The Chief Financial Officer (CFO) is assigned the difficult responsibility of managing the company's finances. But their job goes beyond ensuring happy employees and accurate month-end reports; it's also about understanding how to use the data collected to make decisions that help the business grow.
KPIs are a crucial part of this process. They can tell you how each department is performing and whether they need more resources or training. KPIs can also help you identify areas where your company is performing well, so you can make the most of those strengths while improving where needed.
So what exactly are KPIs, how do they work and how do they benefit your business financially? To help you, we've developed an easy-to-follow guide to KPIs for Finance in 2024.
What are KPIs in finance?
KPI - Key Performance Indicator are indicators to evaluate job performance. Tracking the right financial KPIs allows you to assess the health of your business, identify areas for improvement, and make informed financial decisions.
What are the characteristics of a good KPI in finance?
KPIs in finance need to follow the SMART principle: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-Bound. .
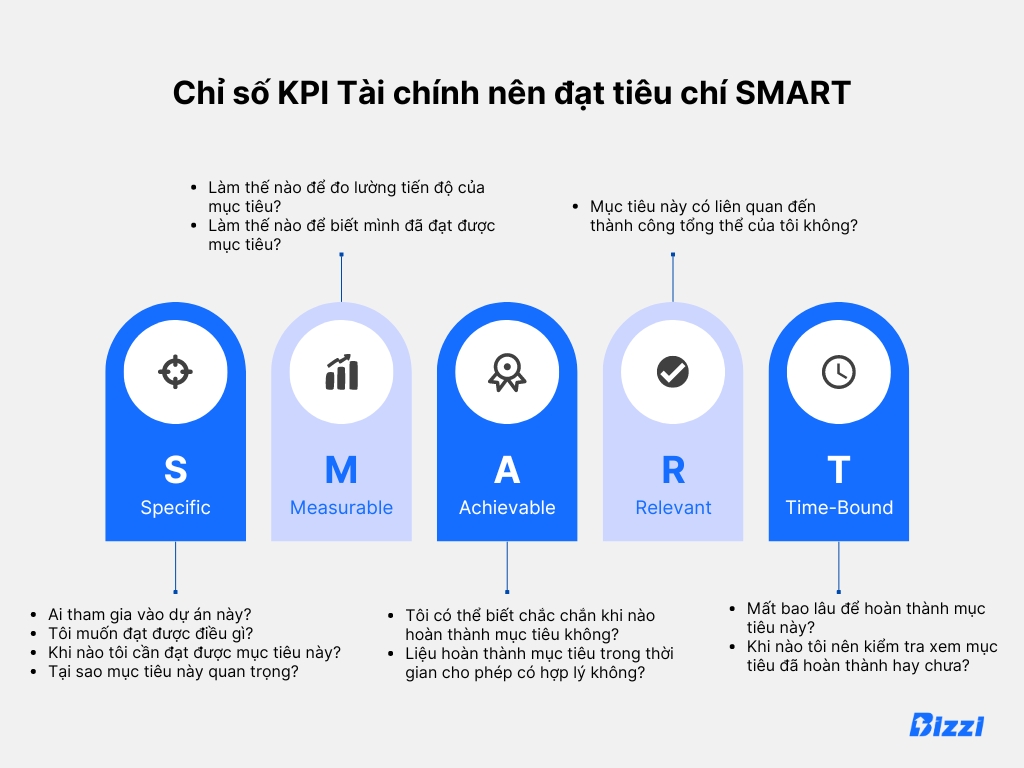
1. Specific:
Each KPI should target a specific area of financial performance to accurately drive and measure success.
For example, if you want to test how effectively debt is managed, you can use the “debt-to-equity ratio”. This measure helps you look at the balance between the amount borrowed and the amount invested in the company.
2. Measurable:
KPIs in finance require quantitative evidence of what is being achieved.
For example, “operating cash flow” measures the cash your company earns from normal business activities. It's like checking your wallet to see how much you've earned after a day's work. By setting a goal, such as using this cash flow to reduce corporate debt 15%, you turn this metric into a specific and measurable tool.
3. Achievable:
Your KPI goals need to be realistic and feasible within the time and resources available.
For example: Reducing the company's operating costs (such as electricity or supplies) by 10% over the next three months is a realistic goal. This goal is challenging but completely doable with a good plan.
4. Reality (Relevant):
Your financial KPIs should be directly tied to strategic business goals.
For example: If the goal is to make more profit, then it makes sense to focus on “gross margin.” This measure involves earning more than it costs to produce your product or service.
5. Time-Bound:
Financial KPIs should include a specific timeline to achieve the goal.
For example, setting a goal of reducing overdue invoices by 10% within 12 months provides a clear, time-bound goal. It's like setting a finish line for a race.
Why is choosing the right KPI indicators in finance important?
For finance teams, choosing the right KPIs will help everyone clearly understand their goals and performance. It's like setting clear, realistic and relevant goals with specific deadlines, helping the entire team focus and work toward a common goal.
Each business will have its own appropriate KPIs. This depends on your goals, industry, and what your company wants to achieve.
For example, if you are running a SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) software business, focusing on ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue), MRR (Annual Recurring Revenue) months) and the service cancellation rate will be more reasonable. On the other hand, if you are operating in the retail sector, inventory turnover and gross profit margin may be more relevant. We will dive into the details of these KPIs later in the article.

KPIs for the finance department: what should you measure?
The answer to this question depends on your industry and company goals.
For example, if you work in the Finance department of an e-commerce company that sells products online, you might want to measure revenue per customer or customer lifetime value.
If you work for a manufacturing company, you may want to track inventory levels and order fulfillment times.
Examples of KPIs for the Chief Financial Officer (CFO) and Head of Finance
As a Head of Finance, determining which KPIs to track can feel overwhelming. This is especially true because each business is unique. Whether you're at a SaaS startup or a traditional manufacturing company, the KPIs you need can look quite different.
The goal is to focus on KPIs that give you the clearest picture of how your business is doing and where you can improve. Whether you're aiming for growth, efficiency, customer satisfaction, or all of the above, the right KPIs can light your way.
As mentioned, below are some important KPIs for Chief Financial Officers (CFOs) and Heads of Finance, pay attention to choosing KPIs that truly match the goals and operating style of the business. Friend.

Net Income
Your company's total income, after all expenses have been subtracted from revenue, provides a clear picture of profits. If you're interested in tracking your core finances, track this KPI.
Gross Profit Margin
Shows how much money you have left over from sales after covering the costs of making the product or providing the service. This is a good measure of how effectively you are using your resources to generate profits.
Inventory Turnover Ratio
For businesses that sell physical products, this is a measure of how quickly your inventory is sold. It is essential to manage inventory levels and understand product circulation levels.
Revenue Per Employee (Revenue Per Employee)
This measure shows how much revenue each employee brings in. It helps you understand whether the team is operating efficiently or if there is room to increase productivity.
Profit Margin
The profit margin KPI shows how much money a company retains as profit after covering all costs. This is a clear indication of the company's financial health and its earnings performance.
Sales Orders per Employee
Show how much revenue each member of your sales team generates. This is a useful way to evaluate the productivity and efficiency of your sales force.
On-time Completion Rate of Sales Orders
This KPI measures how reliable you are in delivering on time. It is important for customer satisfaction and can help you detect problems in the supply chain or manufacturing process.
Customer Complaints and Warranty Claims
Tracking complaints and warranty claims gives you insight into product or service quality and customer satisfaction. This is a direct path to understanding what might be going wrong and where you can improve.
Market Share Growth
Measure your company's sales performance compared to competitors. Market share growth shows that your strategies are working well in capturing more of the market.
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR) & Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
For subscription-based businesses like SaaS, these KPIs indicate how much recurring revenue you can expect each month or year. They are important for understanding revenue stability and growth prospects.
Customer Acquisition Costs & CAC Payback Period
CAC measures the average cost of acquiring a new customer. The payback period indicates how long it will take you to recoup this cost. Both are key factors in measuring the effectiveness of your marketing and sales activities.
Customer Lifetime Value
This is the total amount a customer is expected to spend on your products or services over the course of their time as a customer. It helps you understand the value of investing in customer relationships.
Churn Rate
Especially important for businesses with subscription models, churn rate indicates how many customers you are losing over a given period of time. Lower churn rates mean better customer retention.
Examples of KPIs for finance and staff
Even if you're not the Head of Finance but still work in the Finance department, you may still need to track useful company-wide KPIs.
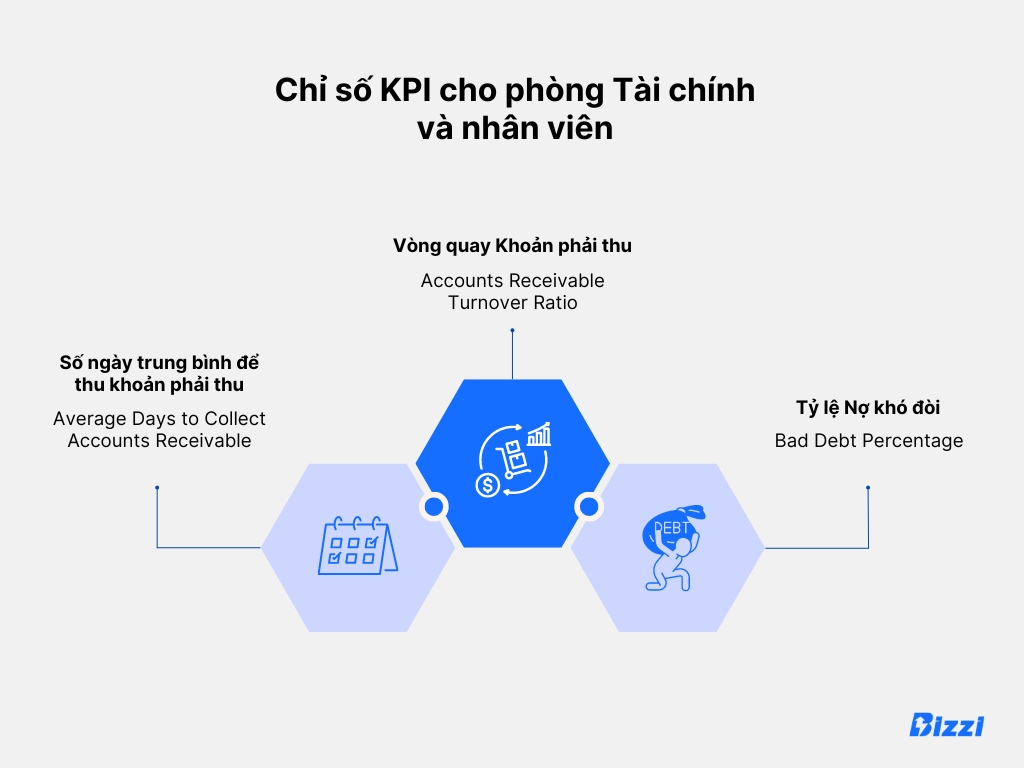
For example, if you work as an assistant in charge of debt management, you might track the following KPIs:
Average Days to Collect Accounts Receivable
This KPI measures the average time required to collect payment from customers. It's important to ensure the business has enough cash for daily operations.
Accounts Receivable Turnover Ratio
This ratio indicates how often a business collects outstanding payments within a year. It helps evaluate whether the company is good at collecting debts, which is important for maintaining healthy cash flow.
Bad Debt Percentage
The bad debt ratio KPI indicates the percentage of money owed to a company that is likely to be uncollected. This is key to understanding the risks a company faces with its current credit and collection policies.
Why are these KPIs important to the Finance Department?
For anyone in the finance department, these KPIs are a toolkit to evaluate business performance.
They help paint a clear picture of a company's financial health, guiding decisions that can improve operations, increase profits, and ensure the company has enough cash to grow.
By tracking these metrics, you're playing an important role in moving your company toward success. They enable you and your team to detect problems before they become problems and seize opportunities to accelerate growth.
So, take a deep dive into these KPIs, understand what they are telling you, and use them to make a positive impact on your company's finances!
Company-wide benefits of measuring KPI indicators
KPIs are a great way to measure the success of any organization, regardless of industry.
Companies can use KPIs to:
- Detect weaknesses: Identify areas where the business is struggling or underperforming.
- Empower employees: Help employees know whether they are doing their job well or need to adjust their performance.
- Trend analysis: Detect sales and revenue trends, helping executives plan for future growth or decline.
- Understanding Marketing insights: Measure the effectiveness of new marketing initiatives so that successful initiatives can be repeated.
- Set clear expectations: Help create a culture of accountability within the company by clearly defining expectations for all participants.
- Smooth transition: Give the company an idea of what is working well so that when there is a change in leadership or management style, there is a system in place for success.
- Implement Data-Driven Strategies: Provides current analytics, equipping executives and team members with the data needed to make more informed decisions.
Bottom line: KPIs are the key to understanding your business's performance, orienting your employees, planning for the future, and making informed decisions. They help you get a clear view of where you are and where you need to go, ensuring everyone is working towards common goals.
Measuring KPI indicators for the finance department: Cost management software What can help?
Although automation solutions that can manage repetitive daily activities and measure KPIs have emerged, many businesses still use manual procedures and spreadsheets to track these tasks. its performance index.
Yes, spreadsheets have certain advantages, but it's like using a classic manual typewriter in this day and age: familiar, but not as fast and flexible as modern technology.
Using cloud-based financial management software, such as Bizzi Expense, offers many benefits for tracking your KPIs and performance metrics:
- Save time: By automating data entry and calculations, this solution saves hours that can be redirected to more strategic tasks.
- Increase accuracy: Automation minimizes the possibility of human error, ensuring your data is reliable.
- Provides real-time insights: Access to current financial data enables faster, more informed decision making.
Bizzi Expense is an expense management solution that allows you to track, analyze and report on your company's expenses.
Bizzi Expense allows you to automatically track cost-related KPIs, meaning Finance can reduce time spent entering and analyzing costs, spending more time on other important tasks.
Are you ready to convert? Schedule a demo today and discover how Bizzi Expense can revolutionize your finance team's KPI tracking.
Monitor Bizzi To quickly receive the latest information:





