administrative penalties as stipulated in Decree 125/2020/ND-CP
In addition to tax arrears, businesses also face specific administrative penalties, depending on the nature of the violation.
Some common penalty frameworks:
- Giving or selling invoices that are not linked to actual transactions of goods or services.
Common fines range from 15–45 million VND for each behavior. - Use of illegal invoices
The penalty can range from 20–50 million VND, not including any tax obligations that need to be collected. - Using invoices to reduce the amount of tax payable.
In addition to being required to pay back taxes, businesses may also be fined:- 20% Underdeclared Tax Amount, or
- 1–3 times the amount of tax evaded, depending on the severity and nature of the violation.
In many cases, the fines and back taxes are combined. much higher compared to the initial “benefits” from purchasing invoices.
Criminal liability under Article 203 of the 2015 Penal Code
When the buying and selling of invoices shows signs of seriousness, is organized, or causes significant damage to the budget, the risks do not stop at administrative penalties but may lead to further consequences. chuyển to criminal prosecution.
For individuals
- It may be Fines or imprisonment from 6 months to 3 years (basic framework).
- Aggravating circumstances (organized crime, large profits, significant damage to the budget):
- The fine could be as much as 1–5 years in prison, or even higher depending on the nature of the case.
For commercial legal entities
- It may be Fines of up to 1 billion VND..
- In serious cases, businesses also face the following risks:
- Temporary suspension of operations.
- This directly affects the existence of the legal entity.
This is a risk that many businesses underestimate, until the case is referred to the investigative authorities.
Financial, operational, and reputational impacts on the business.
Beyond tax and legal issues, the indirect consequences of using unauthorized sales invoices are often long-lasting and difficult to remedy.
Common impacts include:
- Cash flow is tied up.
When an invoice is rejected or pending verification, the business can:- Unable to issue invoices to customers.
- Payment was not collected on time.
→ Cash flow is disrupted, which is especially dangerous for businesses that rely on short-term cash flow.
- Listed as a high-risk business.
Once "tagged," a business will:- Increased frequency of inspections and audits.
- They will face closer scrutiny in subsequent tax periods, even after correcting previous violations.
- Loss of trust from partners and banks.
Businesses that face invoice-related risks often experience:- The partner requested stricter payment terms.
- Banks tighten credit, reduce credit limits, or require additional collateral.
The process by which tax authorities inspect and detect the buying and selling of invoices.
Many businesses believe that simply "manipulating" documents is enough to deceive tax authorities. In reality, current control processes rely heavily on... big data analysis and cross-referencing, no longer dependent on single manual checks.
Data analysis on e-Invoice, eTax, and TMS systems.
The tax authorities use centralized data to:
- Match Revenue – Input – Inventory – Taxes Payable.
- Detect the unusual pattern like:
- Revenue fluctuates dramatically, sometimes increasing and sometimes decreasing.
- The invoice value does not reflect the company's capabilities.
- An unusually high frequency of invoice issuance in a short period of time.
The system can automatically place businesses under surveillance without requiring immediate on-site inspections.
Cross-reference with banks and other data sources.
In many cases, tax data is compared with:
- Banking transactions.
- Anti-money laundering data.
- Customs data, business registration.
Unusual payment transactions (round transfers, unclear details, large but disproportionately large amounts) will be considered. deep inspection trigger point.
Send notifications and requests for explanations from businesses.
When there are signs of risk, the tax authorities will:
- Send a notification or official letter requesting an explanation.
- The following information is required from the business:
- Economic contract.
- Delivery and acceptance documents.
- Payment voucher.
- Detailed inventory list (purchases, sales, and stock levels).
Incomplete or inconsistent explanations often increase the risk of the case being escalated to a higher level of processing.
Draw conclusions and apply corrective measures.
After compiling and evaluating the documents, the tax authorities will:
- Draw a conclusion regarding the legality of the invoice.
- Implement the following measures:
- Tax collection.
- Administrative penalties.
- In cases where there are signs of criminal activity: Transfer the case file to the investigating agency..
More importantly, this result will be Recorded in the risk management systemThis will affect the evaluation of the business in subsequent periods.
Below is Full deployment version in blog format, Satisfied Add introductory paragraphs to each heading., stay true to spirit Bizzi is not a legally binding "anti-violation" tool., which is The platform helps businesses reduce the risk of invoice trading right from the operational stage..
Bizzi's role in preventing invoice trading risks.
In reality, many businesses don't intentionally buy or sell invoices, but still unknowingly fall into the high-risk category due to this. The process of controlling invoices, expenses, and accounts payable is not rigorous enough..
Bizzi does not replace the role of the tax authorities in handling violations, but rather plays a similar role. a layer of preventionThis helps businesses better control variables that can easily lead to invoice risks.
Bizzi's approach principles
Bizzi focuses on three core principles:
- Risk prevention from early morningbefore the invoice is processed.
- Reduce The motivation and need for "buying invoices" to legitimize the expenses.
- Build clean financial and accounting dataConsistent and easily explainable.
Therefore, Bizzi helps businesses significantly reduce their chances of being drawn into invoice trading chains, whether intentionally or unintentionally.
Input invoice control – Bizzi IPA + 3-way reconciliation
Input invoices are the point of greatest risk In invoice trading cases, when businesses receive invoices from unqualified suppliers or those with no real transactions, the entire chain of costs and taxes is jeopardized.
Automatically download, read, and verify invoices.
Bizzi IPA uses RPA + AI to:
- Automatically download electronic invoices from multiple sources.
- Read invoice data, standardize information (Tax Identification Number, invoice number, value, tax rate, etc.).
- Reduce reliance on manual accounting tasks – which are prone to errors.
Verify tax identification number and supplier status.
Upon receiving the invoice, Bizzi provides the following support:
- Look up the supplier's tax identification number (MST).
- Check the operating status (active, inactive, abandoned address, etc.).
This allows businesses to avoid receiving invoices from suppliers:
- It has ceased operation.
- It falls into the high-risk category according to the tax system.
Three-way reconciliation: Invoice – Purchase Order – Retail Price
This is a crucial control layer that helps:
- Verify whether the transaction is genuine.
- Match the invoice with:
- Purchase Order (PO).
- Warehouse receipt/acceptance report (GR).
Bizzi automatically highlights any misalignments:
- Quantity.
- Unit price.
- Types of goods/services.
Risky Invoice Warning
When an anomaly is detected, the system:
- Label invoices as risky.
- This alert prompts the accountant to stop the transaction, request additional documentation, or disqualify the entry early.
This helps businesses Do not inadvertently record illegal sales invoices., which is the main reason leading to tax arrears and penalties.
Output invoice – Bizzi B-invoice
Conversely, output invoices are a factor that directly affects revenue, cash flow, and business reputationIssuing invoices incorrectly or without following proper procedures can easily lead to businesses being scrutinized for potential risks.

Issuing electronic invoices in accordance with regulations.
Bizzi B-invoice support:
- Issuing electronic invoices in accordance with legal regulations.
- Ensure that all mandatory criteria as stipulated in current Decrees and Circulars are met.
There is a verification code from the tax authority.
The invoice was:
- The verification code is issued directly by the tax authority.
- Ensure legal existence on the e-Invoice system.
This helps:
- Avoid the risk of "non-existent" invoices.
- Increase credibility when partners look up invoices.
Synchronize with accounting/ERP
Bizzi synchronizes outgoing invoice data with:
- Accounting software.
- ERP system.
As a result, revenue, taxes, and accounts payable are recorded consistently, reducing the risk of data discrepancies that could lead to suspicions of fraud.
Cost control – Bizzi Expense
One of the underlying causes of invoice trading is Expenses incurred without valid supporting documents.Bizzi Expense helps address this problem at its root.

Link expenses to authentic documents.
Bizzi allows:
- Link each expenditure to its corresponding invoice or supporting document.
- Track expenses by department, project, and purpose of use.
As a result, businesses:
- Reduce "unofficial" expenses.
- Reduce the pressure to buy invoices to legitimize transactions.
Reduce the need to "buy invoices" to legitimize expenses.
When the cost is:
- Create a clear budget plan.
- Transparent approval process.
- To recognize the true nature of things,
Then the need to buy invoices to "beautify the accounting records" has almost disappeared.
Accounts Receivable Management – Bizzi ARM
Invoice risk not only affects taxes but also has a significant impact on other areas. cash flow.
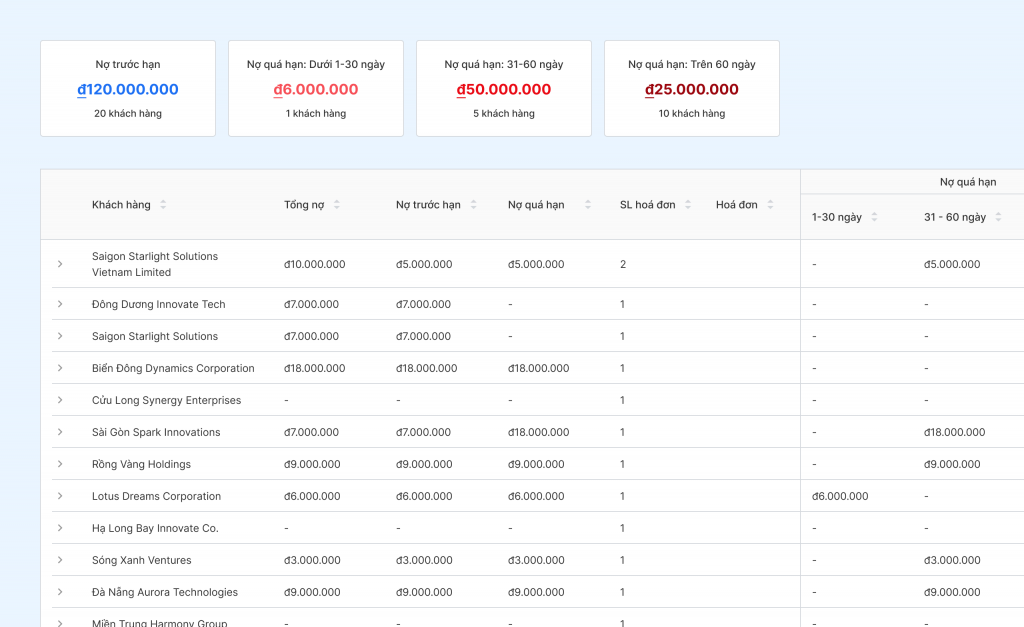
Track cash flow and accounts payable.
Bizzi ARM supports:
- Track accounts receivable and accounts payable.
- Debt reminders and payment schedule management.
Reduce cash flow shock when bills are outstanding.
In the following case:
- Some invoices are pending verification.
- The invoice has not been accepted yet.
The business still:
- Understand the status of accounts receivable and payable.
- Proactively plan your cash flow to minimize the risk of sudden cash flow disruptions.
Bizzi acts as an "AI financial and accounting assistant".
Instead of being just a standalone tool, Bizzi acts as a... AI assistant For the finance and accounting department.
Automated verification, reconciliation, and archiving.
Bizzi helps:
- Reduce manual operations.
- Standardize the invoice verification process.
- Centralized data storage makes it easy to retrieve data when providing explanations.
Keep data clean and transparent.
When the data:
- Purchases, sales, expenses, and accounts payable are consistently controlled.
The business will:
- Significantly reduces the likelihood of being classified as a high-risk business.
- Be more proactive when working with tax authorities, banks, and partners.
Frequently Asked Questions about Invoice Trading
What is invoice trading, and how is it different from fraudulent invoices?
A fictitious invoice is a form of invoice trading.
Can external purchase invoices be considered valid expenses?
No, the expense will be disallowed and may result in penalties.
Can I go to jail if I'm caught buying fake invoices?
Yes, if all the elements constituting the crime under Article 203 of the Penal Code are present.
Is there any software that can help avoid the risks associated with fraudulent invoice trading?
Solutions like Bizzi help control invoices, expenses, and reconciliation, reducing risk from the outset.
Conclude
What is invoice trading? This is no longer a theoretical question, but has become a real risk for many businesses as tax authorities intensify control over electronic invoices and data-driven risk management. The essence of invoice trading lies not in the invoice itself, but in the process of... Invoices not associated with actual economic transactionsThis leads to a range of consequences related to taxation, legal matters, finance, and corporate reputation.
In reality, quite a few businesses unintentional violationHowever, they are still drawn into the risk of invoice trading due to weak internal controls, lax invoicing-expense-accounts receivable processes, or excessive reliance on manual processing. In such cases, the consequences extend beyond disallowed expenses or tax arrears; they can lead to severe penalties, operational disruptions, and loss of trust from partners.
Therefore, instead of only addressing the issue after it has occurred, businesses need to... Proactively prevent the risks of invoice trading right from the source.By standardizing the process of receiving, checking, and reconciling invoices, ensuring transparency in expenses, and building a clear and consistent financial data platform, this is the most sustainable way to protect businesses from increasingly complex tax risks in the current period.
Sign up here to try Bizzi products: https://bizzi.vn/dang-ky-dung-thu/


